Design Guide
Intel 440GX AGPset
Intel440GX AGPset Design Guide
Contents
6.5
Dimm Solution With FET Switches
System Bus Clock Layout 6.3
6.4
82371EB PIIX4E
PIIX4E Power And Ground Pins
ISA and X-Bus Signals
Thermals / Cooling Solutions 20.1
Intel440GX AGPset Platform Reference Design
IntelPentiumII Processor LAI Issue
FET Switches4 DIMM/FET Design
Voltage Regulator Control Silicon
Solution Space for Single Processor Designs With Single-End
Example ATX Placement for a UP Pentium II processor
Example NLX Placement for a UP Intel Pentium II processor
Solution Space for Single Processor Design Based on Results
Motherboard Model MAB12,11,90#, MAB14,13,10, 4 DIMMs
Tables
Intel Pentium II Processor and Intel 440GX AGPset
Intel Pentium II Processor and Intel 440GX AGPset 100 MHz
Date Revision Description
Revision History
Intel440GX AGPset Design Guide
Introduction
Page
About This Design Guide
Introduction
References
Intel Pentium II Processor
Intel Pentium II Processor / Intel 440GX AGPset Overview
VCR
Intel 440GX AGPset
System Bus Interface
Dram Interface
Accelerated Graphics Port Interface
System Clocking
Wired for Management Initiative
PCI-to-ISA/IDE Xcelerator PIIX4E
PCI Interface
Instrumentation
Remote Service Boot
Remote Wake-Up
Power Management
Design Recommendations
Voltage Definitions
General Design Recommendations
Introduction
Motherboard Design
Page
BGA Quadrant Assignment
Major Signal Sections 82443GX Top View
ATX Form Factor
NLX Form Factor
Board Description
Four Layer Board Stack-up
Routing Guidelines
Single Processor Network Topology and Conditions
1 GTL+ Description
2 GTL+ Layout Recommendations
Single Processor Design
Single Processor Recommended Trace Lengths
Recommended Trace Lengths for Single Processor Design
Trace Minimum Length Maximum Length
Dual Processor Recommended Trace Lengths
Dual Processor Systems
Single Processor Systems-Single-End Termination SET
Dual Processor Network Topology and Conditions
SET Trace Length Requirements
SET Trace Length Requirements
Additional Guidelines
Minimizing Crosstalk
Practical Considerations
Design Methodology
12. GTL+ Design Process
Performance Requirements
Recommended 100 MHz System Flight Time Specs
Topology Definition
Pre-Layout Simulation Sensitivity Analysis
Simulation Methodology
Post-Layout Simulation
Placement & Layout
Crosstalk and the Multi-Bit Adjustment Factor
Validation
Flight Time Measurement
Edge Guideline @ Processor Edge Spec @ Processor Core
Signal Quality Measurement
Term Description
Timing Analysis
Timing Term Value
10. Recommended 100 MHz System Timing Parameters
11. Recommended 100 MHz System Flight Time Specs
Timing Term Intel Pentium II Processor Intel 440GX AGPset
12. Data and Associated Strobe
AGP Connector Up Option Layout Guidelines
Connector
AGP Layout and Routing Guidelines
WidthSpace Trace Line Length Line Length Matching
14. Control Signal Line Length Recommendations
On-board AGP Compliant Device Down Option Layout Guidelines
13. Source Synchronous Motherboard Recommendations
16. Control Signal Line Length Recommendations
Compliant 82443GX Graphics Data Routing Device
15. Source Synchronous Motherboard Recommendations
82443GX Memory Subsystem Layout and Routing Guidelines
1 100 MHz 82443GX Memory Array Considerations
To 82443GX MDs & MECCs To DIMM10 DQs To DIMM32 DQs
Register Data Control Clock
Matching the Reference Planes
Adding Additional Decoupling Capacitor
Register
Trace Width vs. Trace Spacing
Memory Layout & Routing Guidelines
Switch 16212 Dimm Module
18. FET Switch DQ Route Example
82443GX Dimm Module
82443GX 0.6 0.4 0.6 0.4 Dimm Module
24. Motherboard Model-DQMB1,5, 4 DIMMs
19. Motherboard Model SRASB#, 4 DIMMs
20. Motherboard Model SCASA#, 4 DIMMs
21. Motherboard Model SCASB#, 4 DIMMs
22. Motherboard Model WEA#, 4 DIMMs
23. Motherboard Model WEB#, 4 DIMMs
24. Motherboard Model MAA140, 4 DIMMs
VCC3
3 4 Dimm Routing Guidelines no FET
PCI Bus Routing Guidelines
25. Motherboard Model MAB12,11,90#, MAB14,13,10, 4 DIMMs
Host Bridge Controller 492 BGA
Decoupling Guidelines Intel 440GX AGPset Platform
014 018 Clock
Intel 440GX AGPset Clock Layout Recommendations
Clock Routing Spacing
System Bus Clock Layout
440GX Ckbf Dlko
PCI Clock Layout
Sdram Clock Layout
Net Trace Length Min Max Cap
Net Trace Length Min Max Card Trace
AGP Clock Layout
Design Checklist
Page
Pull-up and Pull-down Resistor Values
Overview
Intel Pentium II Processor Checklist
Slot Connectivity Sheet 1
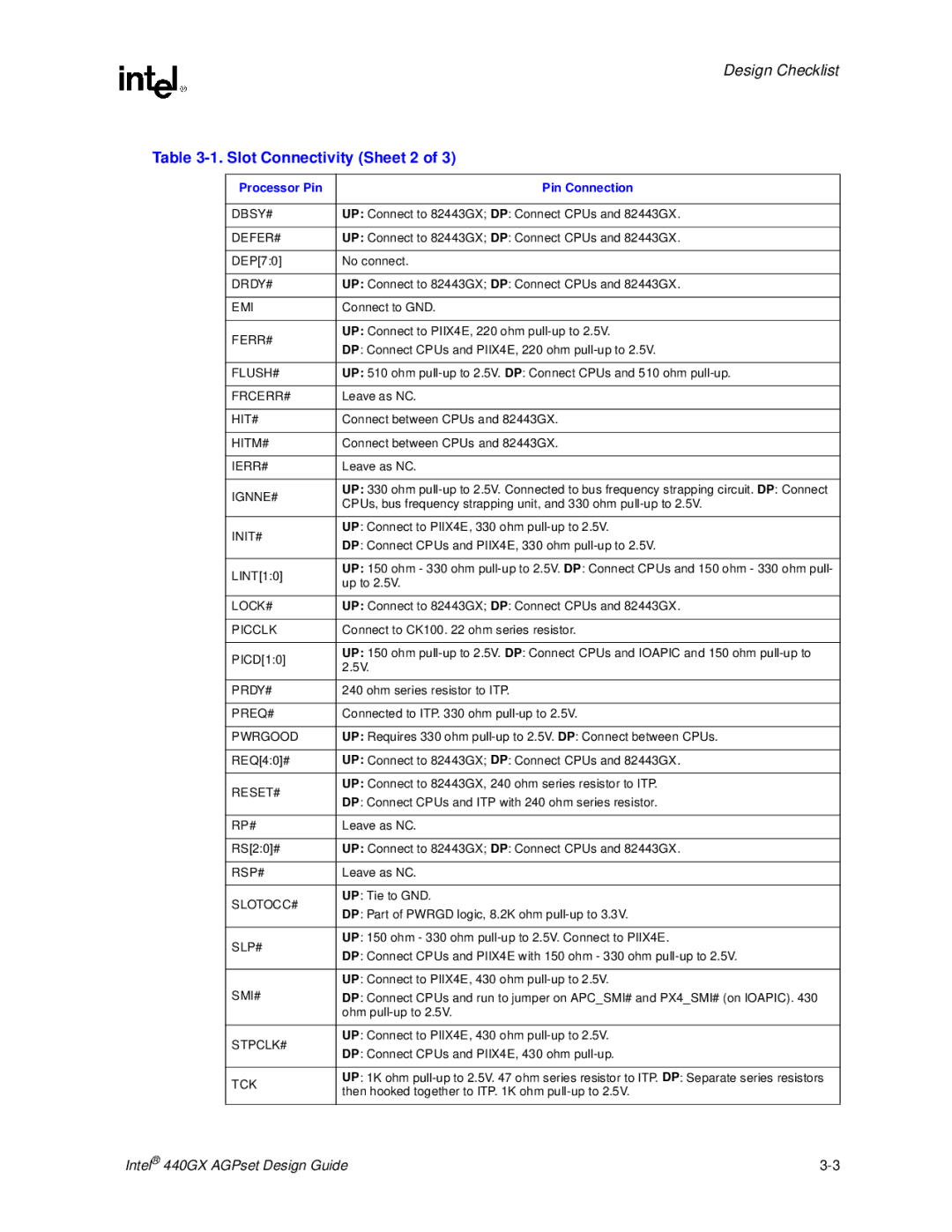
Processor Pin Pin Connection
Slot Connectivity Sheet 2
GND & Power Pin Definition
Slot Connectivity Sheet 3
Vtt VCC3 Reserved NC Vcc
Intel Pentium II Processor Clocks
Intel Pentium II Processor Signals
Design Checklist
Voltage Regulator Module, VRM
Uni-Processor UP Slot 1 Checklist
Dual-Processor DP Slot 1 Checklist
Slot 1 Decoupling Capacitors
SEL100/66#
Intel 440GX AGPset Clocks
1 CK100 100 MHz Clock Synthesizer
Processor Frequency Select
Gcke and Dclkwr Connection
Ckbf Sdram 1 to 18 Clock Buffer
82443GX Host Bridge
1 82443GX Interface
GX Connectivity Sheet 1
GX Connectivity Sheet 2
VTTA, Vttb
2 82443GX GTL+ Bus Interface
3 82443GX PCI Interface
GX Connectivity Sheet 3
Signal Description Register Pulled to ‘0’ Pulled to ‘1’
4 82443GX AGP Interface
Strapping Options
Sdram Connectivity
82443GX Pins/Connection Dimm Pins Pin Function
Intel 440GX AGPset Memory Interface
Sdram Connections
Registered Sdram
Dimm Solution With FET Switches
PIIX4E Connectivity Sheet 1
Signal Names Connection
82371EB PIIX4E
PIIX4E Connections
PIIX4E Connectivity Sheet 2
PIIX4E Connectivity Sheet 3
PIIX4E Connectivity Sheet 4
Motherboard
Signal Resistor
IDE Routing Guidelines
Cabling
IDE
Reset#
PDD150 PDA20
Pin32,34
PCI Bus Signals
PIIX4E Power And Ground Pins
PIIX4E PWR & GND
11. Non-PIIX4E ISA Signals
ISA Signals
ISA and X-Bus Signals
10. Non-PIIX4E PCI Signals
USB Interface
IDE Interface
12. Non-PIIX4E IDE
PLCC32 to TSOP40 PLCC32 to PSOP44 PDIP32 to TDIP40
Flash Design
Dual-Footprint Flash Design
Flash Design Considerations
XD70
Write Protection
13. Flash Vpp Recommendations
Power Management Signals
System and Test Signals
VCC3
Power Button Implementation
Miscellaneous
17 82093AA Ioapic
18.1 Max1617 Temperature Sensor
Manageability Devices
18.2 LM79 Microprocessor System Hardware Monitor
18.3 82558B LOM Checklist
Pin Number Pin Name Resistor Value Comment
Required in both a and B stepping designs
Software/BIOS
USB and Multi-processor Bios
Wake On LAN WOL Header
Thermals / Cooling Solutions
Mechanicals
Design Considerations
Electricals
Design Consideration
Layout Checklist
Applications and Add-in Hardware
Routing and Board Fabrication
Debug Recommendations
Page
In-Target Probe ITP
Slot 1 Test Tools
Debug/Simulation Tools
Logic Analyzer Interface LAI
4 I/O Buffer Models
Debug Features
Intel Pentium II Processor LAI Issue
Bus Functional Model BFM
150 ohm
150 330 ohm
Kohm
430 ohm
Debug Logic Recommendations
A20M# 150 330 ohm
PICD0# 150 ohm PICD1#
Design Considerations
Debug Procedures
Debug Layout
Debug Considerations
Debug Recommendations
Third Party Vendors
Page
Supplier Contact Phone
Slot 1 Connector
Processors
GTL+ Bus Slot 1 Terminator Cards
Voltage Regulator Control Silicon Vendors
Voltage Regulator Modules
Voltage Regulator Control Silicon
Voltage Regulator Modules
Clock Drivers
Power Management Components
FET Switches4 DIMM/FET Design
Intel 440GX AGPset
Other Processor Components
Reference Design Schematics
Page
Intel 440GX AGPset Platform Reference Design
82443GX Component System bus and Dram Interfaces
VRM
Power Connectors Front Panel Jumpers