Chapter 1
IPSec: Concept for secure IP connections
1.1 IPSec Concepts
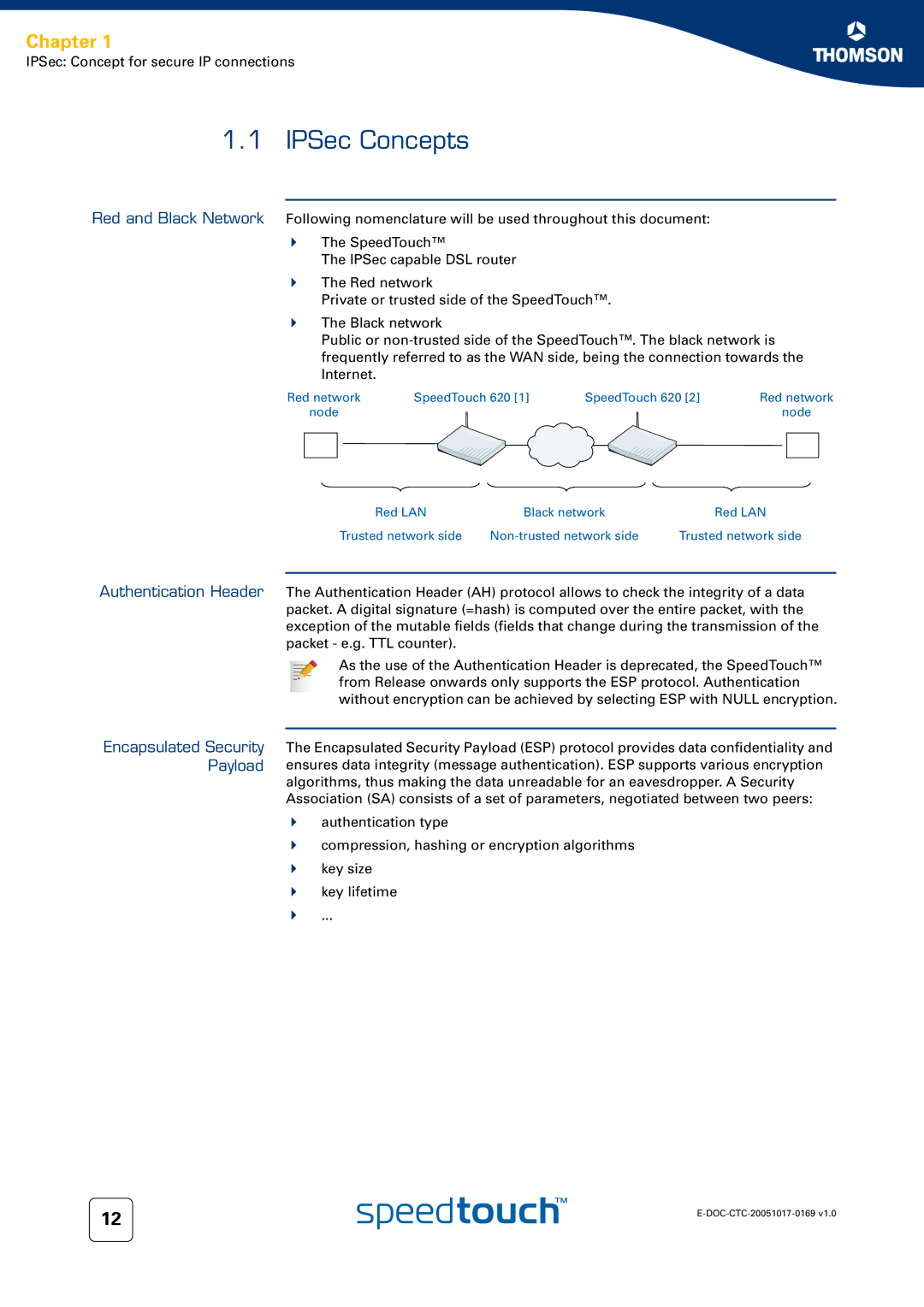
Red and Black Network Following nomenclature will be used throughout this document:
The SpeedTouch™
The IPSec capable DSL router
The Red network
Private or trusted side of the SpeedTouch™.
The Black network
Public or
Red network | SpeedTouch 620 [1] | SpeedTouch 620 [2] | Red network | ||
| node |
|
| node | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Red LAN | Black network | Red LAN |
Trusted network side | Trusted network side |
Authentication Header
Encapsulated Security Payload
The Authentication Header (AH) protocol allows to check the integrity of a data packet. A digital signature (=hash) is computed over the entire packet, with the exception of the mutable fields (fields that change during the transmission of the packet - e.g. TTL counter).
As the use of the Authentication Header is deprecated, the SpeedTouch™ from Release onwards only supports the ESP protocol. Authentication without encryption can be achieved by selecting ESP with NULL encryption.
The Encapsulated Security Payload (ESP) protocol provides data confidentiality and ensures data integrity (message authentication). ESP supports various encryption algorithms, thus making the data unreadable for an eavesdropper. A Security Association (SA) consists of a set of parameters, negotiated between two peers:
authentication type
compression, hashing or encryption algorithms
key size
key lifetime
...
12 | |
|