Data Operations
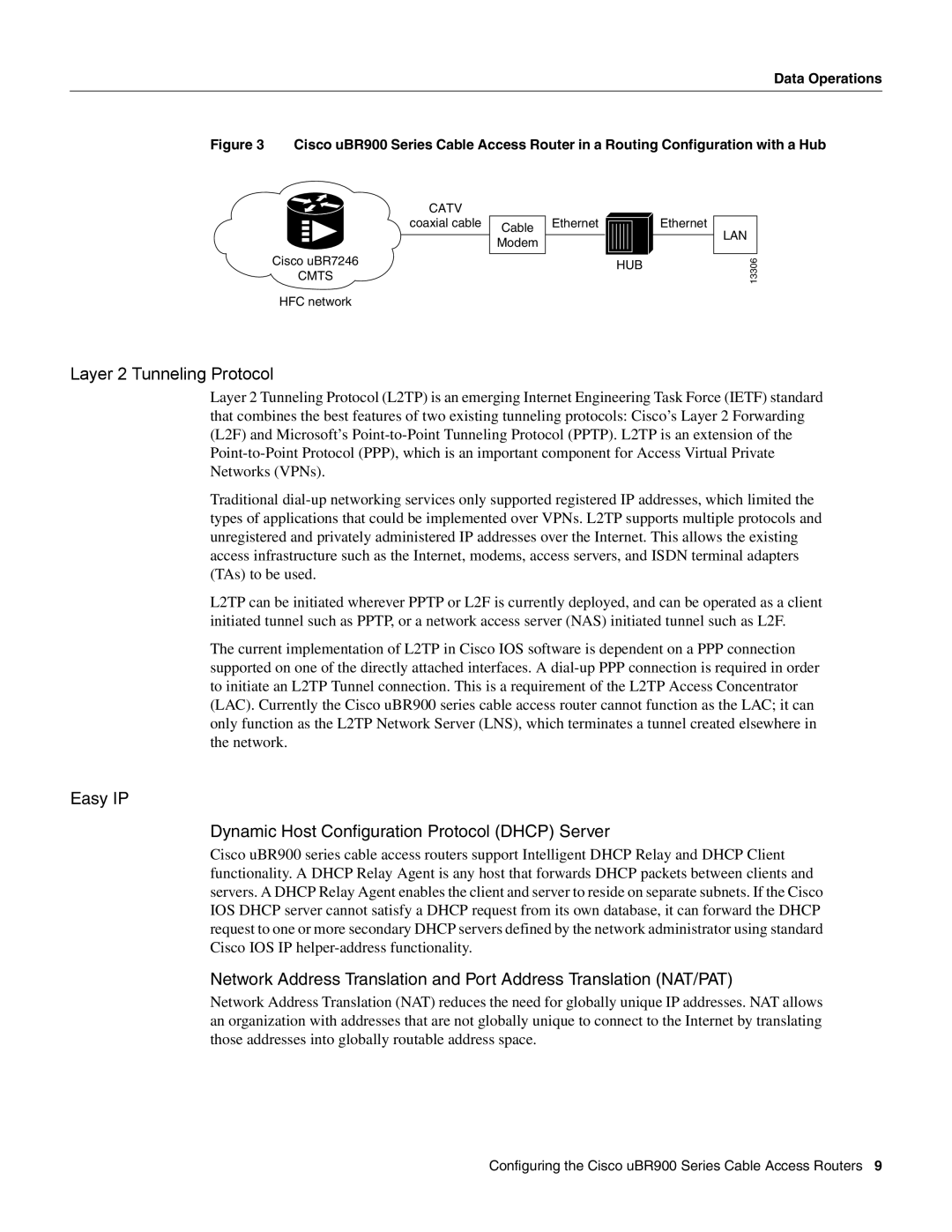
Figure 3 Cisco uBR900 Series Cable Access Router in a Routing Configuration with a Hub
CATV
coaxial cable
Cisco uBR7246
CMTS
HFC network
Cable
Modem
Ethernet
HUB
Ethernet
LAN
13306
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is an emerging Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard that combines the best features of two existing tunneling protocols: Cisco’s Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) and Microsoft’s
Traditional
L2TP can be initiated wherever PPTP or L2F is currently deployed, and can be operated as a client initiated tunnel such as PPTP, or a network access server (NAS) initiated tunnel such as L2F.
The current implementation of L2TP in Cisco IOS software is dependent on a PPP connection supported on one of the directly attached interfaces. A
Easy IP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server
Cisco uBR900 series cable access routers support Intelligent DHCP Relay and DHCP Client functionality. A DHCP Relay Agent is any host that forwards DHCP packets between clients and servers. A DHCP Relay Agent enables the client and server to reside on separate subnets. If the Cisco IOS DHCP server cannot satisfy a DHCP request from its own database, it can forward the DHCP request to one or more secondary DHCP servers defined by the network administrator using standard Cisco IOS IP
Network Address Translation and Port Address Translation (NAT/PAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT) reduces the need for globally unique IP addresses. NAT allows an organization with addresses that are not globally unique to connect to the Internet by translating those addresses into globally routable address space.
Configuring the Cisco uBR900 Series Cable Access Routers 9