Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
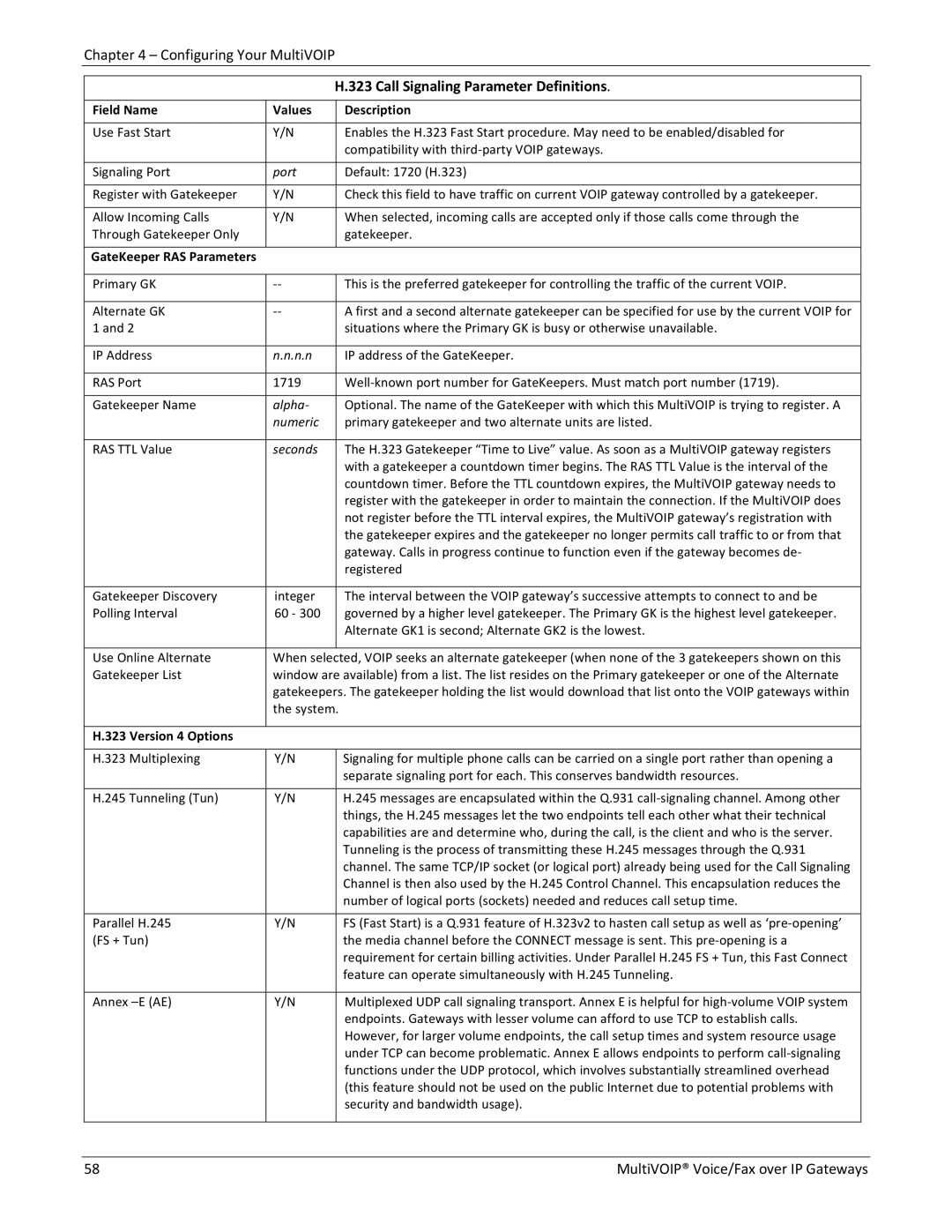
H.323 Call Signaling Parameter Definitions.
Field Name | Values |
|
|
Use Fast Start | Y/N |
|
|
Signaling Port | port |
|
|
Register with Gatekeeper | Y/N |
|
|
Allow Incoming Calls | Y/N |
Through Gatekeeper Only |
|
|
|
GateKeeper RAS Parameters |
|
Description
Enables the H.323 Fast Start procedure. May need to be enabled/disabled for compatibility with third‐party VOIP gateways.
Default: 1720 (H.323)
Check this field to have traffic on current VOIP gateway controlled by a gatekeeper.
When selected, incoming calls are accepted only if those calls come through the gatekeeper.
Primary GK | ‐‐ |
| This is the preferred gatekeeper for controlling the traffic of the current VOIP. |
|
|
| A first and a second alternate gatekeeper can be specified for use by the current VOIP for |
Alternate GK | ‐‐ |
| |
1 and 2 |
|
| situations where the Primary GK is busy or otherwise unavailable. |
|
|
| IP address of the GateKeeper. |
IP Address | n.n.n.n |
| |
|
|
| Well‐known port number for GateKeepers. Must match port number (1719). |
RAS Port | 1719 |
| |
|
|
| Optional. The name of the GateKeeper with which this MultiVOIP is trying to register. A |
Gatekeeper Name | alpha‐ |
| |
| numeric |
| primary gatekeeper and two alternate units are listed. |
|
|
|
|
RAS TTL Value | seconds |
| The H.323 Gatekeeper “Time to Live” value. As soon as a MultiVOIP gateway registers |
|
|
| with a gatekeeper a countdown timer begins. The RAS TTL Value is the interval of the |
|
|
| countdown timer. Before the TTL countdown expires, the MultiVOIP gateway needs to |
|
|
| register with the gatekeeper in order to maintain the connection. If the MultiVOIP does |
|
|
| not register before the TTL interval expires, the MultiVOIP gateway’s registration with |
|
|
| the gatekeeper expires and the gatekeeper no longer permits call traffic to or from that |
|
|
| gateway. Calls in progress continue to function even if the gateway becomes de‐ |
|
|
| registered |
|
|
| The interval between the VOIP gateway’s successive attempts to connect to and be |
Gatekeeper Discovery | integer |
| |
Polling Interval | 60 ‐ 300 |
| governed by a higher level gatekeeper. The Primary GK is the highest level gatekeeper. |
|
|
| Alternate GK1 is second; Alternate GK2 is the lowest. |
|
|
| |
Use Online Alternate | When selected, VOIP seeks an alternate gatekeeper (when none of the 3 gatekeepers shown on this | ||
Gatekeeper List | window are available) from a list. The list resides on the Primary gatekeeper or one of the Alternate | ||
| gatekeepers. The gatekeeper holding the list would download that list onto the VOIP gateways within | ||
| the system. |
| |
|
|
|
|
H.323 Version 4 Options |
|
|
|
H.323 Multiplexing | Y/N |
|
|
H.245 Tunneling (Tun) | Y/N |
Parallel H.245 | Y/N |
(FS + Tun) |
|
|
|
Annex | Y/N |
Signaling for multiple phone calls can be carried on a single port rather than opening a separate signaling port for each. This conserves bandwidth resources.
H.245 messages are encapsulated within the Q.931 call‐signaling channel. Among other things, the H.245 messages let the two endpoints tell each other what their technical capabilities are and determine who, during the call, is the client and who is the server. Tunneling is the process of transmitting these H.245 messages through the Q.931 channel. The same TCP/IP socket (or logical port) already being used for the Call Signaling Channel is then also used by the H.245 Control Channel. This encapsulation reduces the number of logical ports (sockets) needed and reduces call setup time.
FS (Fast Start) is a Q.931 feature of H.323v2 to hasten call setup as well as ‘pre‐opening’ the media channel before the CONNECT message is sent. This pre‐opening is a requirement for certain billing activities. Under Parallel H.245 FS + Tun, this Fast Connect feature can operate simultaneously with H.245 Tunneling.
Multiplexed UDP call signaling transport. Annex E is helpful for high‐volume VOIP system endpoints. Gateways with lesser volume can afford to use TCP to establish calls. However, for larger volume endpoints, the call setup times and system resource usage under TCP can become problematic. Annex E allows endpoints to perform call‐signaling functions under the UDP protocol, which involves substantially streamlined overhead (this feature should not be used on the public Internet due to potential problems with security and bandwidth usage).
58 | MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways |