Configuring High Availability VLANs
Ingress and Egress Traffic Flows
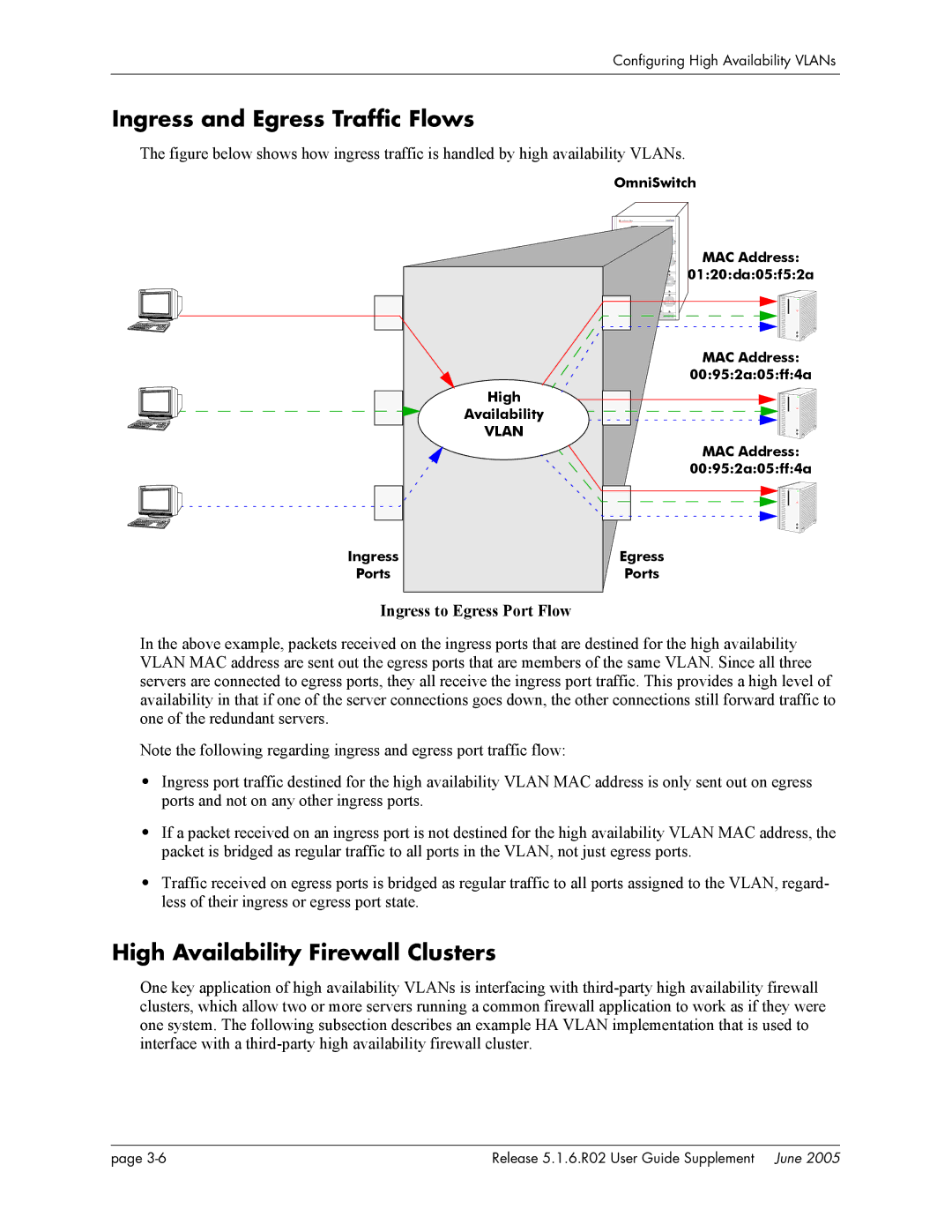
The figure below shows how ingress traffic is handled by high availability VLANs.
Ingress
Ports
OmniSwitch
MAC Address:
01:20:da:05:f5:2a
MAC Address:
00:95:2a:05:ff:4a
High Availability
VLAN
MAC Address: 00:95:2a:05:ff:4a
Egress
Ports
Ingress to Egress Port Flow
In the above example, packets received on the ingress ports that are destined for the high availability VLAN MAC address are sent out the egress ports that are members of the same VLAN. Since all three servers are connected to egress ports, they all receive the ingress port traffic. This provides a high level of availability in that if one of the server connections goes down, the other connections still forward traffic to one of the redundant servers.
Note the following regarding ingress and egress port traffic flow:
•Ingress port traffic destined for the high availability VLAN MAC address is only sent out on egress ports and not on any other ingress ports.
•If a packet received on an ingress port is not destined for the high availability VLAN MAC address, the packet is bridged as regular traffic to all ports in the VLAN, not just egress ports.
•Traffic received on egress ports is bridged as regular traffic to all ports assigned to the VLAN, regard- less of their ingress or egress port state.
High Availability Firewall Clusters
One key application of high availability VLANs is interfacing with
page | Release 5.1.6.R02 User Guide Supplement June 2005 |