PowerLogicTM Series 800 Power Meter | |
Chapter | 3/2011 |
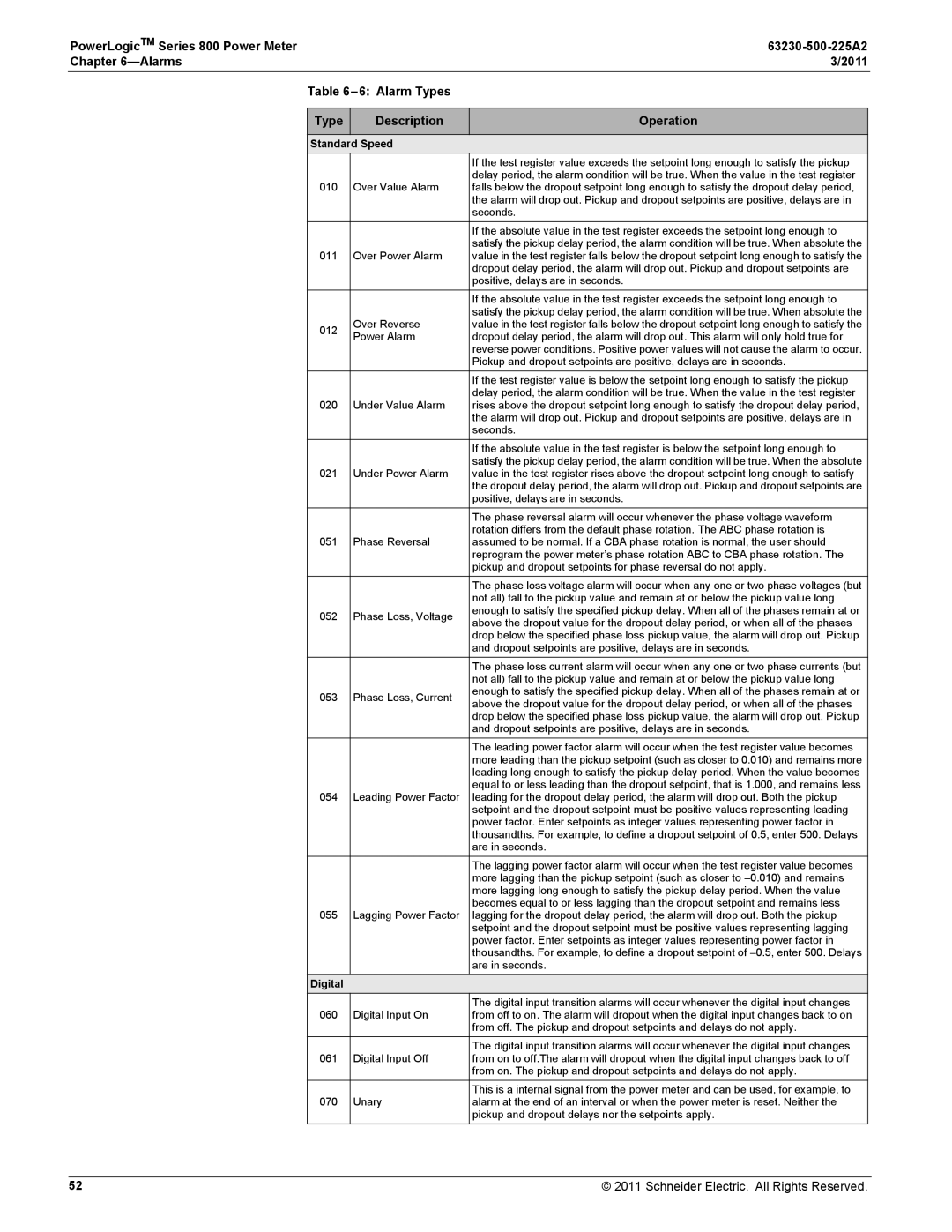
Table
Type
Description
Operation
Standard Speed
|
| If the test register value exceeds the setpoint long enough to satisfy the pickup | |
010 | Over Value Alarm | delay period, the alarm condition will be true. When the value in the test register | |
falls below the dropout setpoint long enough to satisfy the dropout delay period, | |||
|
| the alarm will drop out. Pickup and dropout setpoints are positive, delays are in | |
|
| seconds. | |
|
| If the absolute value in the test register exceeds the setpoint long enough to | |
|
| satisfy the pickup delay period, the alarm condition will be true. When absolute the | |
011 | Over Power Alarm | value in the test register falls below the dropout setpoint long enough to satisfy the | |
|
| dropout delay period, the alarm will drop out. Pickup and dropout setpoints are | |
|
| positive, delays are in seconds. | |
|
| If the absolute value in the test register exceeds the setpoint long enough to | |
| Over Reverse | satisfy the pickup delay period, the alarm condition will be true. When absolute the | |
012 | value in the test register falls below the dropout setpoint long enough to satisfy the | ||
Power Alarm | dropout delay period, the alarm will drop out. This alarm will only hold true for | ||
| |||
|
| reverse power conditions. Positive power values will not cause the alarm to occur. | |
|
| Pickup and dropout setpoints are positive, delays are in seconds. | |
|
| If the test register value is below the setpoint long enough to satisfy the pickup | |
020 | Under Value Alarm | delay period, the alarm condition will be true. When the value in the test register | |
rises above the dropout setpoint long enough to satisfy the dropout delay period, | |||
|
| the alarm will drop out. Pickup and dropout setpoints are positive, delays are in | |
|
| seconds. | |
|
| If the absolute value in the test register is below the setpoint long enough to | |
021 | Under Power Alarm | satisfy the pickup delay period, the alarm condition will be true. When the absolute | |
value in the test register rises above the dropout setpoint long enough to satisfy | |||
|
| the dropout delay period, the alarm will drop out. Pickup and dropout setpoints are | |
|
| positive, delays are in seconds. | |
|
| The phase reversal alarm will occur whenever the phase voltage waveform | |
051 | Phase Reversal | rotation differs from the default phase rotation. The ABC phase rotation is | |
assumed to be normal. If a CBA phase rotation is normal, the user should | |||
|
| reprogram the power meter’s phase rotation ABC to CBA phase rotation. The | |
|
| pickup and dropout setpoints for phase reversal do not apply. | |
|
| The phase loss voltage alarm will occur when any one or two phase voltages (but | |
|
| not all) fall to the pickup value and remain at or below the pickup value long | |
052 | Phase Loss, Voltage | enough to satisfy the specified pickup delay. When all of the phases remain at or | |
above the dropout value for the dropout delay period, or when all of the phases | |||
|
| ||
|
| drop below the specified phase loss pickup value, the alarm will drop out. Pickup | |
|
| and dropout setpoints are positive, delays are in seconds. | |
|
| The phase loss current alarm will occur when any one or two phase currents (but | |
|
| not all) fall to the pickup value and remain at or below the pickup value long | |
053 | Phase Loss, Current | enough to satisfy the specified pickup delay. When all of the phases remain at or | |
above the dropout value for the dropout delay period, or when all of the phases | |||
|
| ||
|
| drop below the specified phase loss pickup value, the alarm will drop out. Pickup | |
|
| and dropout setpoints are positive, delays are in seconds. | |
|
| The leading power factor alarm will occur when the test register value becomes | |
|
| more leading than the pickup setpoint (such as closer to 0.010) and remains more | |
|
| leading long enough to satisfy the pickup delay period. When the value becomes | |
|
| equal to or less leading than the dropout setpoint, that is 1.000, and remains less | |
054 | Leading Power Factor | leading for the dropout delay period, the alarm will drop out. Both the pickup | |
|
| setpoint and the dropout setpoint must be positive values representing leading | |
|
| power factor. Enter setpoints as integer values representing power factor in | |
|
| thousandths. For example, to define a dropout setpoint of 0.5, enter 500. Delays | |
|
| are in seconds. | |
|
| The lagging power factor alarm will occur when the test register value becomes | |
|
| more lagging than the pickup setpoint (such as closer to | |
|
| more lagging long enough to satisfy the pickup delay period. When the value | |
055 | Lagging Power Factor | becomes equal to or less lagging than the dropout setpoint and remains less | |
lagging for the dropout delay period, the alarm will drop out. Both the pickup | |||
|
| setpoint and the dropout setpoint must be positive values representing lagging | |
|
| power factor. Enter setpoints as integer values representing power factor in | |
|
| thousandths. For example, to define a dropout setpoint of | |
|
| are in seconds. | |
Digital |
|
| |
|
| The digital input transition alarms will occur whenever the digital input changes | |
060 | Digital Input On | from off to on. The alarm will dropout when the digital input changes back to on | |
|
| from off. The pickup and dropout setpoints and delays do not apply. | |
|
| The digital input transition alarms will occur whenever the digital input changes | |
061 | Digital Input Off | from on to off.The alarm will dropout when the digital input changes back to off | |
|
| from on. The pickup and dropout setpoints and delays do not apply. | |
|
| This is a internal signal from the power meter and can be used, for example, to | |
070 | Unary | alarm at the end of an interval or when the power meter is reset. Neither the | |
|
| pickup and dropout delays nor the setpoints apply. |
52 | © 2011 Schneider Electric. All Rights Reserved. |