SCSI BUS
(1) DB 7 to 0, P (DATA BUS)
These signals form a bidirectional data bus consisting eight data bits and an odd parity bit.
MSB (27): DB7, LSB (20): DB0
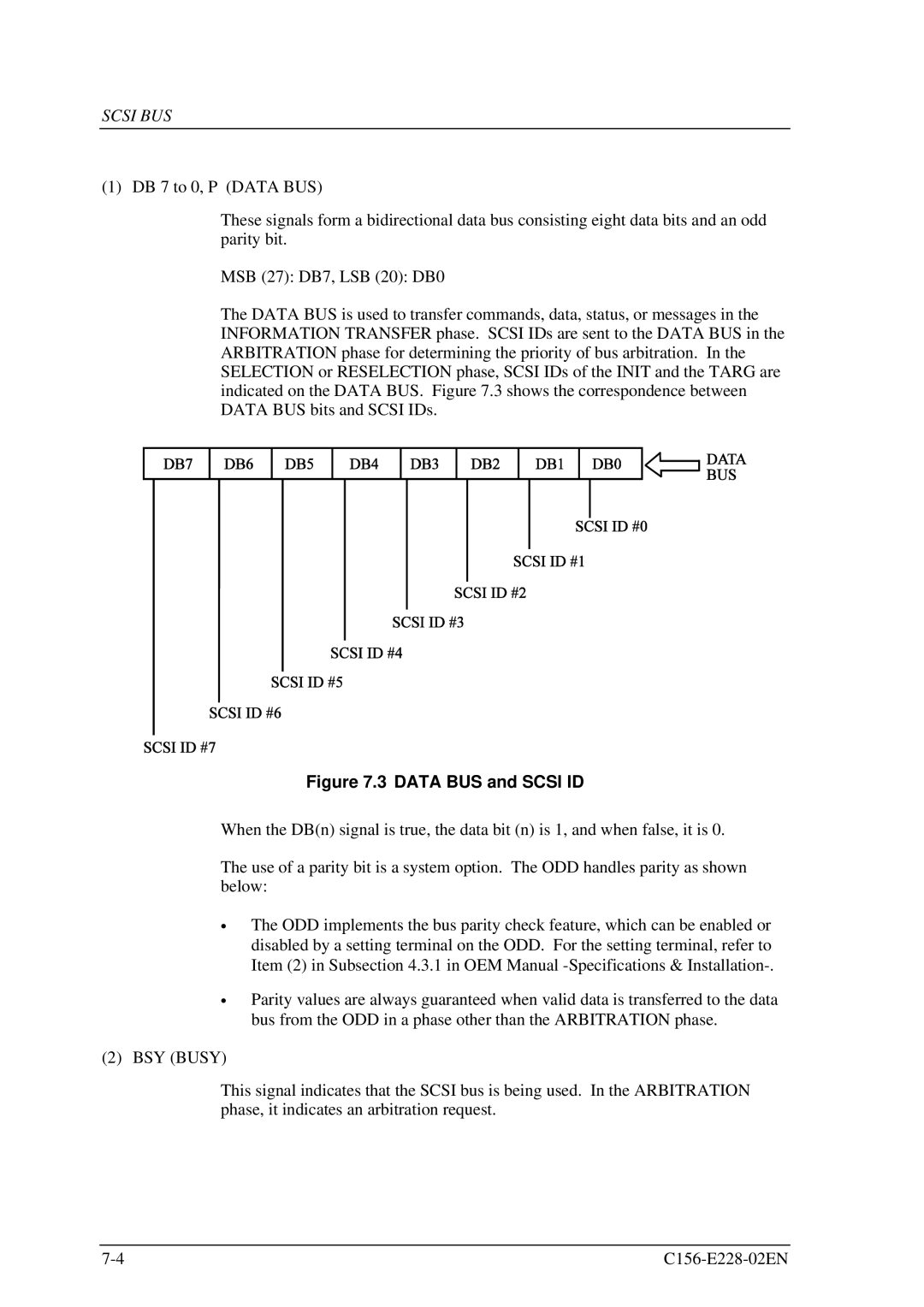
The DATA BUS is used to transfer commands, data, status, or messages in the INFORMATION TRANSFER phase. SCSI IDs are sent to the DATA BUS in the ARBITRATION phase for determining the priority of bus arbitration. In the SELECTION or RESELECTION phase, SCSI IDs of the INIT and the TARG are indicated on the DATA BUS. Figure 7.3 shows the correspondence between DATA BUS bits and SCSI IDs.
Figure 7.3 DATA BUS and SCSI ID
When the DB(n) signal is true, the data bit (n) is 1, and when false, it is 0.
The use of a parity bit is a system option. The ODD handles parity as shown below:
•The ODD implements the bus parity check feature, which can be enabled or disabled by a setting terminal on the ODD. For the setting terminal, refer to Item (2) in Subsection 4.3.1 in OEM Manual
•Parity values are always guaranteed when valid data is transferred to the data bus from the ODD in a phase other than the ARBITRATION phase.
(2)BSY (BUSY)
This signal indicates that the SCSI bus is being used. In the ARBITRATION phase, it indicates an arbitration request.