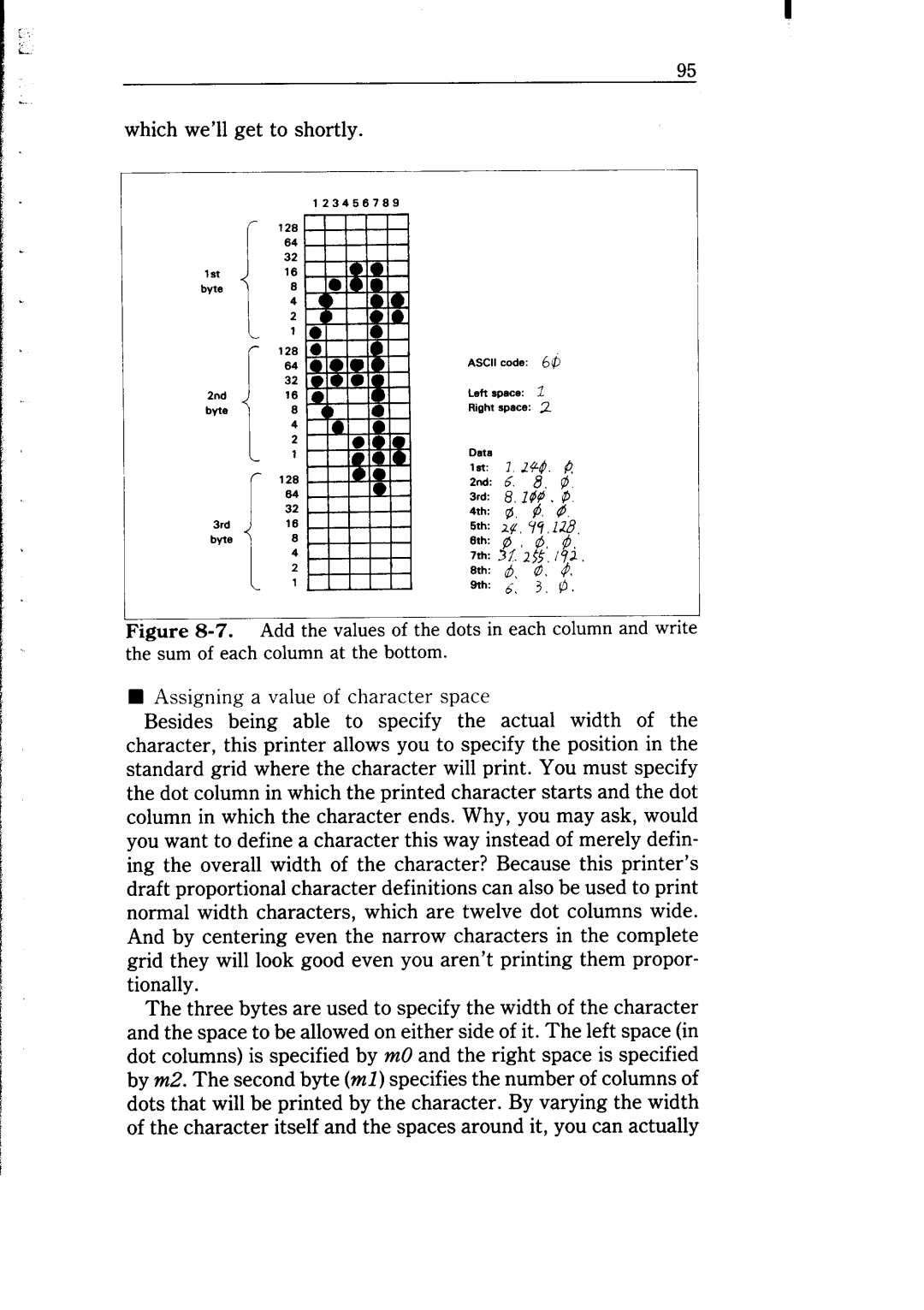
which we’ll get to shortly.
123456769
126
d3zEl64
32
1st16
byte6 4
2
1
126
64
32
2nd16
bvte6 4 2 1
r 126 64 32
3rd16
byte6 4
2
1
95
ASCII code: 66
Left *pace: I
Right space: 2
Figure 8-7. Add thevaluesofthedotsineachcolumnandwrite thesumofeachcolumnatthebottom.
nAssigningavalueofcharacterspace
Besides being able to specify the actual width of the character, this printer allows you to specify the position in the standard grid where the character will print. You must specify the dot column in which the printed character starts and the dot column in which the character ends. Why, you may ask, would you want to define a character this way instead of merely defin- ing the overall width of the character? Because this printer’s draft proportional character definitions can also be used to print normal width characters, which are twelve dot columns wide. And by centering even the narrow characters in the complete grid they will look good even you aren’t printing them propor- tionally.
The three bytes are used to specify the width of the character and the space to be allowed on either side of it. The left space (in dot columns) is specified by m0 and the right space is specified by m2. The second byte (ml) specifies the number of columns of dots that will be printed by the character. By varying the width of the character itself and the spaces around it, you can actually