Voice Over IP Operations
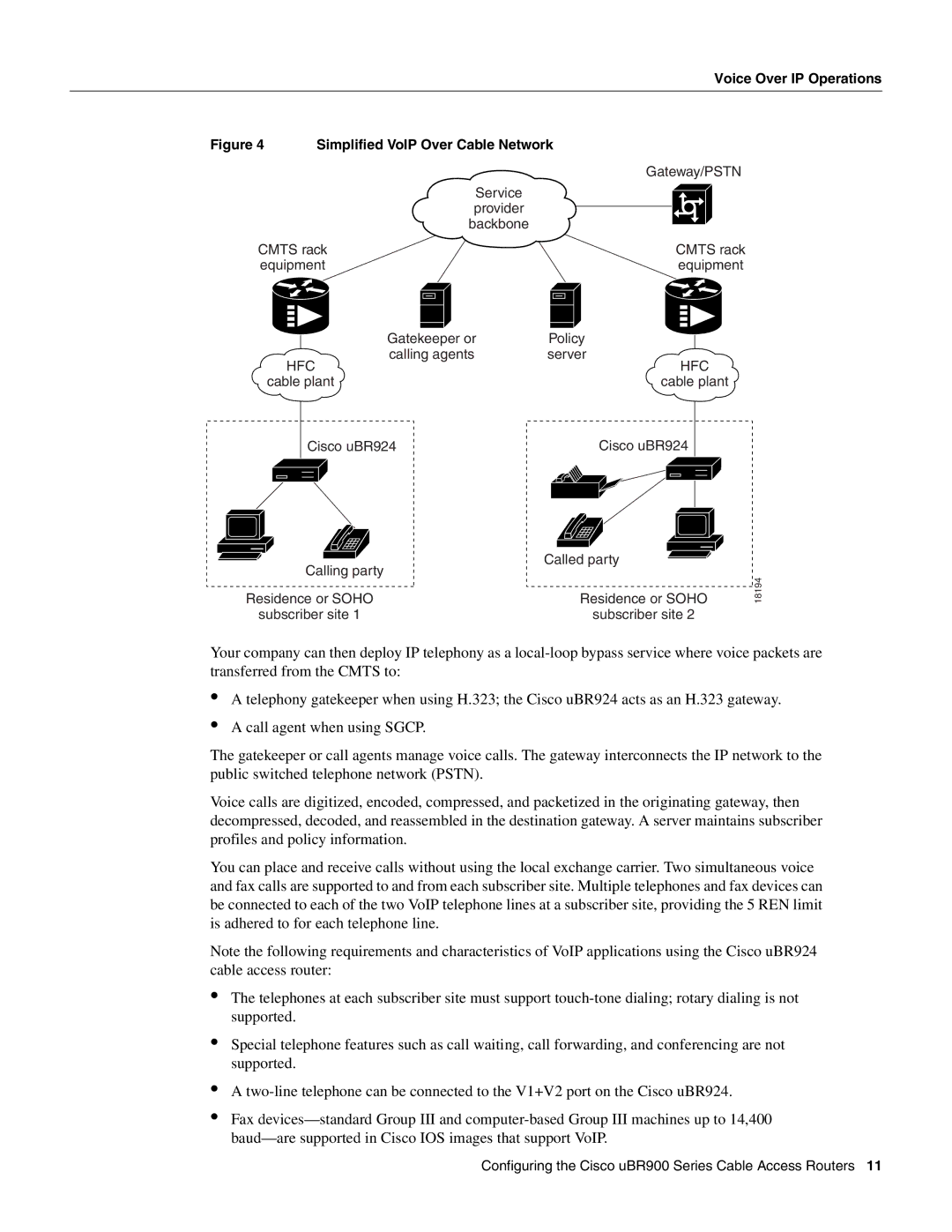
Figure 4 | Simplified VoIP Over Cable Network |
Gateway/PSTN
Service provider backbone
CMTS rack | CMTS rack |
equipment | equipment |
Gatekeeper or | Policy |
calling agents | server |
HFC | HFC |
cable plant | cable plant |
Cisco uBR924 | Cisco uBR924 |
| Calling party | Called party |
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
| |
Residence or SOHO | Residence or SOHO | |||
| subscriber site 1 | subscriber site 2 | ||
18194
Your company can then deploy IP telephony as a
•
•
A telephony gatekeeper when using H.323; the Cisco uBR924 acts as an H.323 gateway.
A call agent when using SGCP.
The gatekeeper or call agents manage voice calls. The gateway interconnects the IP network to the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
Voice calls are digitized, encoded, compressed, and packetized in the originating gateway, then decompressed, decoded, and reassembled in the destination gateway. A server maintains subscriber profiles and policy information.
You can place and receive calls without using the local exchange carrier. Two simultaneous voice and fax calls are supported to and from each subscriber site. Multiple telephones and fax devices can be connected to each of the two VoIP telephone lines at a subscriber site, providing the 5 REN limit is adhered to for each telephone line.
Note the following requirements and characteristics of VoIP applications using the Cisco uBR924 cable access router:
•The telephones at each subscriber site must support
•Special telephone features such as call waiting, call forwarding, and conferencing are not supported.
•A
•Fax
Configuring the Cisco uBR900 Series Cable Access Routers 11