|
|
| Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
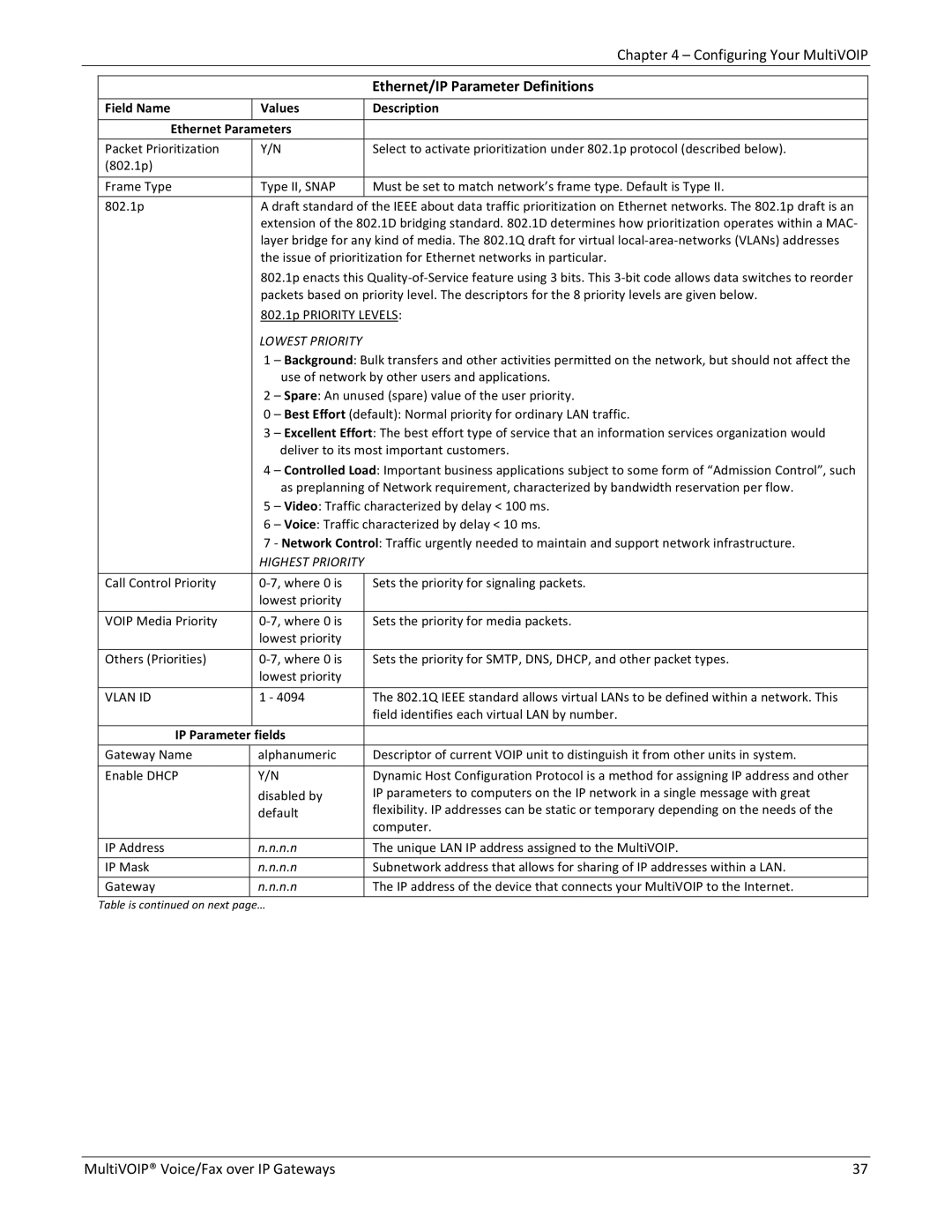
| Ethernet/IP Parameter Definitions |
|
|
| Description |
| Field Name | Values | |
|
|
|
|
| Ethernet Parameters |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Packet Prioritization | Y/N | Select to activate prioritization under 802.1p protocol (described below). |
| (802.1p) |
|
|
|
|
| Must be set to match network’s frame type. Default is Type II. |
| Frame Type | Type II, SNAP | |
| 802.1p | A draft standard of the IEEE about data traffic prioritization on Ethernet networks. The 802.1p draft is an | |
|
| extension of the 802.1D bridging standard. 802.1D determines how prioritization operates within a MAC‐ | |
|
| layer bridge for any kind of media. The 802.1Q draft for virtual local‐area‐networks (VLANs) addresses | |
|
| the issue of prioritization for Ethernet networks in particular. | |
|
| 802.1p enacts this Quality‐of‐Service feature using 3 bits. This 3‐bit code allows data switches to reorder | |
|
| packets based on priority level. The descriptors for the 8 priority levels are given below. | |
|
| 802.1p PRIORITY LEVELS: | |
|
| LOWEST PRIORITY |
|
|
| 1 – Background: Bulk transfers and other activities permitted on the network, but should not affect the | |
|
| use of network by other users and applications. | |
|
| 2 – Spare: An unused (spare) value of the user priority. | |
|
| 0 – Best Effort (default): Normal priority for ordinary LAN traffic. | |
|
| 3 – Excellent Effort: The best effort type of service that an information services organization would | |
|
| deliver to its most important customers. | |
|
| 4 – Controlled Load: Important business applications subject to some form of “Admission Control”, such | |
|
| as preplanning of Network requirement, characterized by bandwidth reservation per flow. | |
|
| 5 – Video: Traffic characterized by delay < 100 ms. | |
|
| 6 – Voice: Traffic characterized by delay < 10 ms. | |
|
| 7 ‐ Network Control: Traffic urgently needed to maintain and support network infrastructure. | |
|
| HIGHEST PRIORITY |
|
|
|
| Sets the priority for signaling packets. |
| Call Control Priority | 0‐7, where 0 is | |
|
| lowest priority |
|
|
|
|
|
| VOIP Media Priority | 0‐7, where 0 is | Sets the priority for media packets. |
|
| lowest priority |
|
|
|
|
|
| Others (Priorities) | 0‐7, where 0 is | Sets the priority for SMTP, DNS, DHCP, and other packet types. |
|
| lowest priority |
|
|
|
|
|
| VLAN ID | 1 ‐ 4094 | The 802.1Q IEEE standard allows virtual LANs to be defined within a network. This |
|
|
| field identifies each virtual LAN by number. |
|
|
|
|
| IP Parameter | fields |
|
| Gateway Name | alphanumeric | Descriptor of current VOIP unit to distinguish it from other units in system. |
|
|
| Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a method for assigning IP address and other |
| Enable DHCP | Y/N | |
|
| disabled by | IP parameters to computers on the IP network in a single message with great |
|
| default | flexibility. IP addresses can be static or temporary depending on the needs of the |
|
|
| computer. |
| IP Address | n.n.n.n | The unique LAN IP address assigned to the MultiVOIP. |
|
|
| Subnetwork address that allows for sharing of IP addresses within a LAN. |
| IP Mask | n.n.n.n | |
|
|
| The IP address of the device that connects your MultiVOIP to the Internet. |
| Gateway | n.n.n.n | |
Table is continued on next page…
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways | 37 |