|
|
| Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
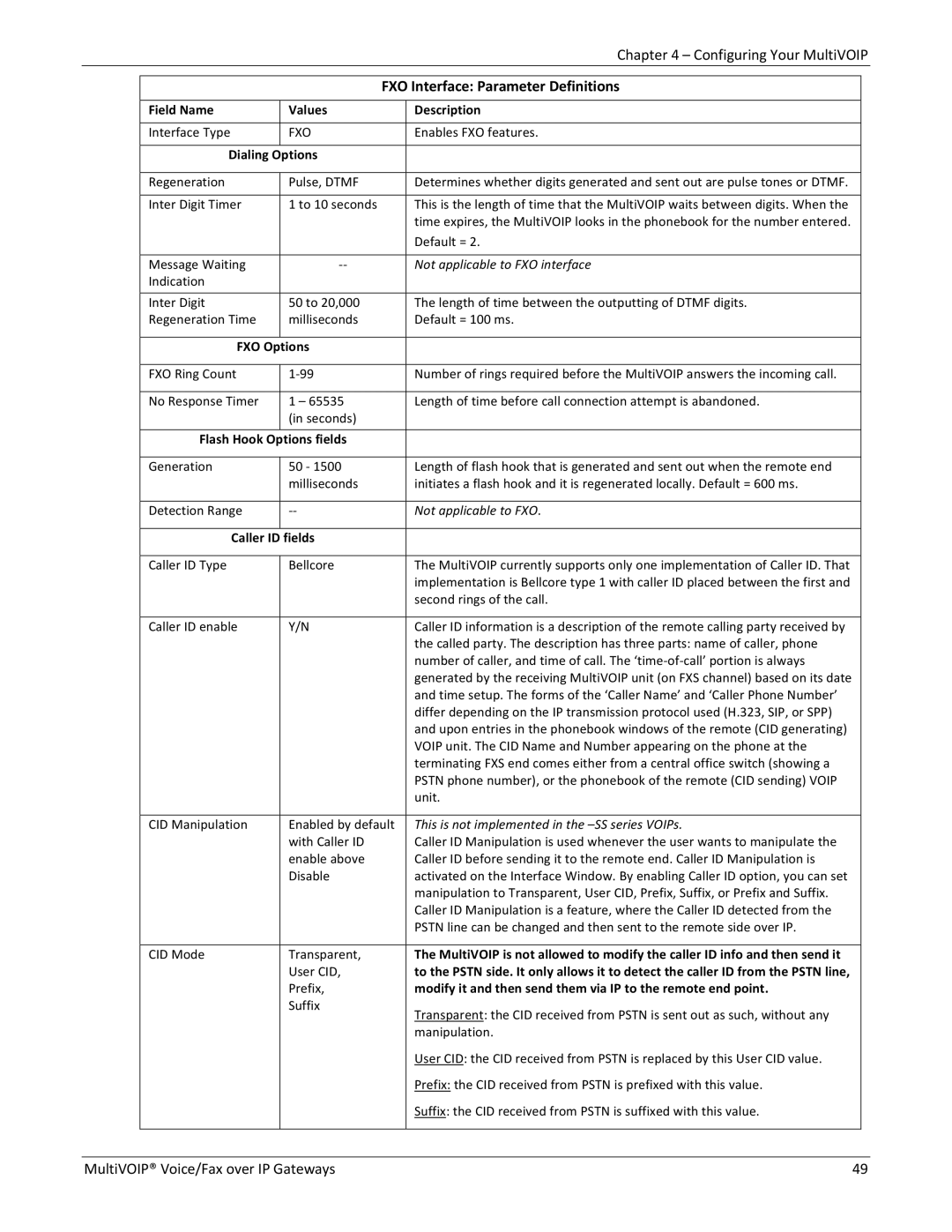
| FXO Interface: Parameter Definitions |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| Field Name | Values | Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Interface Type | FXO | Enables FXO features. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Dialing Options |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| Regeneration | Pulse, DTMF | Determines whether digits generated and sent out are pulse tones or DTMF. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Inter Digit Timer | 1 to 10 seconds | This is the length of time that the MultiVOIP waits between digits. When the |
|
|
|
| time expires, the MultiVOIP looks in the phonebook for the number entered. |
|
|
|
| Default = 2. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Message Waiting | ‐‐ | Not applicable to FXO interface |
|
| Indication |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Inter Digit | 50 to 20,000 | The length of time between the outputting of DTMF digits. |
|
| Regeneration Time | milliseconds | Default = 100 ms. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| FXO Options |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| FXO Ring Count | 1‐99 | Number of rings required before the MultiVOIP answers the incoming call. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No Response Timer | 1 – 65535 | Length of time before call connection attempt is abandoned. |
|
|
| (in seconds) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Flash Hook Options fields |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| Generation | 50 ‐ 1500 | Length of flash hook that is generated and sent out when the remote end |
|
|
| milliseconds | initiates a flash hook and it is regenerated locally. Default = 600 ms. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Detection Range | ‐‐ | Not applicable to FXO. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Caller ID fields |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| Caller ID Type | Bellcore | The MultiVOIP currently supports only one implementation of Caller ID. That |
|
|
|
| implementation is Bellcore type 1 with caller ID placed between the first and |
|
|
|
| second rings of the call. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Caller ID enable | Y/N | Caller ID information is a description of the remote calling party received by |
|
|
|
| the called party. The description has three parts: name of caller, phone |
|
|
|
| number of caller, and time of call. The ‘time‐of‐call’ portion is always |
|
|
|
| generated by the receiving MultiVOIP unit (on FXS channel) based on its date |
|
|
|
| and time setup. The forms of the ‘Caller Name’ and ‘Caller Phone Number’ |
|
|
|
| differ depending on the IP transmission protocol used (H.323, SIP, or SPP) |
|
|
|
| and upon entries in the phonebook windows of the remote (CID generating) |
|
|
|
| VOIP unit. The CID Name and Number appearing on the phone at the |
|
|
|
| terminating FXS end comes either from a central office switch (showing a |
|
|
|
| PSTN phone number), or the phonebook of the remote (CID sending) VOIP |
|
|
|
| unit. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CID Manipulation | Enabled by default | This is not implemented in the |
|
|
| with Caller ID | Caller ID Manipulation is used whenever the user wants to manipulate the |
|
|
| enable above | Caller ID before sending it to the remote end. Caller ID Manipulation is |
|
|
| Disable | activated on the Interface Window. By enabling Caller ID option, you can set |
|
|
|
| manipulation to Transparent, User CID, Prefix, Suffix, or Prefix and Suffix. |
|
|
|
| Caller ID Manipulation is a feature, where the Caller ID detected from the |
|
|
|
| PSTN line can be changed and then sent to the remote side over IP. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CID Mode | Transparent, | The MultiVOIP is not allowed to modify the caller ID info and then send it |
|
|
| User CID, | to the PSTN side. It only allows it to detect the caller ID from the PSTN line, |
|
|
| Prefix, | modify it and then send them via IP to the remote end point. |
|
|
| Suffix | Transparent: the CID received from PSTN is sent out as such, without any |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| manipulation. |
|
|
|
| User CID: the CID received from PSTN is replaced by this User CID value. |
|
|
|
| Prefix: the CID received from PSTN is prefixed with this value. |
|
|
|
| Suffix: the CID received from PSTN is suffixed with this value. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways | 49 |