C H A P T E R 2 | Intel Express 460T Standalone Switch Users Guide |
MAC-Based VLANs
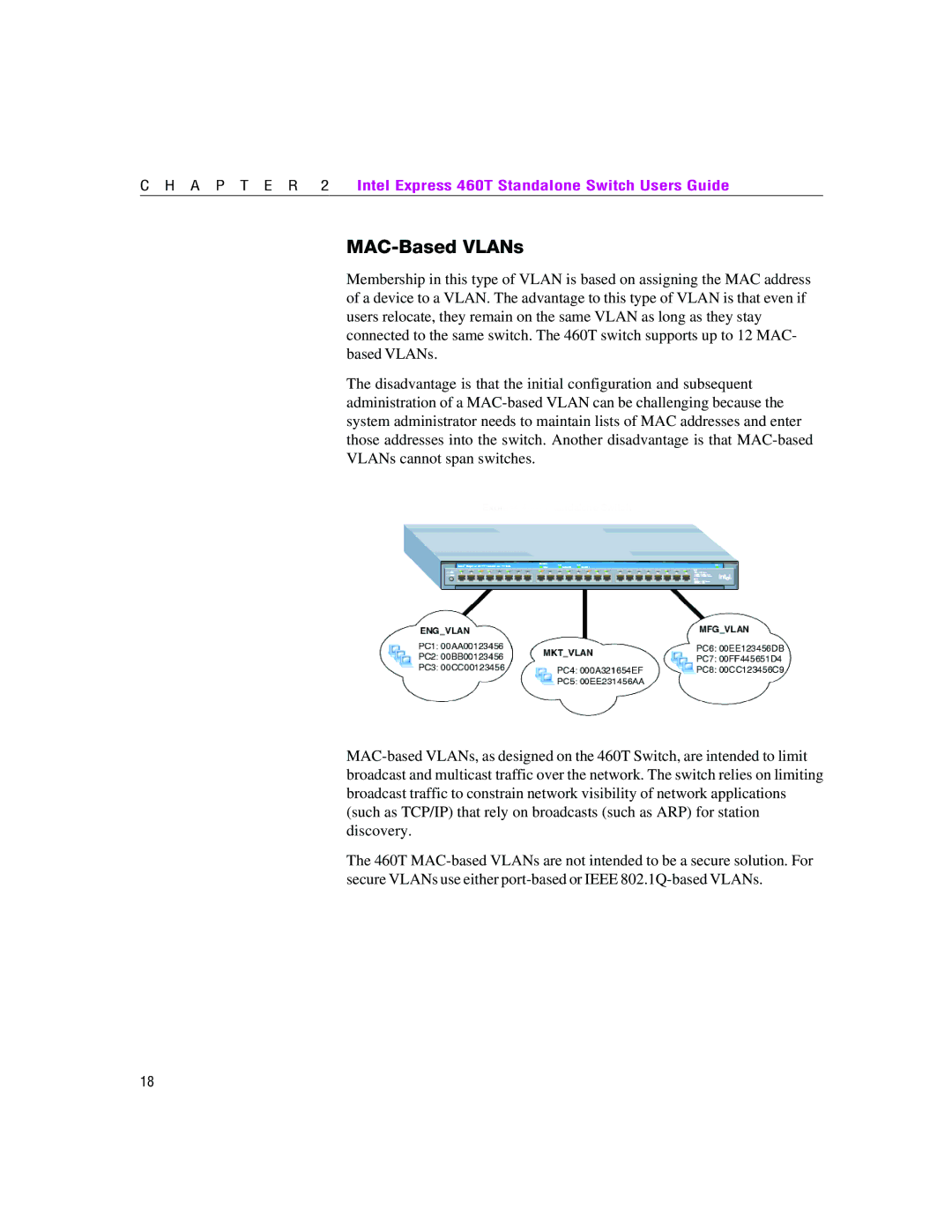
Membership in this type of VLAN is based on assigning the MAC address of a device to a VLAN. The advantage to this type of VLAN is that even if users relocate, they remain on the same VLAN as long as they stay connected to the same switch. The 460T switch supports up to 12 MAC- based VLANs.
The disadvantage is that the initial configuration and subsequent administration of a MAC-based VLAN can be challenging because the system administrator needs to maintain lists of MAC addresses and enter those addresses into the switch. Another disadvantage is that MAC-based VLANs cannot span switches.
MAC-based VLANs, as designed on the 460T Switch, are intended to limit broadcast and multicast traffic over the network. The switch relies on limiting broadcast traffic to constrain network visibility of network applications (such as TCP/IP) that rely on broadcasts (such as ARP) for station discovery.
The 460T MAC-based VLANs are not intended to be a secure solution. For secure VLANs use either port-based or IEEE 802.1Q-based VLANs.