iQ Series, Ultrasonic Hand Held Systems User’s Manual
Theory of Operation
Plastic welding is the most common application of ultrasonic assembly. To perform ultrasonic plastic welding, the vibrating tip is brought into contact with one of the work pieces. Pressure is applied and ultrasonic energy travels through the material generating frictional heat at the contact point of the two parts. The frictional heat melts a molded ridge of plastic on one of the pieces and the molten material flows between the two surfaces. When the vibration stops, the material solidifies forming a permanent bond.
Probe Configuration
A basic ultrasonic probe package consists of:
1.A probe which houses the transducer to convert the elec- trical energy supplied by the generator into mechanical vibrations.
2.A horn to transfer the mechanical vibrations from the probe to the parts to be welded.
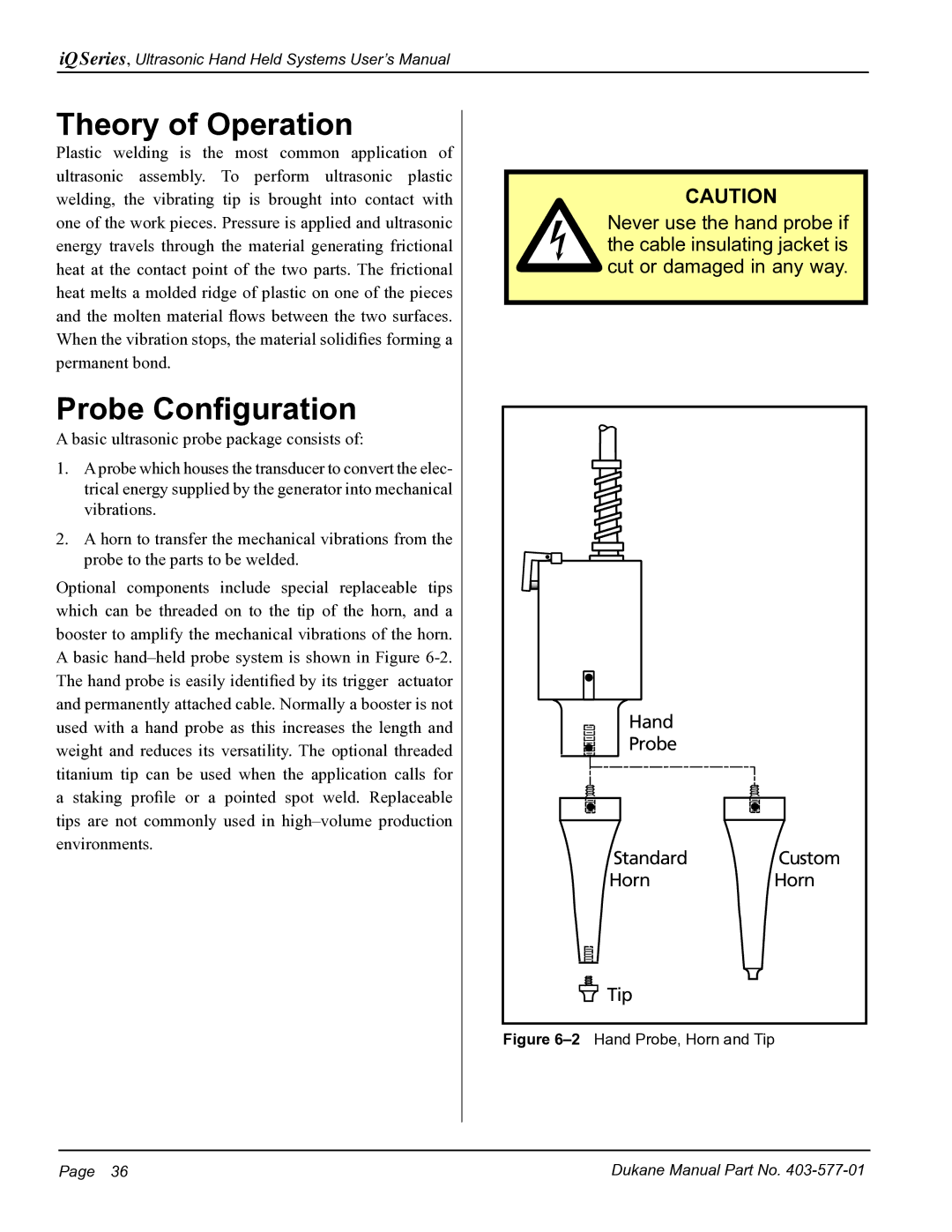
Optional components include special replaceable tips which can be threaded on to the tip of the horn, and a booster to amplify the mechanical vibrations of the horn. A basic
CAUTION Never use the hand probe if the cable insulating jacket is cut or damaged in any way.
Hand
Probe
Standard Custom
HornHorn
![]() Tip
Tip
Figure 6–2 Hand Probe, Horn and Tip
Page 36 | Dukane Manual Part No. |