8 GB | 2 GB |
|
|
12 GB | 2 GB | 1 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
16 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
24 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 1 GB |
|
|
|
|
32 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB |
|
|
|
|
16 GB | 4 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 GB | 4 GB | 2 GB |
|
32 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
48 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 2 GB |
|
|
|
|
64 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB |
|
|
|
|
32 GB | 8 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 GB | 8 GB | 4 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
64 GB | 8 GB | 8 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
96 GB | 8 GB | 8 GB | 4 GB |
|
|
|
|
128 GB | 8 GB | 8 GB | 8 GB |
Memory Sparing Support
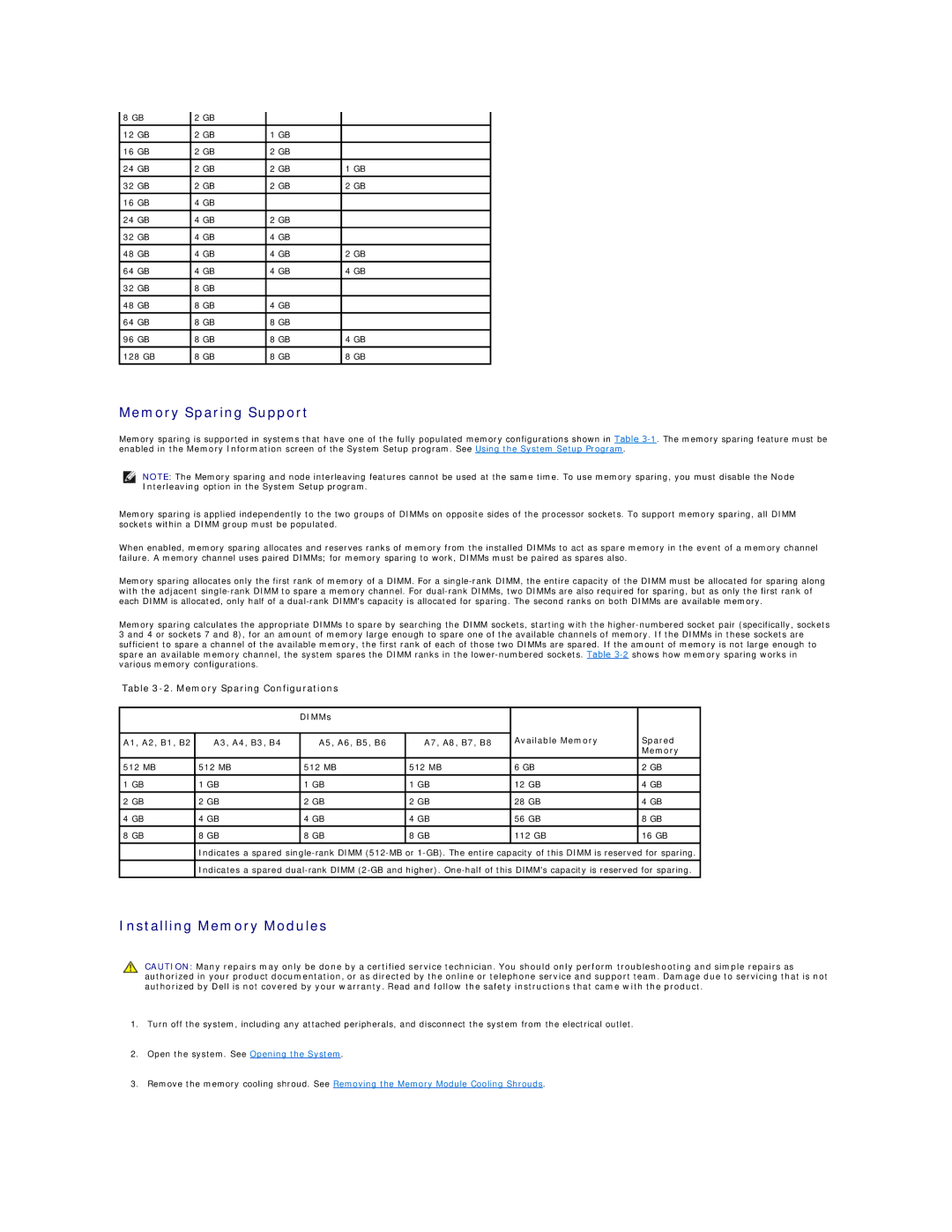
Memory sparing is supported in systems that have one of the fully populated memory configurations shown in Table
NOTE: The Memory sparing and node interleaving features cannot be used at the same time. To use memory sparing, you must disable the Node Interleaving option in the System Setup program.
Memory sparing is applied independently to the two groups of DIMMs on opposite sides of the processor sockets. To support memory sparing, all DIMM sockets within a DIMM group must be populated.
When enabled, memory sparing allocates and reserves ranks of memory from the installed DIMMs to act as spare memory in the event of a memory channel failure. A memory channel uses paired DIMMs; for memory sparing to work, DIMMs must be paired as spares also.
Memory sparing allocates only the first rank of memory of a DIMM. For a
Memory sparing calculates the appropriate DIMMs to spare by searching the DIMM sockets, starting with the
Table 3-2. Memory Sparing Configurations
|
| DIMMs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Available Memory | Spared |
A1, A2, B1, B2 | A3, A4, B3, B4 | A5, A6, B5, B6 | A7, A8, B7, B8 | ||
|
|
|
|
| Memory |
512 MB | 512 MB | 512 MB | 512 MB | 6 GB | 2 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 12 GB | 4 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 2 GB | 28 GB | 4 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | 56 GB | 8 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 GB | 8 GB | 8 GB | 8 GB | 112 GB | 16 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Indicates a spared | ||||
|
|
| |||
| Indicates a spared | ||||
Installing Memory Modules
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or telephone service and support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the product.
1.Turn off the system, including any attached peripherals, and disconnect the system from the electrical outlet.
2.Open the system. See Opening the System.
3.Remove the memory cooling shroud. See Removing the Memory Module Cooling Shrouds.