SCSI BUS
(3) Signal sources
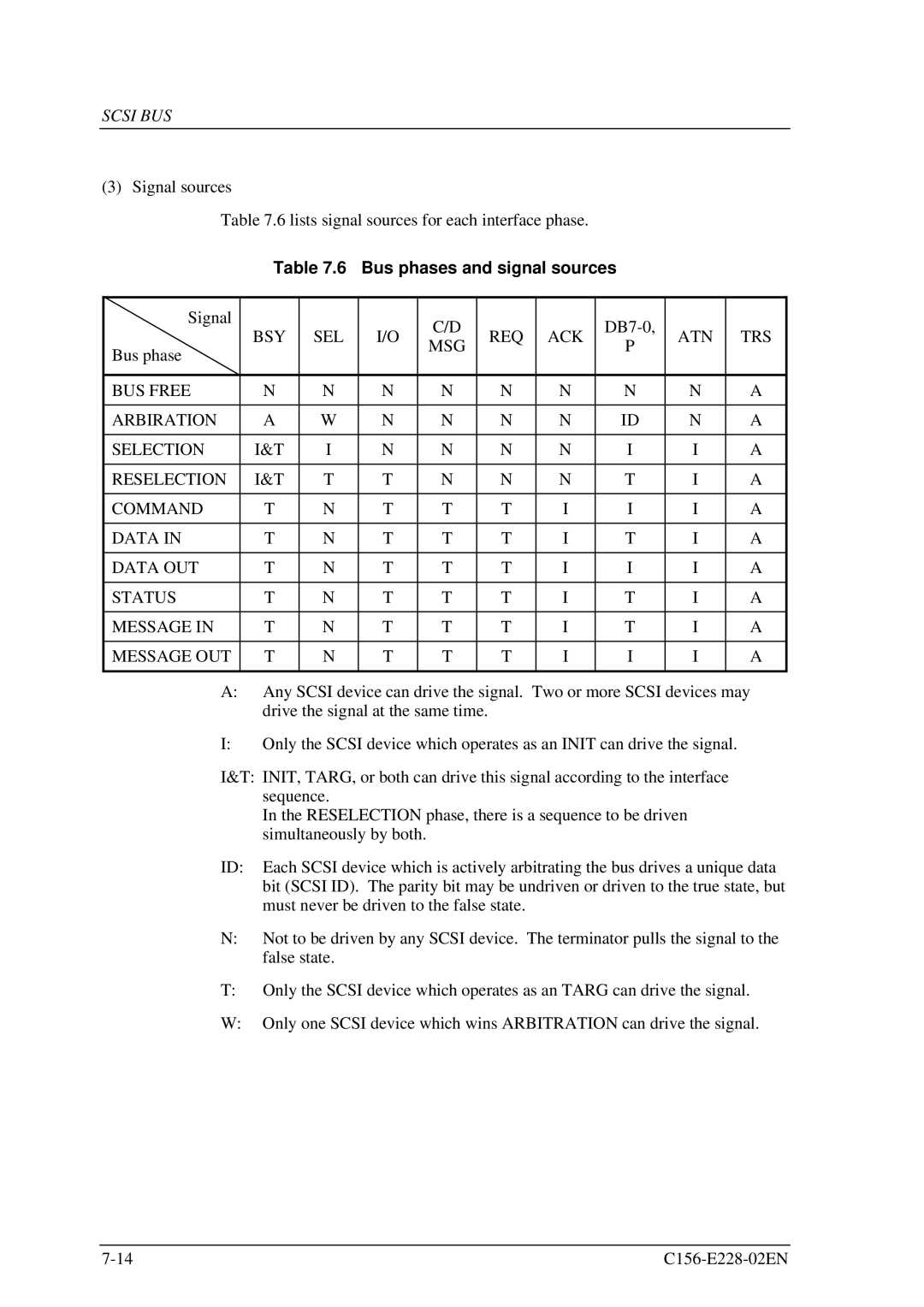
Table 7.6 lists signal sources for each interface phase.
Table 7.6 Bus phases and signal sources
Signal | BSY | SEL | I/O | C/D | REQ | ACK | ATN | TRS | ||
| ||||||||||
Bus phase | MSG | P | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
BUS FREE | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
ARBIRATION | A | W | N | N | N | N | ID | N | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
SELECTION | I&T | I | N | N | N | N | I | I | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
RESELECTION | I&T | T | T | N | N | N | T | I | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
COMMAND | T | N | T | T | T | I | I | I | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
DATA IN | T | N | T | T | T | I | T | I | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
DATA OUT | T | N | T | T | T | I | I | I | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
STATUS | T | N | T | T | T | I | T | I | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
MESSAGE IN | T | N | T | T | T | I | T | I | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
MESSAGE OUT | T | N | T | T | T | I | I | I | A | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A:Any SCSI device can drive the signal. Two or more SCSI devices may drive the signal at the same time.
I:Only the SCSI device which operates as an INIT can drive the signal.
I&T: INIT, TARG, or both can drive this signal according to the interface sequence.
In the RESELECTION phase, there is a sequence to be driven simultaneously by both.
ID: Each SCSI device which is actively arbitrating the bus drives a unique data bit (SCSI ID). The parity bit may be undriven or driven to the true state, but must never be driven to the false state.
N:Not to be driven by any SCSI device. The terminator pulls the signal to the false state.
T:Only the SCSI device which operates as an TARG can drive the signal.
W:Only one SCSI device which wins ARBITRATION can drive the signal.