4.14 VOLTAGE INPUT SCALING
Any of the input channels (1 through 5) may be programmed as Voltage channels. Each Voltage channel includes unique m and b constants for "scaling" data to your application. These constants default to +1.00000 and 000000, respectively, when the channel is first programmed as a Voltage channel but the user may reprogram them as necessary. The following pages include examples for common transducers.
4.14.1 MATCHING TRANSDUCERS TO THE OM-550
Some transducers provide a "voltage" output; others provide a "current" output. This section explains how to use resistors to match either output to the input.
Currents must be converted to a voltage and voltages must be attenuated (reduced) if they can exceed the maximum input (±2.0000 VDC). This process is called Matching, which means converting or attenuating the transducer's output to an acceptable level without overloading it.
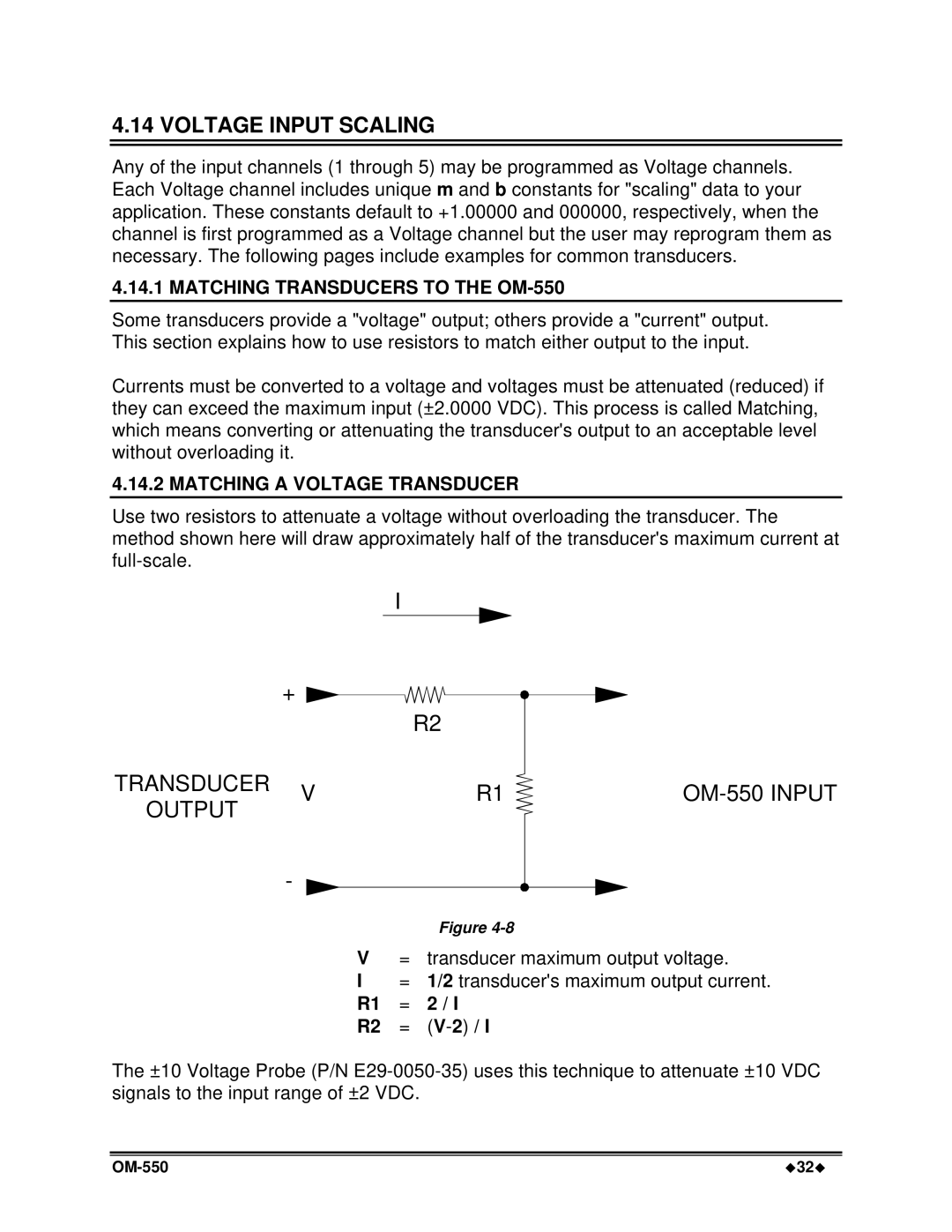
4.14.2 MATCHING A VOLTAGE TRANSDUCER
Use two resistors to attenuate a voltage without overloading the transducer. The
method shown here will draw approximately half of the transducer's maximum current at
I
+ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() R2
R2
TRANSDUCER | V | R1 |
|
OUTPUT
-
Figure
V= transducer maximum output voltage.
I= 1/2 transducer's maximum output current.
R1 = 2 / I
R2 = (V-2) / I
The ±10 Voltage Probe (P/N
u32u |