Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
|
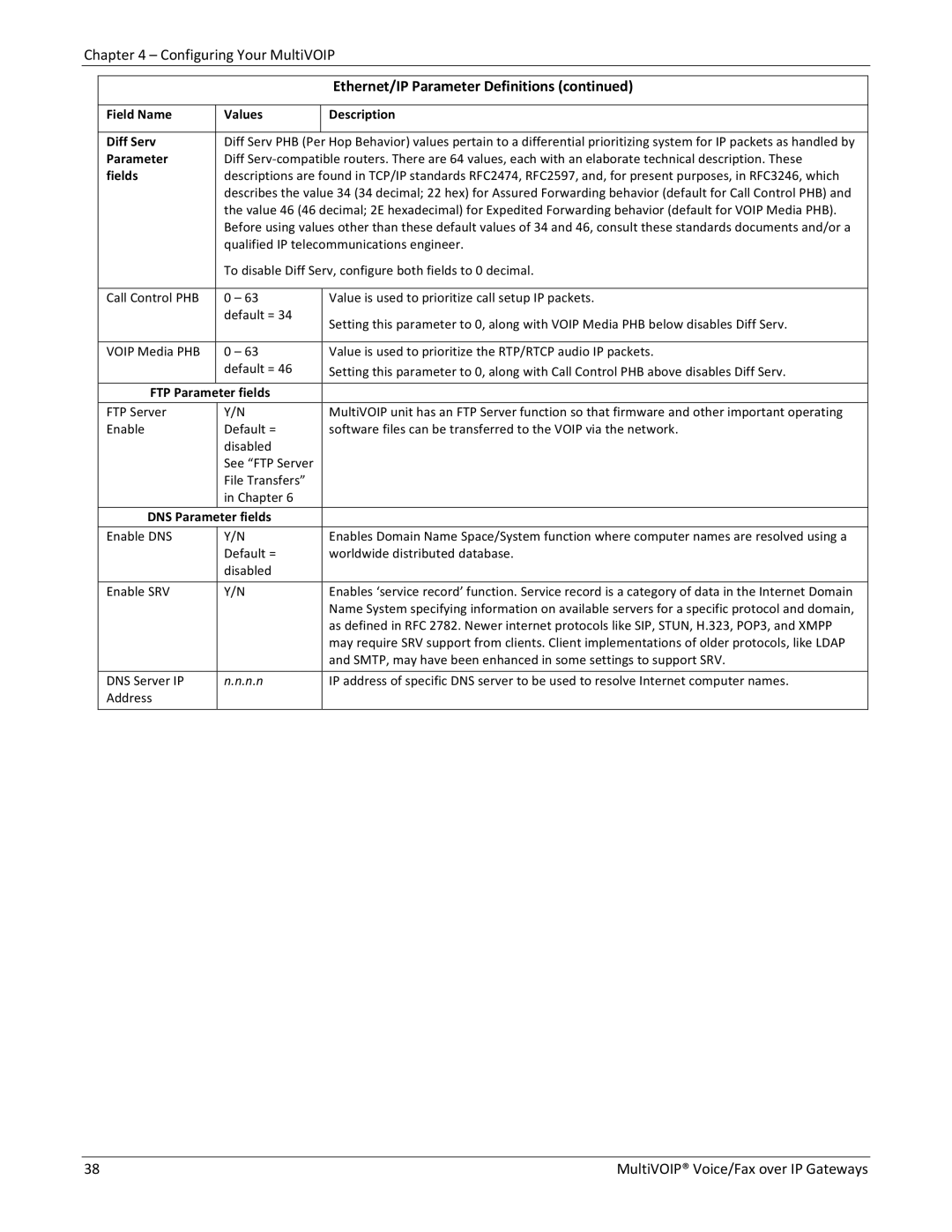
| Ethernet/IP Parameter Definitions (continued) |
|
|
|
Field Name | Values | Description |
|
|
|
Diff Serv | Diff Serv PHB (Per Hop Behavior) values pertain to a differential prioritizing system for IP packets as handled by | |
Parameter | Diff Serv‐compatible routers. There are 64 values, each with an elaborate technical description. These | |
fields | descriptions are found in TCP/IP standards RFC2474, RFC2597, and, for present purposes, in RFC3246, which | |
| describes the value 34 (34 decimal; 22 hex) for Assured Forwarding behavior (default for Call Control PHB) and | |
| the value 46 (46 decimal; 2E hexadecimal) for Expedited Forwarding behavior (default for VOIP Media PHB). | |
| Before using values other than these default values of 34 and 46, consult these standards documents and/or a | |
| qualified IP telecommunications engineer. | |
| To disable Diff Serv, configure both fields to 0 decimal. | |
|
| Value is used to prioritize call setup IP packets. |
Call Control PHB | 0 – 63 | |
| default = 34 | Setting this parameter to 0, along with VOIP Media PHB below disables Diff Serv. |
|
| |
|
|
|
VOIP Media PHB | 0 – 63 | Value is used to prioritize the RTP/RTCP audio IP packets. |
| default = 46 | Setting this parameter to 0, along with Call Control PHB above disables Diff Serv. |
|
|
|
FTP Parameter fields |
| |
|
| MultiVOIP unit has an FTP Server function so that firmware and other important operating |
FTP Server | Y/N | |
Enable | Default = | software files can be transferred to the VOIP via the network. |
| disabled |
|
| See “FTP Server |
|
| File Transfers” |
|
| in Chapter 6 |
|
|
|
|
DNS Parameter fields |
| |
Enable DNS | Y/N | Enables Domain Name Space/System function where computer names are resolved using a |
| Default = | worldwide distributed database. |
| disabled |
|
|
|
|
Enable SRV | Y/N | Enables ‘service record’ function. Service record is a category of data in the Internet Domain |
|
| Name System specifying information on available servers for a specific protocol and domain, |
|
| as defined in RFC 2782. Newer internet protocols like SIP, STUN, H.323, POP3, and XMPP |
|
| may require SRV support from clients. Client implementations of older protocols, like LDAP |
|
| and SMTP, may have been enhanced in some settings to support SRV. |
|
| IP address of specific DNS server to be used to resolve Internet computer names. |
DNS Server IP | n.n.n.n | |
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
38 | MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways |