7.6 Bus Phases
Bus Settle Delay (Min)
7 |
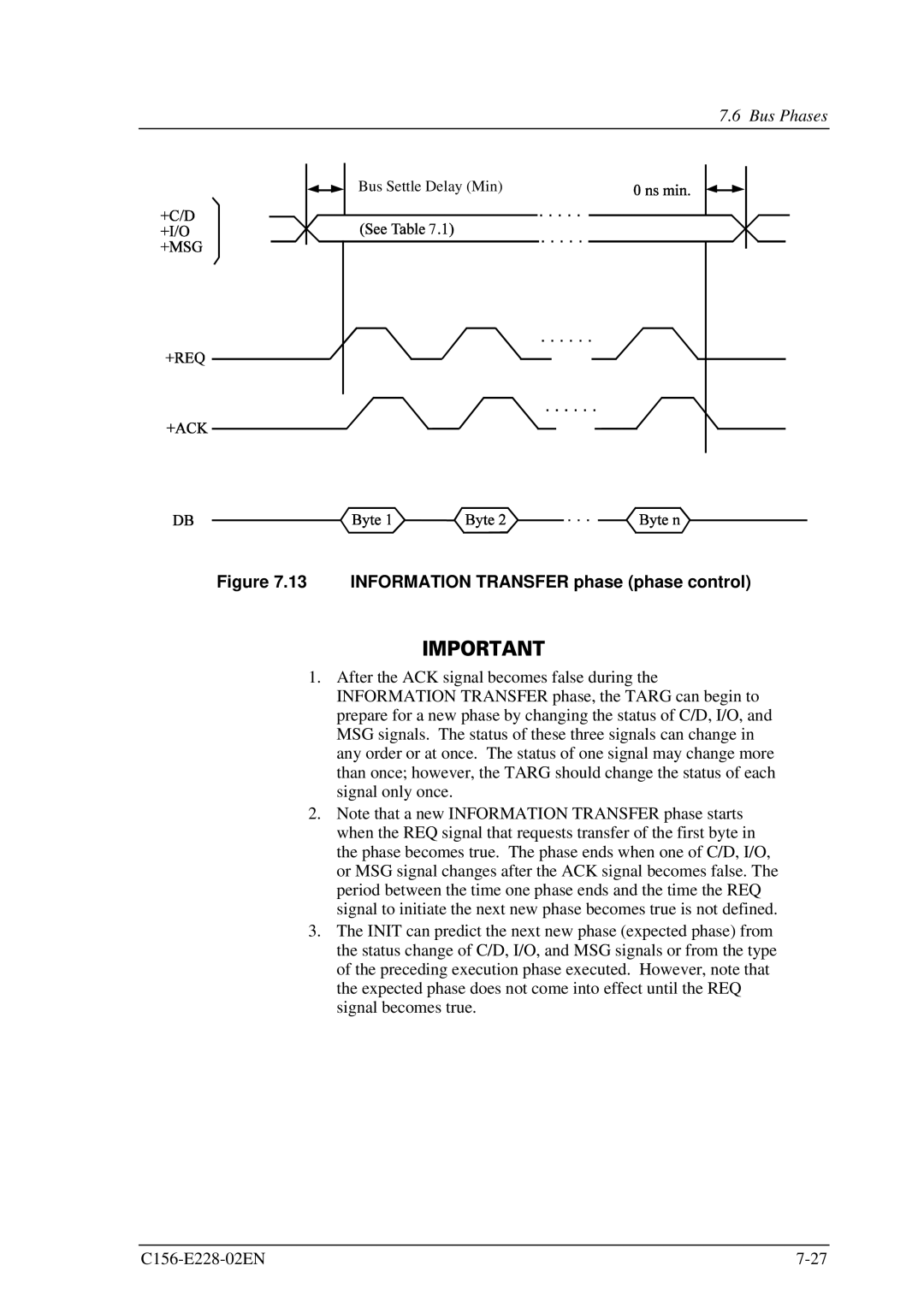
Figure 7.13 INFORMATION TRANSFER phase (phase control)
1.After the ACK signal becomes false during the INFORMATION TRANSFER phase, the TARG can begin to prepare for a new phase by changing the status of C/D, I/O, and MSG signals. The status of these three signals can change in any order or at once. The status of one signal may change more than once; however, the TARG should change the status of each signal only once.
2.Note that a new INFORMATION TRANSFER phase starts when the REQ signal that requests transfer of the first byte in the phase becomes true. The phase ends when one of C/D, I/O, or MSG signal changes after the ACK signal becomes false. The period between the time one phase ends and the time the REQ signal to initiate the next new phase becomes true is not defined.
3.The INIT can predict the next new phase (expected phase) from the status change of C/D, I/O, and MSG signals or from the type of the preceding execution phase executed. However, note that the expected phase does not come into effect until the REQ signal becomes true.