Introduction to WCCP
WCCP was originally implemented on Cisco routers,
You configure WCCP to redirect traffic to an HP EFS WAN Accelerator or group of
HP EFS WAN Accelerators:
so that the HP EFS WAN Accelerators do not have to be physically
to redirect traffic to an HP EFS WAN Accelerator or group of HP EFS WAN Accelerators to provide load balancing and failover support.
You can configure WCCP on the
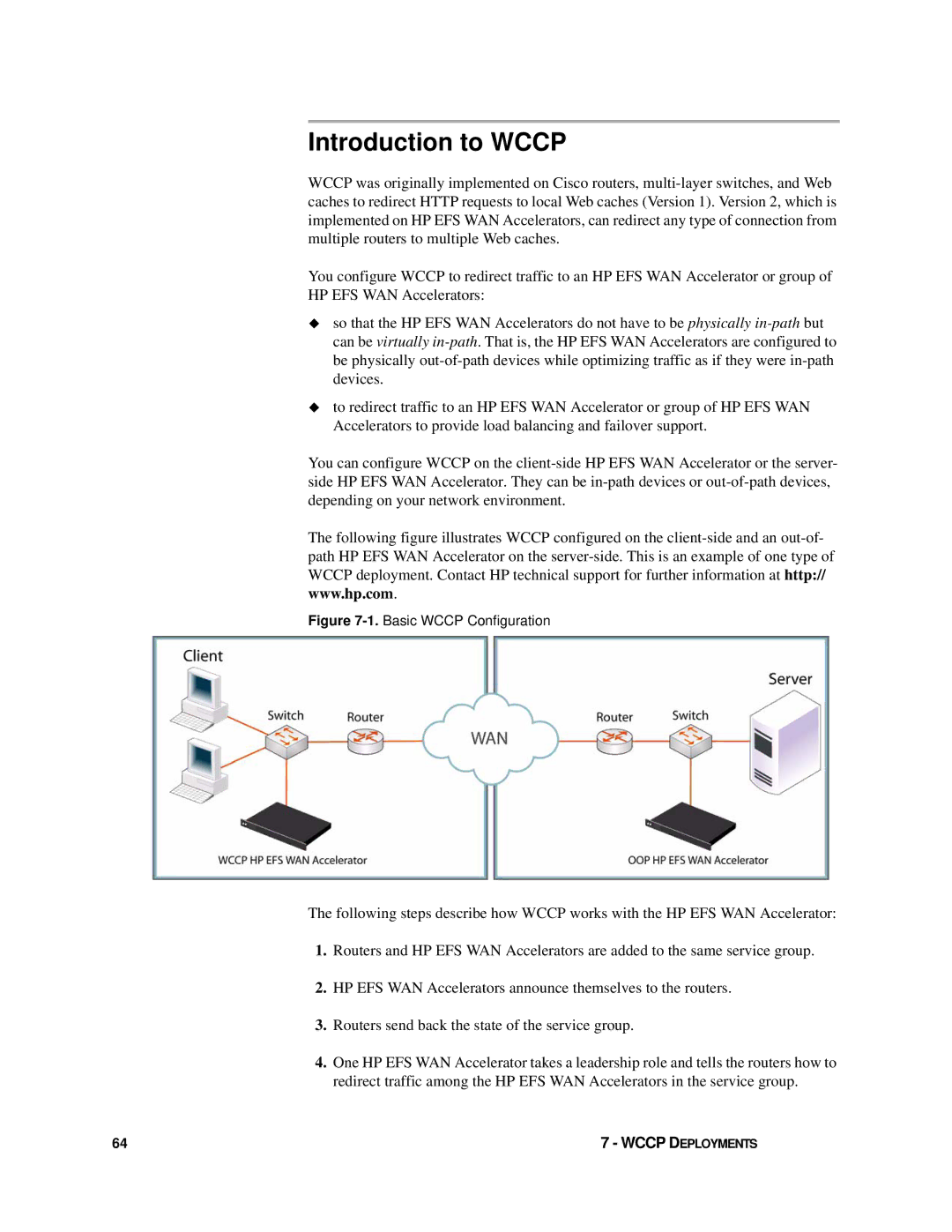
The following figure illustrates WCCP configured on the
Figure 7-1. Basic WCCP Configuration
The following steps describe how WCCP works with the HP EFS WAN Accelerator:
1.Routers and HP EFS WAN Accelerators are added to the same service group.
2.HP EFS WAN Accelerators announce themselves to the routers.
3.Routers send back the state of the service group.
4.One HP EFS WAN Accelerator takes a leadership role and tells the routers how to redirect traffic among the HP EFS WAN Accelerators in the service group.
64 | 7 - WCCP DEPLOYMENTS |