You can use the
This command returns the IP address and the EthernetID (in addition to other information) of servers on the local subnet that have started up from the installation disk.
Similarly, servers awaiting setup use the service name
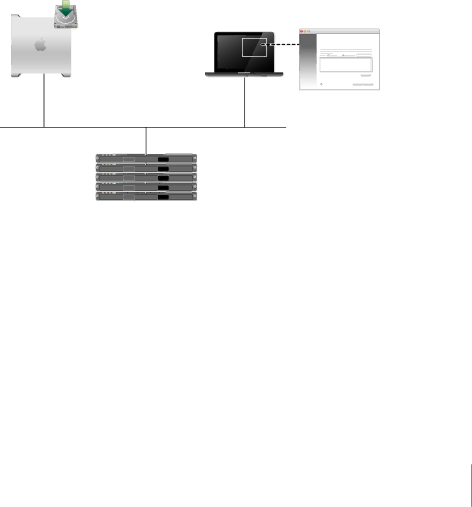
Starting Up from a NetBoot Environment
If you have an existing NetBoot infrastructure, this is the easiest way to perform mass installation and deployment. You can use this method for clusters that have no optical drive or existing system software.
Mac OS X
Server Administrator
computer
NetBoot target |
|
|
|
| Initiate server | |
servers |
|
|
|
| installation | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Target servers
Destination
This method can also be used in environments where large numbers of servers must be installed in an efficient manner.
This section won’t tell you how to create the necessary NetBoot infrastructure. If you want to set up NetBoot and NetInstall options for your network, servers, and client computers, see the manuals at www.apple.com/server/resources/.
This section has instructions to create a NetInstall image from the Mac OS X Server Install Disk and start a server from it. There is no need to make preparations to the hard disk.
Chapter 5 Installation and Deployment
91
