Data Operations
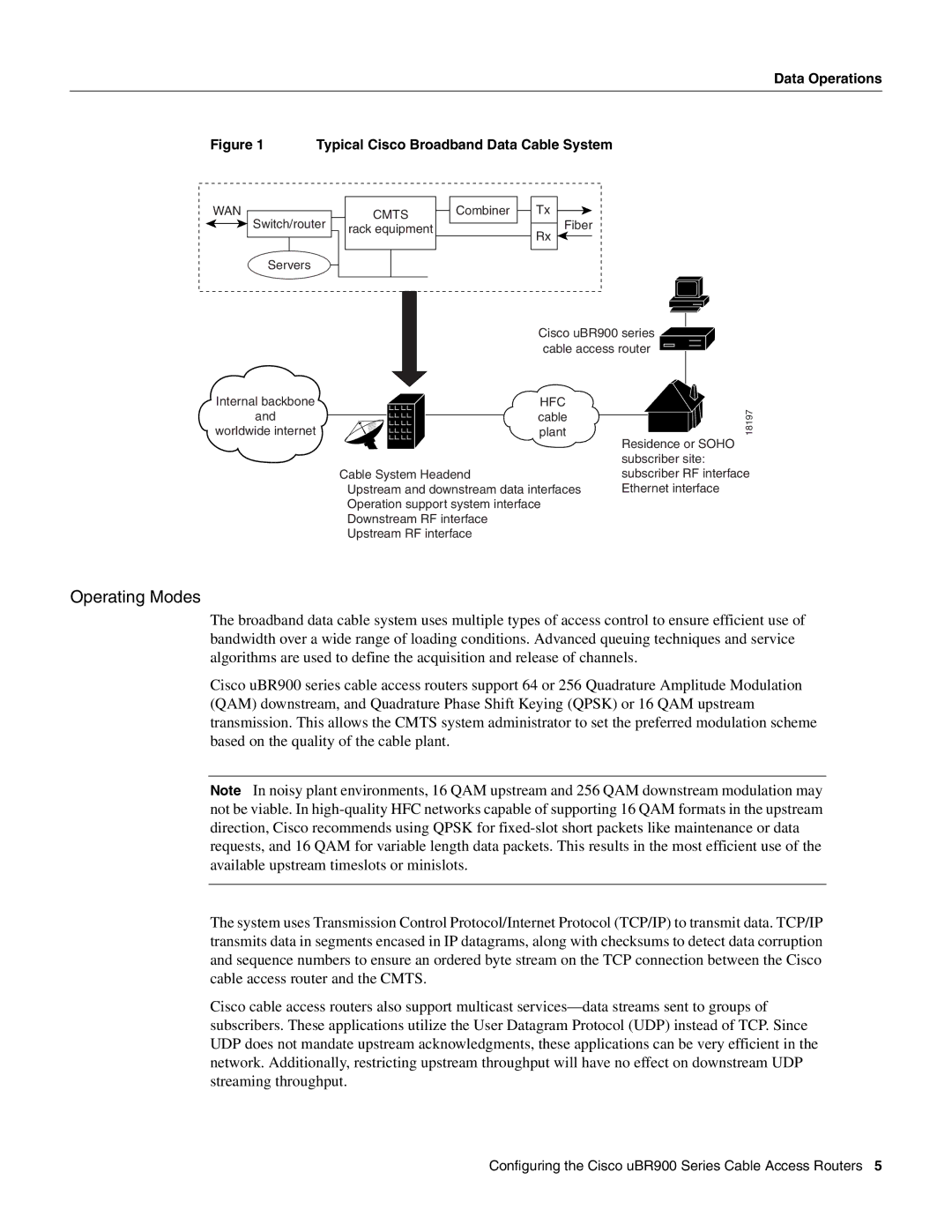
Figure 1 Typical Cisco Broadband Data Cable System
WAN
Switch/router
|
| Combiner |
|
| Tx |
CMTS |
|
| |||
|
|
|
| ||
rack equipment |
|
|
| Rx | |
|
|
|
|
| |
Fiber
Servers
Cisco uBR900 series ![]() cable access router
cable access router ![]()
Internal backbone
and
worldwide internet
HFC
cable plant
Cable System Headend
Upstream and downstream data interfaces Operation support system interface Downstream RF interface
Upstream RF interface
18197
Residence or SOHO subscriber site: subscriber RF interface Ethernet interface
Operating Modes
The broadband data cable system uses multiple types of access control to ensure efficient use of bandwidth over a wide range of loading conditions. Advanced queuing techniques and service algorithms are used to define the acquisition and release of channels.
Cisco uBR900 series cable access routers support 64 or 256 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) downstream, and Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) or 16 QAM upstream transmission. This allows the CMTS system administrator to set the preferred modulation scheme based on the quality of the cable plant.
Note In noisy plant environments, 16 QAM upstream and 256 QAM downstream modulation may not be viable. In
The system uses Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) to transmit data. TCP/IP transmits data in segments encased in IP datagrams, along with checksums to detect data corruption and sequence numbers to ensure an ordered byte stream on the TCP connection between the Cisco cable access router and the CMTS.
Cisco cable access routers also support multicast
Configuring the Cisco uBR900 Series Cable Access Routers 5