Contents
Frequency and Period Measurement Errors
Zeroauto ZEROAUTO?
IMMediate
Chapter Multimeter Command Reference
Appendix a
Appendix B
Contents
HEWLETT-PACKARD Warranty Statement
Documentation History
Manufacturer’s Name
July 31 Jim White, QA Manager
Business Reply Mail
Page
HP E1312A and HP E1412A Multimeter Module Setup
Using This Chapter
Setting the Module Address Switch
Setting the Line Frequency Reference
Interrupt Priority
Checking the Line Frequency Reference
Page
Switch Module Analog Bus Connections
Multimeter Functional Connections
Voltage Measurement Connections
Wire Ohms Measurement Connections
HP E1312A and HP E1412A Multimeter Module Setup Chapter
Initial Operation
Function Prototype
HP E1312A and HP E1412A Multimeter Module Setup Chapter
Thermal EMF Errors
Measurement Tutorial
DC Voltage Measurements
Loading Errors dc volts Leakage Current Errors
Thermoelectric Voltages
Rejecting Power Line Noise Voltages
Common Mode Rejection CMR
Noise Caused by Magnetic Loops
Noise Caused by Ground Loops
Wire Ohms Measurements
Resistance Measurements
Set to 2-wire ohms function
Power Dissipation Effects
Errors in High Resistance Measurements
Making High-Speed DC and Resistance Measurements
DC Current Measurement Errors
True RMS AC Measurements
Crest Factor Errors non-sinusoidal inputs
Common Crest Factors Example
Loading Errors ac volts
Temperature Coefficient Errors
AC Measurements Below Full Scale
Function and Range Change Internal Offset Correction
Low-Level Measurement Errors
Voltage Measured = Vin2+ Noise2
AC Current Measurement Errors
Frequency and Period Measurement Errors
Making High-Speed AC Voltage or Current Measurements
Measurement Configuration
AC Signal Filter DC Input Resistance
Number of Power Line Cycles Nplc Resolution
Chapter HP E1312A/E1412A Multimeter Application Information
SENSeZEROAUTO Offonceon
Math Operations CALCulate Subsystem
Null Relative Function
DB Measurements
CONFfunction
DBm Measurements
Storing the dB Reference Value
Storing the dBm Reference Resistance Value
HP E1312A/E1412A Multimeter Application Information Chapter
Triggering the Multimeter
TRIGgerSOURce EXTernal
Checking the Trigger Source
Bus Triggering
Wait-for-Trigger State
Checking the Trigger Count Inserting a Trigger Delay
Example Setting the Trigger Count
Example Inserting a Trigger Delay
Default Trigger Delays
Querying Delay Time Sample Count
Example Setting the Sample Count
Checking the Sample Count
HP E1312A and HP E1412A Multimeter Application Examples
HP VTL Software Visa
MEASure Command
Making Multimeter Measurements
MEASURE1 Source Code File
MEASURE2 Source Code File
MEASURE3 Source Code File
Init
MEASURE4 Source Code File
Synchronizing Multimeter With a Switch Module
HP E1412A Multimeter and Switch Module Synchronization
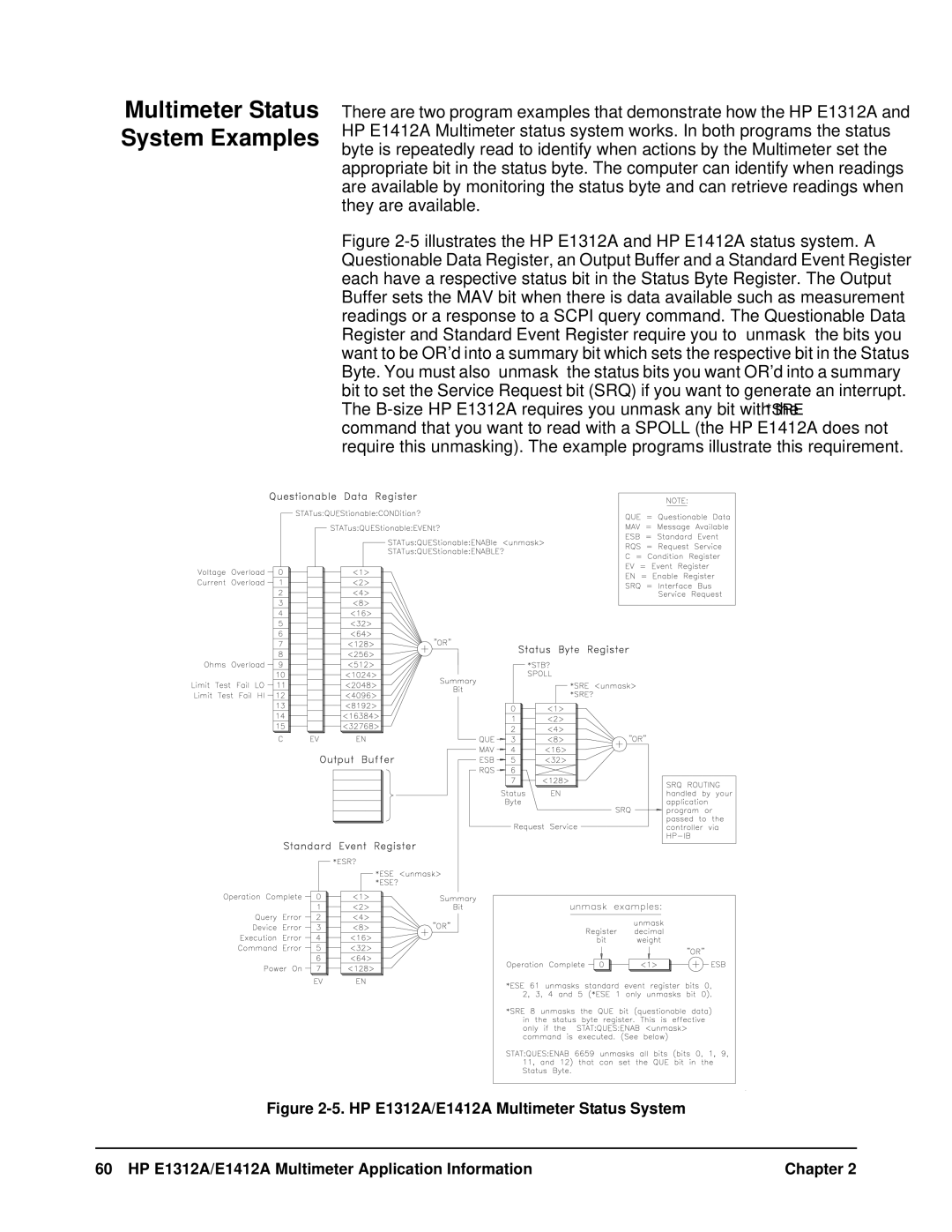
See -5 for the HP E1312A/E1412A Multimeter status system
Set up the Multimeter
Now set up the switch module
Check the multimeter for system errors
Retrieve the readings from the multimeter
Multimeter Status System Examples
Synchopc Source Code File
RST CLS *ESE Init OPC
Synchmav Source Code File
RST Init FETC?
End Loop Check the multimeter for system errors
Limittst Source Code File
Loop
Device Configuration
Programming Example
Page
HP E1312A/E1412A Multimeter Application Information Chapter
Command Types
Common Command Format
Command Format
Command
Abbreviated Commands Implied Commands
Separator
Linking Commands
Parameters
Multimeter Range and Resolution Tables
PLC
Scpi Command Reference
AC Voltage Range versus Resolution
AC Current Range versus Resolution
Related Commands INITiate, TRIGger
ABORt
Aborting a Measurement
CALCulate
Subsystem Syntax
Valid Math/Measurement Function Combinations
AVERageAVERage?
AVERageCOUNt?
AVERageMAXimum?
AVERageMINimum?
DBREFerence
DBREFerence?
DBMREFerence
DBMREFerence?
FUNCtion
FUNCtion?
Parameter Summary Example
Example Query the Calculate Math Function
LIMitLOWer
LIMitLOWer?
LIMitUPPer
LIMitUPPer?
NULLOFFSet
NULLOFFSet?
STATe
STATe?
CALibration
COUNt?
LFRequency
Comments
Example Query the Line Frequency Setting
LFRequency?
SECureCODE
Example Enter a New Calibration Security Code
SECureSTATe
SECureSTATe?
STRing
Example Set the Calibration State to Unsecured
STRing?
VALue
VALue?
Example Query the Calibration Message
Zeroauto
CALibration?
CAL?
CONFigure
Command Setting
Default Settings for CONFigure Command by Function
Function Range Resolution
CURRentAC
Example Making AC Current Measurements
CURRentDC
Example Making DC Current Measurements
ResolutionMINMAXDEF selects the frequency function
Example Making 4-Wire Ohms Measurements
FRESistance
PERiod
Resolution Minmaxdef
Example Making 2-Wire Ohms Measurements
VOLTageAC
Example Making AC Voltage Measurements
VOLTageDC
Example Making DC Voltage Measurements
VOLTageDCRATio
Sense HI and LO input
CONFigure?
String Returned
Data
POINts?
FETCh?
Example Transferring Stored Readings to Output Buffer
INITiate
IMMediate
Example Placing Multimeter in Wait-For-Trigger State
Example Query the Input Impedance Mode
INPut
IMPedanceAUTO
IMPedanceAUTO?
MEASure
CURRentAC?
MEASCURRAC? 1,MAX
CURRentDC?
MEASCURRDC? .1,MAX
FREQuency?
FRESistance?
MEASFRES? 1500,MAX
PERiod?
RESistance?
VOLTageAC?
VOLTageDC?
VOLTageDCRATio?
Example Making DC Voltage Ratio Measurements
OUTPut
TTLTrgSTATe
RST Condition OUTPTTLTn OFF
TTLTrgSTATe?
Example Route Voltmeter Complete to Trigger Line
Example Query Voltmeter Complete Destination
READ?
Example Transfer Readings Directly to Output Buffer
SAMPle
COUNt
RST Condition Sampcoun Example Set the Sample Count
Example Query the Sample Count
SAMPCOUN?
SENSe
Zero Auto Offonceon AUTO?
Example Query the Measurement Function
Function
CURRentACRANGe
CURRentACRANGe?
Example Query the AC Current Measurement Range
Example Disable AC Current Autoranging
Example Query the AC Current Autorange Mode
CURRentACRANGeAUTO
CURRentACRANGeAUTO?
CURRentACRESolution
CURRentACRESolution?
CURRentDCAPERture
CURRentDCAPERture?
Example Set an Aperture Time of 16.7ms
Example Query the Aperture Time
CURRentDCNPLC
CURRentDCNPLC?
Example Query the DC Current Integration Time
CURRentDCRANGe
CURRentDCRANGe?
Example Set the DC Current Range to 3A
Example Query the DC Current Measurement Range
Example Disable DC Current Autoranging
Example Query the DC Current Autorange Mode
CURRentDCRANGeAUTO
CURRentDCRANGeAUTO?
CURRentDCRESolution
CURRentDCRESolution?
DETectorBANDwidth
DETectorBANDwidth?
FREQuencyAPERture
FREQuencyAPERture?
Example Query the Detector Bandwidth
FREQuencyVOLTageRANGe
FREQuencyVOLTageRANGe?
Example Set the Voltage Range for Frequency Measurements to
Example Query the Measurement Range
Example Disable Autoranging
Example Query the Autorange Mode
FREQuencyVOLTageRANGeAUTO
FREQuencyVOLTageRANGeAUTO?
FRESistanceAPERture
FRESistanceAPERture?
FRESistanceNPLC
FRESistanceNPLC?
Example Query the Integration Time
FRESistanceRANGe
FRESistanceRANGe?
FRESistanceRANGeAUTO
FRESistanceRANGeAUTO?
FRESistanceRESolution
FRESistanceRESolution?
Example Query the Resolution
RST Condition Fresres 1mΩ 1E-03
PERiodAPERture
PERiodAPERture?
RST Condition 0.1 100ms Example Set the Aperture Time
PERiodVOLTageRANGe
PERiodVOLTageRANGe?
Example Set the Voltage Range for Period Measurements to
Example Query the Period Voltage Range
PERiodVOLTageRANGeAUTO
PERiodVOLTageRANGeAUTO?
RESistanceAPERture
RESistanceAPERture?
RESistanceNPLC
RESistanceNPLC?
RESistanceRANGe
RESistanceRANGe?
RST Condition Resrang 1kΩ Example Change the Range
RESistanceRANGeAUTO
RESistanceRANGeAUTO?
RESistanceRESolution
RESistanceRESolution?
Example Change the Resolution
VOLTageACRANGe
VOLTageACRANGe?
Example Disable AC Voltage Autoranging
VOLTageACRANGeAUTO
VOLTageACRANGeAUTO?
VOLTageACRESolution
VOLTageACRESolution?
RST Condition 1E-04 Example Change the Resolution
VOLTageDCAPERture
VOLTageDCAPERture?
VOLTageDCNPLC
VOLTageDCNPLC?
VOLTageDCRANGe
VOLTageDCRANGe?
VOLTageDCRANGeAUTO
VOLTageDCRANGeAUTO?
VOLTageDCRESolution
VOLTageDCRESolution?
Example Disable Autozero
Example Query the Autozero Mode
PRESet
QUEStionableENABle
STATus
QUEStionableCONDition?
QUEStionableENABle?
QUEStionableEVENt?
ERRor?
Example Reading the Error Queue
SYSTem
VERSion?
TRIGger
RST Condition Trigcoun Example Set the Trigger Count
DELay
Example Set the Trigger Delay
Example Query the Trigger Count
DELay?
DELayAUTO
Example Query the Trigger Delay
Example Disable Automatic Trigger Delay
DELayAUTO?
Example Query the Trigger Delay Mode
Related Commands INITiate, READ?, MEAS?
SOURce
Example Set the Sample Source
SOURce?
Example Query the Trigger Source
Ieee 488.2 Common Command Quick Reference
Category Command Title Description
Example Enable All Error Events
ESE and *ESE?
ESR?
SRE and *SRE?
RST does not affect
STB?
Scpi Command Quick Reference
HP E1412A C-size 6½-Digit Multimeters
Data
67sMINMAX
Zeroauto Offonceon
HP E1312A and HP E1412A Multimeter Specifications
DC Characteristics
Measuring Characteristics
60 Hz 50 Hz
Operating Characteristics
AC Characteristics
True RMS AC
True RMS AC Voltage
System Speeds 10
Frequency and Period Characteristics
Accuracy Specifications ±% of reading 1
Configuration Rates 14/sec Autorange Time
General Specifications
To Calculate Total Measurement Error
Understanding the % of reading Error
Total Measurement Error
Interpreting Multimeter Specifications
Number of Digits and Overrange
Accuracy
Configuring for High Accuracy Measurements
DC Voltage, DC Current, and Resistance Measurements
Execution Errors
112Program mnemonic too long
113Undefined header
121Invalid character in number
123Numeric overflow
To -168Block data errors
To -178Expression errors
221Settings conflict
211Trigger ignored
350Too many errors
330Self-test failed
440Query Unterminated after indefinite response
Cannot achieve requested resolution
Cannot use overload as math reference
Cal signal measurement out of range
Cal signal frequency out of range
Cal secured
Invalid secure code
No cal for this function or range
HP E1312A and HP E1412A Multimeter Error Messages Appendix B
Measurement Speed and Accuracy Trade-offs
Measurement Speed and Accuracy Trade-offs Appendix C
HP E1312A/E1412 Special Function
Minimize Number Command Response Sessions
General Guidelines for Increasing Measurement Speed
Avoid Function Changes Avoid Aperture Changes
Set Autozero to Once or OFF Turn Autorange
Decrease Aperture Time or NPLCs
Setting the Resolution
INITFETCH?
Index
197
Index
124
Index
Index
Error, 180
See online help
Cycles, 27, 38, 123, 132, 140
Errors
130
Setting resolution, 15, 38
160
Index