Appendix A Reference
Cabling Guidelines
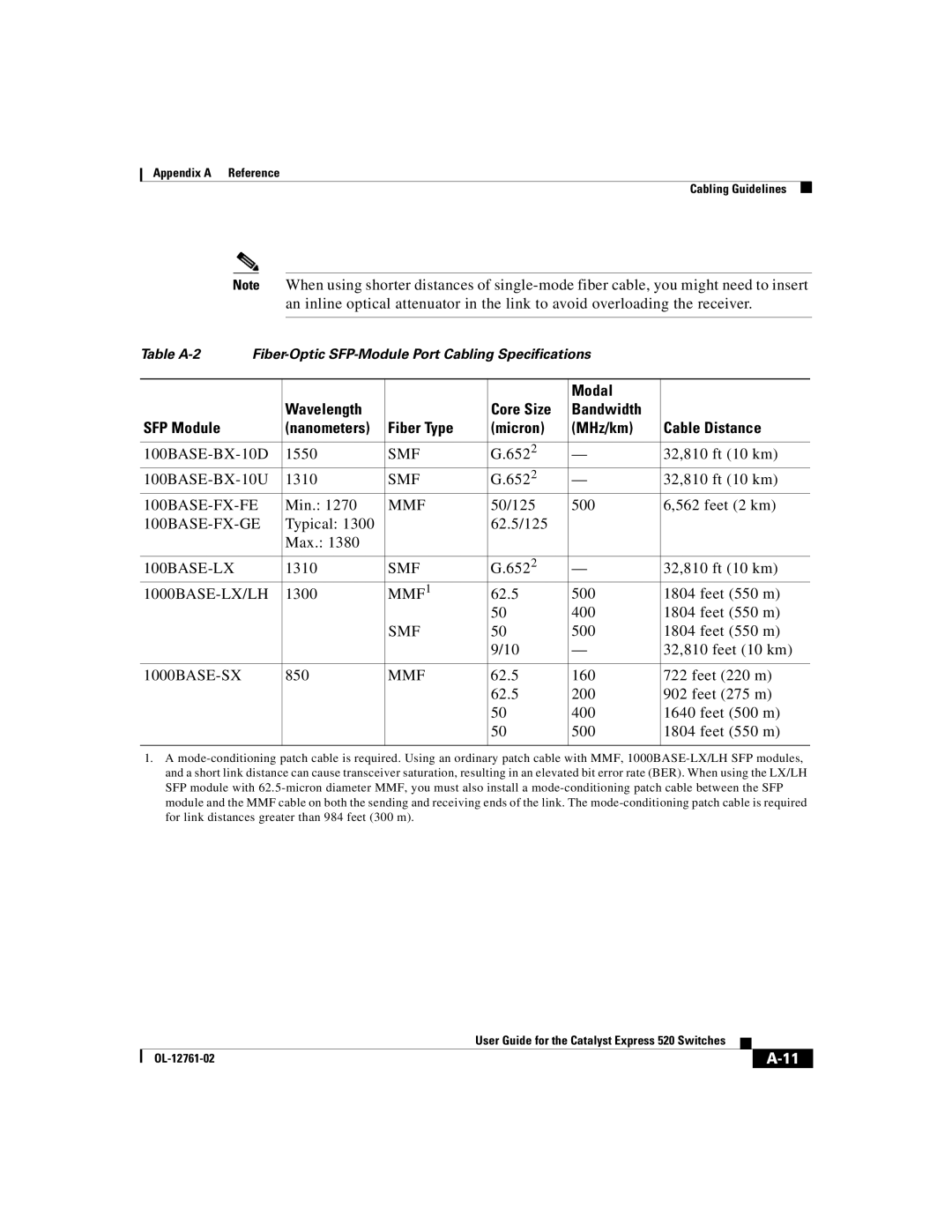
Note When using shorter distances of
an inline optical attenuator in the link to avoid overloading the receiver.
Table |
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Modal |
|
|
| Wavelength |
| Core Size | Bandwidth |
|
SFP Module |
| (nanometers) | Fiber Type | (micron) | (MHz/km) | Cable Distance |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
1550 | SMF | G.6522 | — | 32,810 ft (10 km) | ||
1310 | SMF | G.6522 | — | 32,810 ft (10 km) | ||
Min.: 1270 | MMF | 50/125 | 500 | 6,562 feet (2 km) | ||
Typical: 1300 |
| 62.5/125 |
|
| ||
|
| Max.: 1380 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1310 | SMF | G.6522 | — | 32,810 ft (10 km) | |
1300 | MMF1 | 62.5 | 500 | 1804 feet (550 m) | ||
|
|
|
| 50 | 400 | 1804 feet (550 m) |
|
|
| SMF | 50 | 500 | 1804 feet (550 m) |
|
|
|
| 9/10 | — | 32,810 feet (10 km) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 850 | MMF | 62.5 | 160 | 722 feet (220 m) | |
|
|
|
| 62.5 | 200 | 902 feet (275 m) |
|
|
|
| 50 | 400 | 1640 feet (500 m) |
|
|
|
| 50 | 500 | 1804 feet (550 m) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.A
|
| User Guide for the Catalyst Express 520 Switches |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
| ||
|
|
|