Stylus C40UX/C40SX/C20UX/C20SX | Revision A |
2.2 Electrical Circuit Operating Principles
The electric circuit of the Stylus C40UX/C40SX/C20UX/C20SX consists of the following boards.
Main board: | C413 MAIN (USB) | |
| C413 | |
Power supply board: | C417 | PSB/PSE Board |
NOTE: The
C413 MAIN-C (USB)
C413 MAIN-B (Parallel)
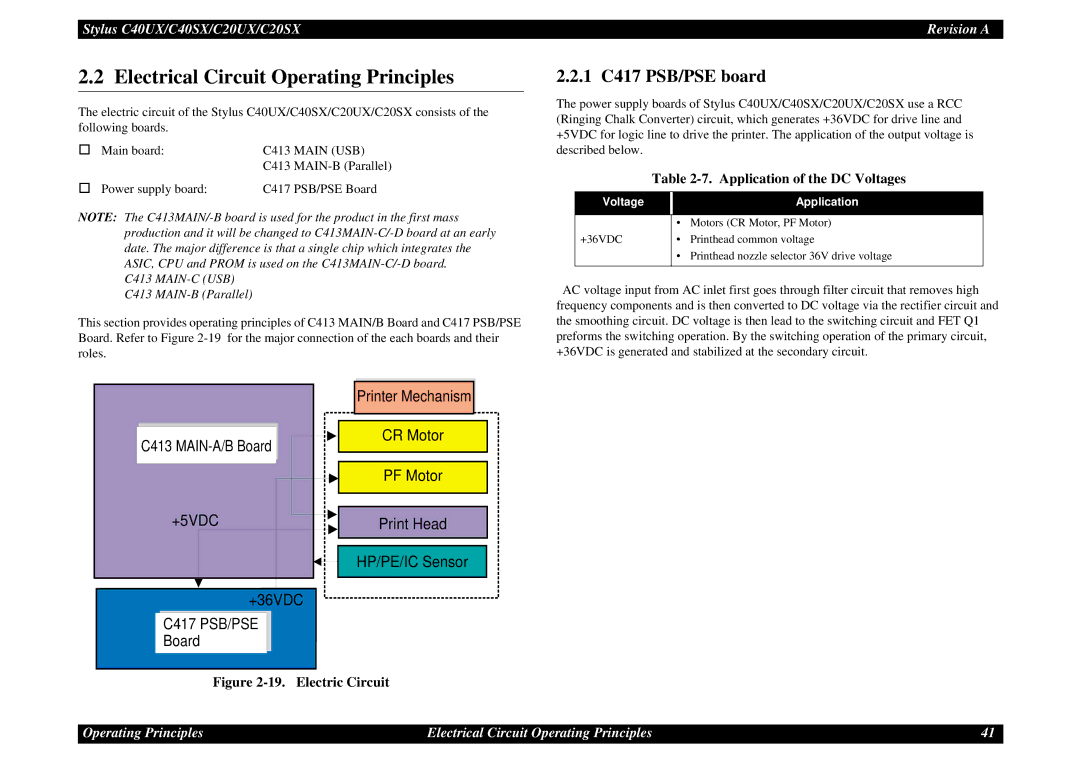
This section provides operating principles of C413 MAIN/B Board and C417 PSB/PSE Board. Refer to Figure
2.2.1 C417 PSB/PSE board
The power supply boards of Stylus C40UX/C40SX/C20UX/C20SX use a RCC (Ringing Chalk Converter) circuit, which generates +36VDC for drive line and +5VDC for logic line to drive the printer. The application of the output voltage is described below.
Table 2-7. Application of the DC Voltages
Voltage |
| Application |
|
| |
| • Motors (CR Motor, PF Motor) | |
+36VDC | • | Printhead common voltage |
| • | Printhead nozzle selector 36V drive voltage |
|
|
|
AC voltage input from AC inlet first goes through filter circuit that removes high frequency components and is then converted to DC voltage via the rectifier circuit and the smoothing circuit. DC voltage is then lead to the switching circuit and FET Q1 preforms the switching operation. By the switching operation of the primary circuit, +36VDC is generated and stabilized at the secondary circuit.
C413 ![]()
![]()
+5VDC
+36VDC
C417 PSB/PSE
Board
Printer Mechanism ![]()
![]()
CR Motor
PF Motor
Print Head
HP/PE/IC Sensor
Figure 2-19. Electric Circuit
Operating Principles | Electrical Circuit Operating Principles | 41 |