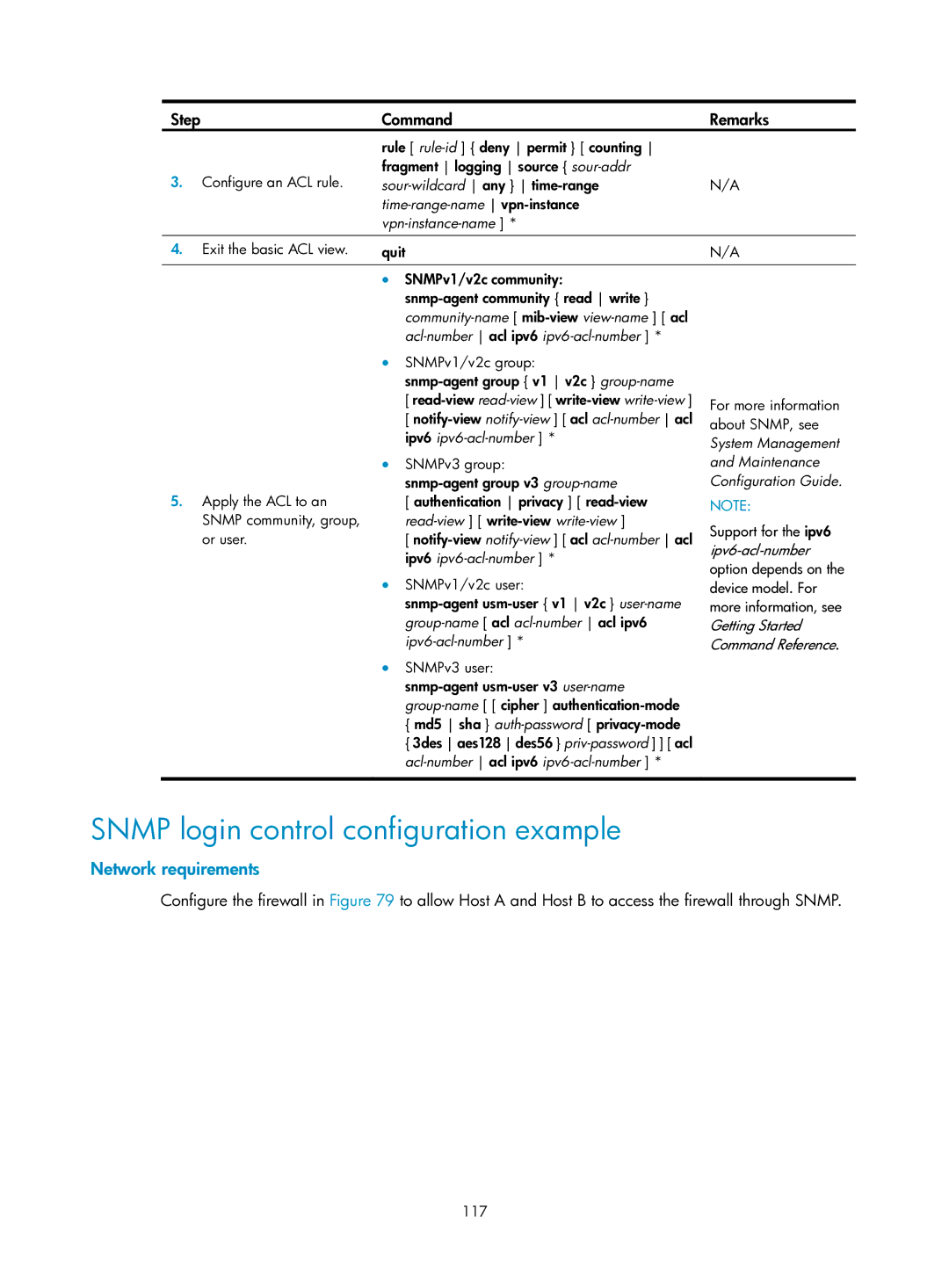
Step | Command | Remarks |
3.Configure an ACL rule.
rule [
4. Exit the basic ACL view. | quit | N/A |
|
|
|
| • SNMPv1/v2c community: |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
• | SNMPv1/v2c group: |
| |
| [ |
| [ |
| ipv6 |
• | SNMPv3 group: |
5. Apply the ACL to an | |
[ authentication privacy ] [ | |
SNMP community, group, |
|
or user. | [ |
| ipv6 |
• | SNMPv1/v2c user: |
| |
|
|
|
|
• | SNMPv3 user: |
| |
| |
| { md5 sha } |
| { 3des aes128 des56 } |
|
For more information about SNMP, see System Management and Maintenance Configuration Guide.
NOTE:
Support for the ipv6
SNMP login control configuration example
Network requirements
Configure the firewall in Figure 79 to allow Host A and Host B to access the firewall through SNMP.
117