www.ti.com
Procedures for Common Operations
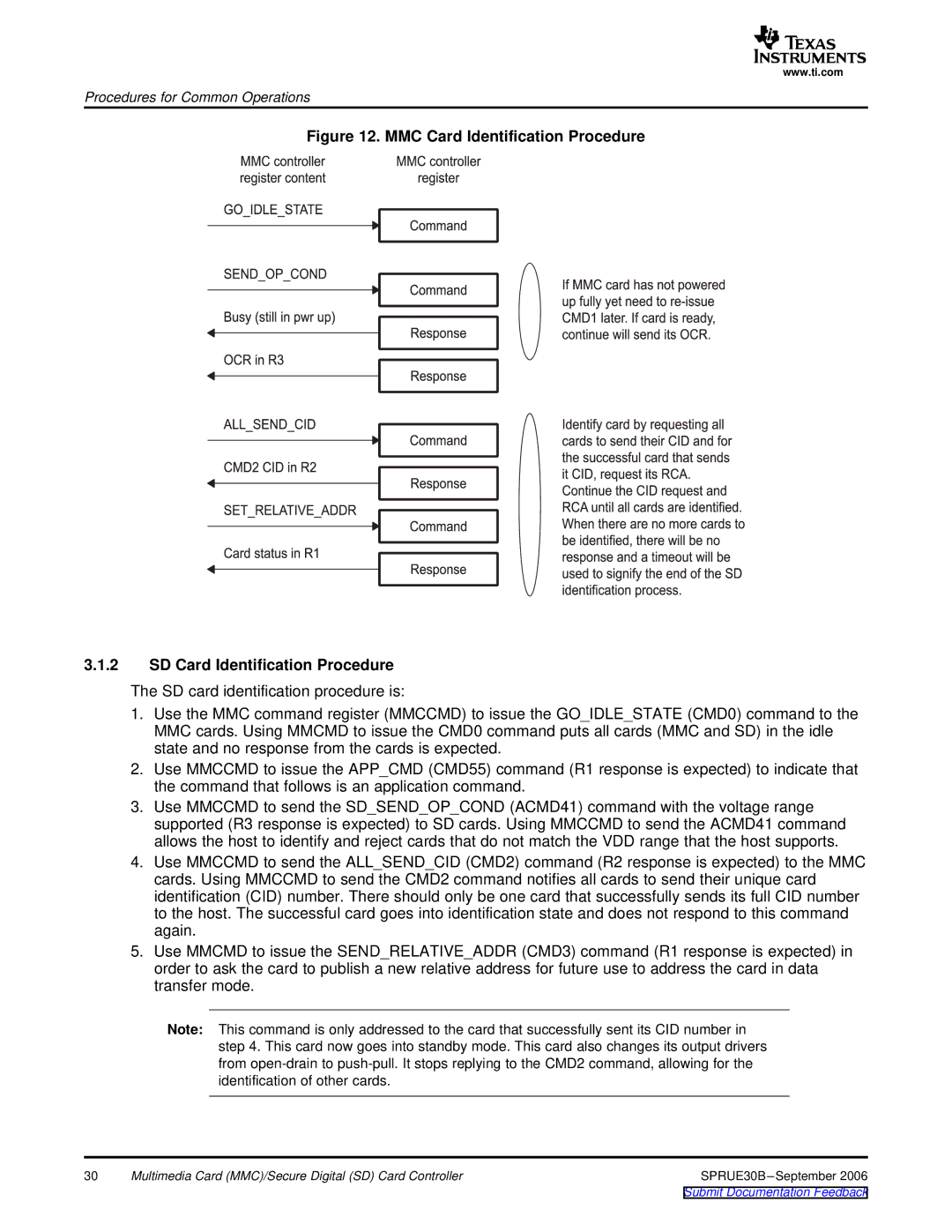
Figure 12. MMC Card Identification Procedure
3.1.2SD Card Identification Procedure
The SD card identification procedure is:
1.Use the MMC command register (MMCCMD) to issue the GO_IDLE_STATE (CMD0) command to the MMC cards. Using MMCMD to issue the CMD0 command puts all cards (MMC and SD) in the idle state and no response from the cards is expected.
2.Use MMCCMD to issue the APP_CMD (CMD55) command (R1 response is expected) to indicate that the command that follows is an application command.
3.Use MMCCMD to send the SD_SEND_OP_COND (ACMD41) command with the voltage range supported (R3 response is expected) to SD cards. Using MMCCMD to send the ACMD41 command allows the host to identify and reject cards that do not match the VDD range that the host supports.
4.Use MMCCMD to send the ALL_SEND_CID (CMD2) command (R2 response is expected) to the MMC cards. Using MMCCMD to send the CMD2 command notifies all cards to send their unique card identification (CID) number. There should only be one card that successfully sends its full CID number to the host. The successful card goes into identification state and does not respond to this command again.
5.Use MMCMD to issue the SEND_RELATIVE_ADDR (CMD3) command (R1 response is expected) in order to ask the card to publish a new relative address for future use to address the card in data transfer mode.
Note: This command is only addressed to the card that successfully sent its CID number in step 4. This card now goes into standby mode. This card also changes its output drivers from
30 | Multimedia Card (MMC)/Secure Digital (SD) Card Controller | SPRUE30B |