Intel IXP400 Software
Programmer’s Guide
Intel IXP400 Software
IXP400 Software Version
Contents
1.1
100
118
152
Contents Access-Layer Components
225
17.9
Operating System
Adsl Driver
Figures
102
Tables
AQM
300
Revision History
Date Revision Description
Hardware Supported by this Release
Introduction1
Versions Supported by this Document
Intended Audience
About the Processors
How to Use this Document
Chapters Description
Related Documents
Document Title Document #
Document Title Document #
Acronyms
Acronym Description
CPU
HSS
MSB
SIP
Software Architecture Overview
High-Level Overview
Deliverable Model
Software Architecture Overview
Operating System Support
Access Library Source Code Documentation
Development Tools
Release Directory Structure
Ixposal Include Src Ixp400xscalesw
\---include +---npeMh
Polled and Interrupt Operation
Threading and Locking Policy
Statistics and MIBs
Global Dependency Chart
Global Dependencies
This page is intentionally left blank
What’s New
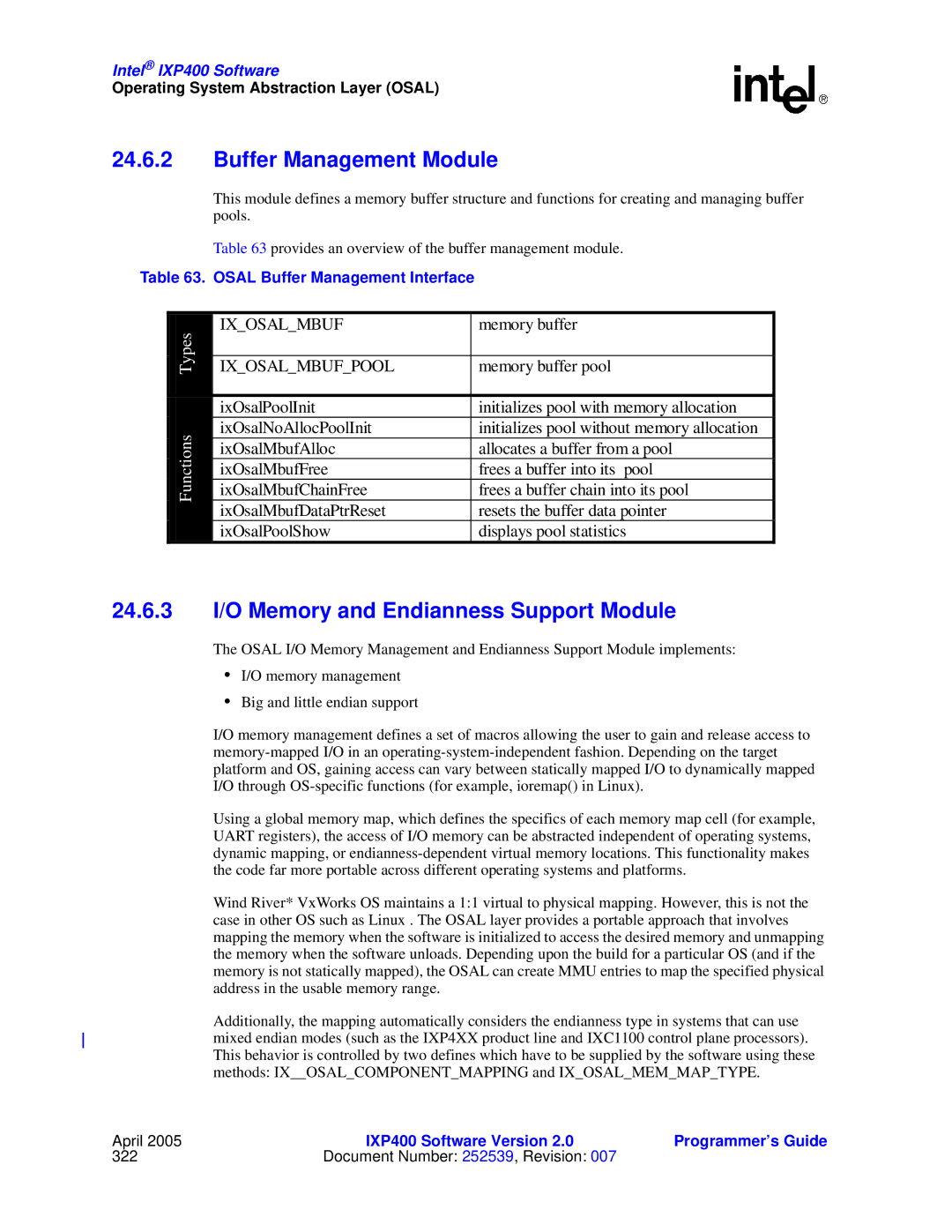
Buffer Management
Overview
Buffer Management
Intel IXP400 Software Buffer Flow
Ixpbuf User Interface
Raw Buffers
Ixpbuf Structure
Ixpbuf Structure and Macros
Osal Ixpbuf structure and macros
API User Interface to Ixpbuf
Pool Management Fields
Ixmbuf OS-Dependent Buffer Format
Ixpbuf ixctrl Structure
Ixne IXP400 NPE Shared Structure
Mapping of Ixmbuf to Shared Structure
Ixpbuf NPE Shared Structure
Ixnext Ixosalmbufnextbufferinpktptr
Ixmbuf Structure
Internal Ixmbuf Field Format Sheet 1
Ixreserved
Internal Ixmbuf Field Format Sheet 2
Field / Macro Purpose Used by Access-Layer?
Ixmbuf Field Details Sheet 1
VxWorks* Mblk Buffer
Mapping to OS Native Buffer Types
Ixmbuf Field Details Sheet 2
Linux* skbuff Buffer
Ixmbuf to Mblk Mapping
Following fields will get updated in the skbuffer
Buffer Translation Functions
Caching Strategy
Tx Path
Caching Strategy Summary
Rx Path
Buffer Management Tx Cache Flushing Example
Intel IXP400 Software
This page is intentionally left blank
Access-Layer Components ATM Driver Access IxAtmdAcc API
IxAtmdAcc Component Features
Access-Layer Components ATM Driver Access IxAtmdAcc API
Utopia Port-Configuration Service
Configuration Services
ATM Traffic-Shaping Services
VC-Configuration Services
Transmission Services
Scheduled Transmission
Buffer Transmission for a Scheduled Port
Schedule Table Description
Transmission Triggers Tx-Low Notification
Transmit-Done Processing
Tx Done Recycling Using a Threshold Level
Transmit Done Based on a Threshold Level
Tx Done Recycling Using a Polling Mechanism
Transmit Disconnect
Receive Services
Tx Disconnect
Receive Processing
Receive Triggers Rx-Free-Low Notification
Receive Based on a Threshold Level
Rx Using a Threshold Level
RX Using a Polling Mechanism
Receive Disconnect
Buffer Management
Buffer Contents
Buffer Allocation
Ixpbuf Fields Modified During Reception Sheet 1
Ixpbuf Fields Required for Transmission
Ixpbuf Fields of Available Buffers for Reception
Field Description
Buffer-Size Constraints
Error Handling
API-Usage Errors
Buffer-Chaining Constraints
Real-Time Errors
Real-Time Errors
Cause Consequences and Side Effects Corrective Action
IxAtmm Component Features
Access-Layer Components ATM Manager IxAtmm API
IxAtmm Overview
Access-Layer Components ATM Manager IxAtmm API
Utopia Level-2 Port Initialization
ATM-Port Management Service Model
Services Provided by Ixatmm
Tx/Rx Control Configuration
Configuration of Traffic Control Mechanism
Management Interfaces
Error Handling
Dependencies
Memory Requirements
Performance
Access-Layer Components ATM Transmit Scheduler IxAtmSch
IxAtmSch Component Features
Supported Traffic Types
Access-Layer Components ATM Transmit Scheduler IxAtmSch API
Traffic Type Supported Num VCs
Connection Admission Control CAC Function
Scheduling and Traffic Shaping
Schedule Table
Minimum Cells Value minCellsToSchedule
Schedule Service Model
Maximum Cells Value maxCells
Timing and Idle Cells
IxAtmSch Data Memory Usage
Code Size
Data Memory
Per VC Data Per Port Data Total
Latency
Access-Layer Components Security IxCryptoAcc API
IxCryptoAcc API Architecture
Access-Layer Components Security IxCryptoAcc API
IxCryptoAcc Interfaces
Basic API Flow
Context Registration and the Cryptographic Context Database
Basic IxCryptoAcc API Flow
Intel IXP400 Software
IxCryptoAcc API Call Process Flow for CCD Updates
IxCryptoAcc Data Memory Usage Sheet 1
Buffer and Queue Management
Memory Requirements
Structure Size in Bytes Total Size in Bytes
Dependencies
IxCryptoAcc Data Memory Usage Sheet 2
Other API Functionality
IxCryptoAccHashKeyGenerate
Import and Export of Cryptographic Technology
IPSec Services
Endianness
IPSec Background and Implementation
IxCryptoAcc, NPE and IPSec Stack Scope
IPSec Packet Formats
Relationship Between IPSec Protocol and Algorithms
Authentication Header
Reference ESP Dataflow
Reference AH Dataflow
ESP Data Flow
Hardware Acceleration for IPSec Services
IPSec API Call Flow
IPSec API Call Flow
Special API Use Cases
Hmac with Key Size Greater Than 64 Bytes
CCM Operation Flow
AES CBC Encryption For MIC
IPSec Assumptions, Dependencies, and Limitations
WEP Services
WEP Background and Implementation
Hardware Acceleration for WEP Services
WEP Frame with Request Parameters
IxCryptoAccXscaleWepPerform
WEP API Call Flow
IxCryptoAccNpeWepPerform
NPE Microcode Images
WEP Perform API Call Flow
SSL and TLS Protocol Usage Models
Authentication
Combined Mode Operations
Encryption/Decryption
Supported Encryption Algorithms
Supported Encryption and Authentication Algorithms
Encryption Algorithms
Cipher Key Sizes Parity Bit Actual Key Size
Electronic Code Book ECB
Counter Mode CTR
Cipher Modes
Cipher Block Chaining CBC
Supported Authentication Algorithms
Authentication Algorithms
Authentication Algorithm Data Block Size Bits Key Size Bits
114 Document Number 252539, Revision
Features
Access-Layer Components DMA Access Driver IxDmaAcc API
Assumptions
DMA Access-Layer API
Access-Layer Components DMA Access Driver IxDmaAcc API
IxDmaAcc Component Overview
Parameters Description
IxDmaAccDescriptorManager
Destination Address
Transfer Mode
Source Address
Transfer Width
Addressing Modes
Transfer Length
Supported Modes
Transfer Mode
Increment
122 Document Number 252539, Revision
Data Flow
Control Flow
DMA Initialization
IxDmaAcc Control Flow
DMA Configuration and Data Transfer
IxDMAcc Initialization
DMA Transfer Operation
Restrictions of the DMA Transfer
Little Endian
Access-Layer Components Ethernet Access IxEthAcc API
IxEthAcc Overview
Access-Layer Components Ethernet Access IxEthAcc API
Ethernet Access Layers Architectural Overview
Role of the Ethernet NPE Microcode
Queue Manager
4 MAC/PHY Configuration
Learning/Filtering Database
Ethernet Access Layers Component Features
Ethernet Access Layers Block Diagram
Data Plane
Ethernet Frame Transmission
Port Initialization
Transmission Flow
Transmit Buffer Management and Priority
Ethernet Transmit Frame Data Buffer Flow
TxEnetDone
Ethernet Frame Reception
Using Chained IXOSALMBUFs for Transmission / Buffer Sizing
Tx Fifo Priority
Receive Flow
Ethernet Receive Frame API Overview
Buffer Sizing
Receive Buffer Management and Priority
Supplying Buffers
Programmer’s Guide
Codelet or client application
Freeing Buffers
Rx Fifo Priority QoS Mode
Recycling Buffers
Additional Receive Path Information
No Receive Polling
Data-Plane Endianness
Control Path
Maximum Ethernet Frame Size
IxEthAcc and Secondary Components
MII I/O
MAC Duplex Settings
Ethernet MAC Control
Frame Check Sequence
MAC Filtering
Promiscuous Mode
Non-Promiscuous Mode
1.6 802.3x Flow Control
NPE Loopback
Initialization
Shared Data Structures
Emergency Security Port Shutdown
Ixosalmbuf Structure Format
Ixpneflags Field Format
Queue Field Description Eth
150 Document Number 252539, Revision
Ixosalmbuf Port ID Field Format
Ixpneflags.linkprot Field Values
Management Information
Ixosalmbuf Port ID Field Values
Field Bit Values
Managed Objects for Ethernet Receive
Object Increment Criteria
Managed Objects for Ethernet Transmit
Access-Layer Components Ethernet Database IxEthDB API
IxEthDB Functional Behavior
MAC Address Learning and Filtering
Access-Layer Components Ethernet Database IxEthDB API
Learning and Filtering
Node
Other MAC Learning/Filtering Usage Models
Learning/Filtering General Characteristics
Port Definitions
Provisioning Static and Dynamic Entries
Port Dependency Map
Aging
Frame Size Filtering
Database Maintenance
Record Management
Filtering Example Based Upon Maximum Frame Size
Source MAC Address Firewall
MAC Address Block/Admission
10.3.4 802.1Q Vlan
Invalid MAC Address Filtering
Untagged MAC Frame Format
Background Vlan Data in Ethernet Frames
Vlan Tagged MAC Frame Format
Acceptable Frame Type Filtering
Database Records Associated With Vlan IDs
Vlan Tag Format
Ingress Tagging and Tag Removal
Port-Based Vlan Membership Filtering
Port and VLAN-Based Egress Tagging and Tag Removal
Special Conditions
Tag Mode Frame Status Action
Egress Vlan Tagging/Untagging Behavior Matrix
Port ID Extraction
10.3.5 802.1Q User Priority / QoS Support
Priority Aware Transmission
Receive Priority Queuing
QoS on Receive for 802.1Q Tagged Frames
Priority to Traffic Class Mapping
QoS on Receive for Untagged Frames
Background 802.3 and 802.11 Frame Formats
Default Priority to Traffic Class Mapping
10.3.6 802.3 / 802.11 Frame Conversion
IEEE802.11 Frame Format
IEEE802.11 Frame Control FC Field Format
AP-STA and AP-AP Modes
How the 802.3 / 802.11 Frame Conversion Feature Works
Receive Path
To 802.11 Header Conversion Rules
Field AP to STA mode AP to AP mode
Transmit Path
Input 802.11 Frame Values Output 802.3 Frame Field Values
10.3.6.3 802.3 / 802.11 API Details
11 to 802.3 Header Conversion Rules
Frame Type
IxEthDB API
Spanning Tree Protocol Port Settings
Initialization
IxEthDB Feature Set
Feature Set
Additional Database Features
User-Defined Field
Promiscuous-Mode Requirement
Dependencies on IxEthAcc Configuration
Database Clear
FCS Appending
180 Document Number 252539, Revision
Access-Layer Components Ethernet PHY IxEthMii API
Supported PHYs
Access-Layer Components Ethernet PHY IxEthMii API
PHYs Supported by IxEthMii
Access-Layer Components Feature Control IxFeatureCtrl API
Hardware Feature Control
Product ID Values
Using the Product ID-Related Functions
Access-Layer Components Feature Control IxFeatureCtrl API
Bits Description
Using the Feature Control Register Functions
Feature Control Register Values Sheet 1
Feature Control Register Values Sheet 2
Software Configuration
Component Check by Other APIs
Document Number 252539, Revision 187
188 Document Number 252539, Revision
Access-Layer Components HSS-Access IxHssAcc API
IxHssAcc API Overview
Access-Layer Components HSS-Access IxHssAcc API Features
IxHssAcc Interfaces
Access-Layer Components HSS-Access IxHssAcc API
HSS and Hdlc Theory and Coprocessor Operation
Intel X S cale C ore
HSS Tx Clock Output frequencies and PPM Error
HSS Output Clock Jitter and Error Characterization
HSS Tx Freq Pj Max ns Cj Max ns Aj Max ns
Jitter Type Jitter Definition
Jitter Definitions
HSS Frame Output Characterization
Actual Frame Length µs
High-Level API Call Flow
Key Assumptions
IxHssAcc Component Dependencies
HSS Port Initialization Details
IxHssAccPortInit
198 Document Number 252539, Revision
HSS Channelized Operation
Channelized Connect and Enable
IxHssAccChanConnect
200 Document Number 252539, Revision
Channelized Tx/Rx Methods
Channelized Connect
CallBack
Polled
Channelized Transmit and Receive
Channelized Disconnect
Packetized Connect and Enable
HSS Packetized Operation
IxHssAccPktPortConnect
Document Number 252539, Revision 205
Packetized Tx
Packetized Connect
Document Number 252539, Revision 207
Packetized Rx
Packetized Transmit
Document Number 252539, Revision 209
Packetized Receive
Buffer Allocation Data-Flow Overview
13.6.5 56-Kbps, Packetized Raw Mode
Data Flow in Packetized Service
Packetized Disconnect
212 Document Number 252539, Revision
HSS Packetized Receive Buffering
Data Flow in Channelized Service
HSS Packetized Transmit Buffering
Document Number 252539, Revision 215
HSS Channelized Receive Operation
HSS Channelized Transmit Operation
218 Document Number 252539, Revision
Microcode Images
Access-Layer Components NPE-Downloader IxNpeDl API
Loading NPE Microcode from a File Versus Loaded from Memory
NPE Microcode Library Customization
Access-Layer Components NPE-Downloader IxNpeDl API
Standard Usage Example
NPE Image Compatibility
NPE-A Images
Image Name Description
NPE-B Images
NPE-C Images Sheet 1
IxNpeDl Uninitialization
Custom Usage Example
NPE-C Images Sheet 2
Deprecated APIs
Access-Layer Components NPE Message Handler IxNpeMh API
Interrupt-Driven Operation
Access-Layer Components NPE Message Handler IxNpeMh API
Initializing the IxNpeMh
Polled Operation
Uninitializing IxNpeMh
Sending an NPE Message
Customer / Demo Code
Sending an NPE Message with Response
Client
IxNpeMh
IxNpeMh
Receiving Unsolicited Messages from NPE to Software Client
Client Customer / Demo Code
IxNpeMh Component Dependencies
232 Document Number 252539, Revision
Introduction
Access-Layer Components Parity Error Notifier IxParityENAcc
Background
Network Processing Engines
Scrubbing/Memory Scrub
DDR Sdram Memory Controller Unit MCU
Switching Coprocessor in NPE B Swcp
AHB Queue Manager AQM
Expansion Bus Controller
Interrupt Prioritization
Parity Error Interrupts
Interrupt Bit Default Priority Software
Secondary Effects of Parity Interrupts
Feature Hardware Component Software Support Recoverable
Features
IxParityENAcc API Details
IxParityENAcc Dependency Diagram
IxParityENAcc API Usage Scenarios
Summary Parity Error Notification Scenario
Parity Error Notification Sequence
Parity Error Interrupt Deassertion Conditions Sheet 1
Interrupt Bit Source API Invoked by
Summary Parity Error Recovery Scenario
Parity Error Interrupt Deassertion Conditions Sheet 2
Summary Parity Error Prevention Scenario
Parity Error Notification Detailed Scenarios
Data Abort with No Parity Error
Data Abort followed by Unrelated Parity Error Notification
Data Abort Caused by Parity Error
Data Abort with both Related and Unrelated Parity Errors
Access-Layer Components Performance Profiling IxPerfProfAcc
Intel XScale Core PMU
Internal Bus PMU
Counter Buffer Overflow
Idle-Cycle Counter Utilities ‘Xcycle’
Interrupt Handling
IxPerfProfAcc Dependencies
Using the API
Threading
API Usage for Intel XScale Core PMU
Event and Clock Counting
254 Document Number 252539, Revision
Time-Based Sampling
Display Performance Counters
Display Clock Counter
Event-Based Sampling
Iii. Print out the first five elements
258 Document Number 252539, Revision
C0112788 No lower symbol found. Module kernel
Using Intel XScale Core PMU to Determine Cache Efficiency
Internal Bus PMU
IxPerfProfAccBusPmuStart
Xcycle Idlecycle Counter
Perform the same calculation for the rest of the PECs
Display Xcycle Measurement
Access-Layer Components Queue Manager IxQMgr API
Features and Hardware Interface
Access-Layer Components Queue Manager IxQMgr API
Document Number 252539, Revision 267
Dispatcher
Configuration Values
AQM Configuration Attributes
Attribute Description Values
Dispatcher Modes
270 Document Number 252539, Revision
AQM
Livelock Prevention
Dispatcher in Context of a Polling Mechanism
Document Number 252539, Revision 273
274 Document Number 252539, Revision
Access-Layer Components Synchronous Serial Port IxSspAcc
IxSspAcc API Details
IxSspAcc Dependencies
IxSspAcc API Usage Models
Interrupt Mode
Initialization and General Data Model
278 Document Number 252539, Revision
Interrupt Scenario
Polling Mode
Init Transmit Receive
282 Document Number 252539, Revision
Access-Layer Components Time Sync IxTimeSyncAcc API
Ieee 1588 PTP Protocol Overview
Access-Layer Components Time Sync IxTimeSyncAcc API
Synchronization Sequence
Ieee 1588 Hardware Assist Block
Overview
Block Diagram of Intel IXP46X Network Processor
Detailed Information
Hardware Feature Options Default State
IPv6 and VLAN-Tagged Ethernet Frames
Ieee 1588 PTP Client Application
IxTimeSyncAcc API Details
IxTimeSyncAcc
Additional Hardware Information
Document Number 252539, Revision 289
IxTimeSyncAcc API Usage Scenarios
Interrupt Mode Operations
Polling for Transmit and Receive Timestamps
Polled Mode Operations
Interrupt Servicing of Target Time Reached Condition
Polling for Auxiliary Snapshot Values
Access-Layer Components UART-Access IxUARTAcc API
Interface Description
Access-Layer Components UART-Access IxUARTAcc API
Fifo Versus Polled Mode
Uart / OS Dependencies
Uart Services Models
296 Document Number 252539, Revision
Access-Layer Components USB Access ixUSB API
USB Controller Background
Packet Formats
Access-Layer Components USB Access ixUSB API
IN, OUT, and Setup Token Packet Format
SOF Token Packet Format
Handshake Packet Format
Transaction Formats
Data Packet Format
Bits 023 Bytes
Action Token Packet Data Packet Handshake Packet
Bulk Transaction Formats
Isochronous Transaction Formats
Action Token Packet Data Packet
Control Transaction Formats
Control Write Setup
Control Transaction Formats, Set-Up Stage
Interrupt Transaction Formats
API interfaces Available for Access Layer
IxUSB Setup Requests
IxUSB API Interfaces
Host-Device Request Summary Sheet 1
Request Name
Configuration
Host-Device Request Summary Sheet 2
IxUSB Send and Receive Requests
IxUSB Endpoint Stall Feature
Frame Synchronization
IxUSB Error Handling
Stall on OUT Transactions
Detailed Error Codes
Error due to unknown reasons
USB Data Flow
USB Dependencies
ATM Codelet IxAtmCodelet
Codelets
Codelets
Ethernet Access Codelet IxEthAccCodelet
Crypto Access Codelet IxCryptoAccCodelet
DMA Access Codelet IxDmaAccCodelet
Ethernet AAL-5 Codelet IxEthAal5App
HSS Access Codelet IxHssAccCodelet
Parity Error Notifier Codelet IxParityENAccCodelet
Time Sync Codelet IxTimeSyncAccCodelet
Performance Profiling Codelet IxPerfProfAccCodelet
USB Rndis Codelet IxUSBRNDIS
Operating System Abstraction Layer Osal
Operating System Abstraction Layer Osal
Osal Architecture
Core Module
OS-Independent Core Module
OS-Dependent Module
Buffer Management Module
Backward Compatibility Module
Osal Library Structure
Buffer Translation Module
Document Number 252539, Revision 317
C lu d e
Osal Modules and Related Interfaces
Core Module
IPC
Osal Core Interface Sheet 1
Thread
Osal Core Interface Sheet 2
24.6.3 I/O Memory and Endianness Support Module
Buffer Management Module
Osal Buffer Management Interface
Ixosalmmapvirttophys
Osal I/O Memory and Endianness Interface Sheet 1
Supporting a New OS
Osal I/O Memory and Endianness Interface Sheet 2
Supporting New Platforms
Example 1. Global Memory Map Definitions
Ixstaticmap
Device Support
Adsl Driver
Adsl Driver Overview
Adsl API
Adsl Line Open/Close Overview
Example of Adsl Line Open Call Sequence
Limitations and Constraints
2C Driver IxI2cDrv
26.3 I2C Driver API Details
I2C Driver IxI2cDrv
Arbitration Loss Error
2C Driver IxI2cDrv
26.4 I2C Driver API Usage Models
Bus Error
Master-Interrupt Mode
Initialization
Slave-Polling Mode
I2C Driver IxI2cDrv Slave-Interrupt Mode
Support Functions
Example Sequence Flows for Slave Mode
Sequence Flow Diagram for Slave Transmit in Interrupt Mode
Sequence Flow Diagram for Slave Receive in Polling Mode
26.4.3 I2C Using Gpio Versus Dedicated I2C Hardware
Sequence Flow Diagram for Slave Transmit in Polling Mode
340 Document Number 252539, Revision
Basics of Endianness
Endianness in Intel IXP400 Software
Endianness in Intel IXP400 Software
Endianness When Memory is Shared
Nature of Endianness Hardware or Software?
Coding Pitfalls Little-Endian/Big-Endian
Software Considerations and Implications
Casting a Pointer Between Types of Different Sizes
Network Stacks and Protocols
Here is what the macro ntohl looks like in actual code
Macro Source Code
Best Practices in Coding of Endian-Independence
Macro Examples Endian Conversion
Avoid
346 Document Number 252539, Revision
April
Document Number 252539, Revision 347
Supporting Little-Endian Mode
Reasons for Choosing a Particular LE Coherency Mode
Hardware Switches
Silicon Endianness Controls
Intel XScale Core Endianness Mode
MMU
Byteswapen Bit
Little-Endian Data Coherence Enable/Disable
MMU P-Attribute Bit
Forcebyteswap Bit
Summary of Silicon Controls
Silicon Versions
PCI Bus Swap
Endian Hardware Summary
IXP46X network processors A-0 stepping
Part Number Brief Description
APB Peripherals
April 2005
NPE Downloader IxNpeDl
Ethernet Access Component IxEthAcc
NPE Message Handler IxNpeMh
Data Plane
Ixosalmbuf Data Payload
One Half-Word-Aligned Ethernet Frame LE Address Coherent
Intel XScale Core Read of IP Header LE Data Coherent
Learning Database Function
Ethernet Access MIB Statistics
Intel IXP400 Software IxEthAcc and IxEthDB Summary
Intel IXP400 Software OS Abstraction
27.5.4 PCI
ATM and HSS
Endian Conversion Macros
VxWorks* Considerations
Intel IXP400 Software Macros
#defines
VxWorks* Data Coherent Swap Code
Intel IXP400 Software Versions
Software Versions
Intel IXP400 Software Version Little-Endian Support Yes/No