|
|
FortiBridge operating principles | Example FortiBridge application |
FortiBridge operating principles
This chapter describes a typical transparent mode FortiGate network and how to add a FortiBridge unit to this network to provide fail open protection. This chapter also contains detailed information about how FortiBridge units operate and concludes with descriptions of adding a FortiBridge unit to an HA cluster and connecting a FortiBridge unit other FortiGate interfaces.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•Example FortiBridge application
•Normal mode operation
•Bypass mode operation
•FortiBridge power failure
•Example FortiGate HA cluster FortiBridge application
•Example configuration with other FortiGate interfaces
Example FortiBridge application
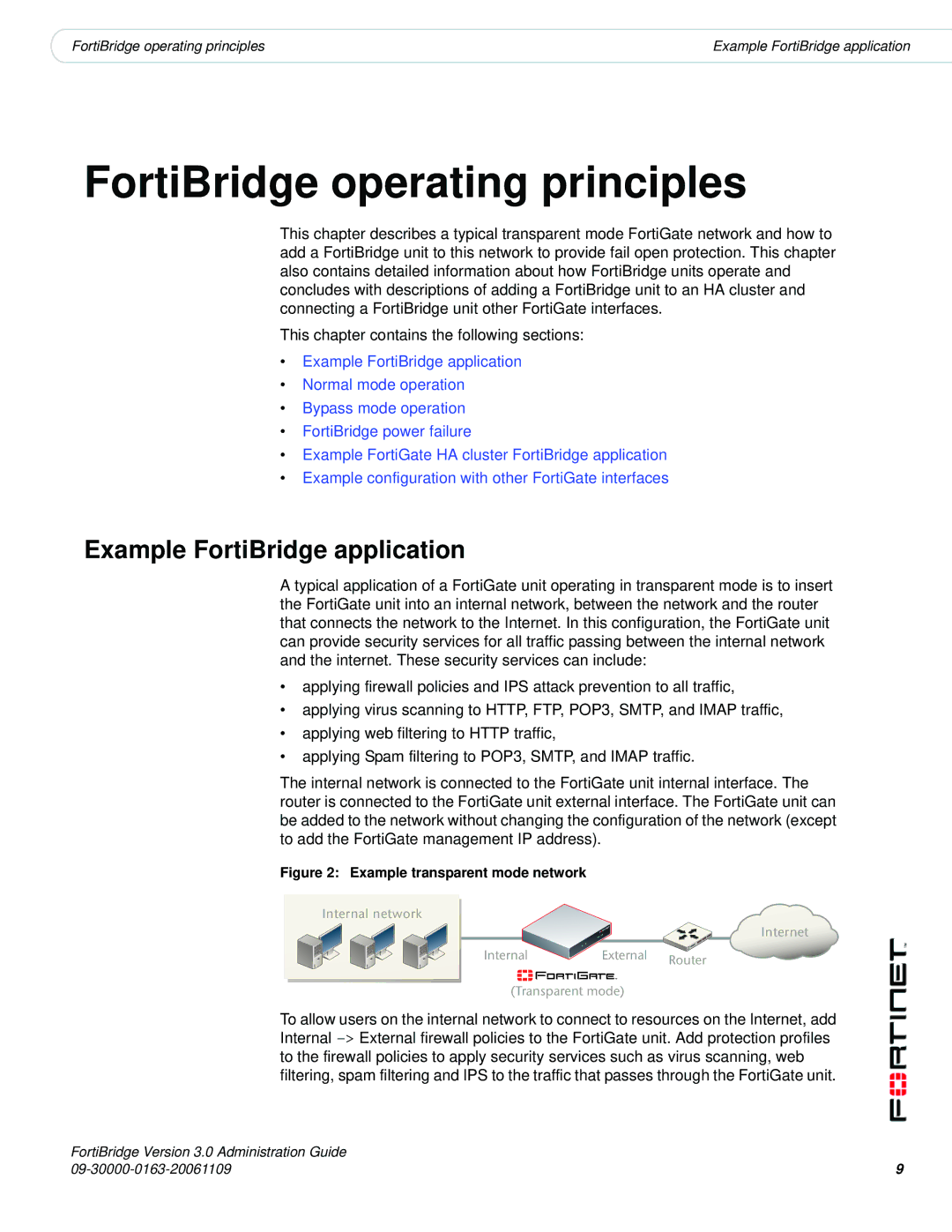
A typical application of a FortiGate unit operating in transparent mode is to insert the FortiGate unit into an internal network, between the network and the router that connects the network to the Internet. In this configuration, the FortiGate unit can provide security services for all traffic passing between the internal network and the internet. These security services can include:
•applying firewall policies and IPS attack prevention to all traffic,
•applying virus scanning to HTTP, FTP, POP3, SMTP, and IMAP traffic,
•applying web filtering to HTTP traffic,
•applying Spam filtering to POP3, SMTP, and IMAP traffic.
The internal network is connected to the FortiGate unit internal interface. The router is connected to the FortiGate unit external interface. The FortiGate unit can be added to the network without changing the configuration of the network (except to add the FortiGate management IP address).
Figure 2: Example transparent mode network
Internal network
Internet
Internal | External | Router |
|
|
(Transparent mode)
To allow users on the internal network to connect to resources on the Internet, add Internal
FortiBridge Version 3.0 Administration Guide | 9 |