Page
Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Trademarks
Rabbit Semiconductor
Table of Contents
Rabbit Internal I/O Registers
Parallel Ports 129
Rabbit 3000 Clocks 209
Appendix B. Rabbit 3000 Revisions 273
Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Introduction
Features and Specifications Rabbit
User’s Manual
1shows a block diagram of the Rabbit
CPU
Summary of Rabbit 3000 Advantages
Feature Rabbit
Differences Rabbit 3000 vs. Rabbit
Serial ports with support for SDLC/HDLC IrDA
Rabbit 3000 Design Features
Rabbit 8-bit Processor vs. Other Processors
1 5 V Tolerant Inputs
Overview of On-Chip Peripherals and Features
Serial Ports
System Clock
4 32.768 kHz Oscillator Input
Parallel I/O
Cascaded Output Registers for Parallel Ports D and E
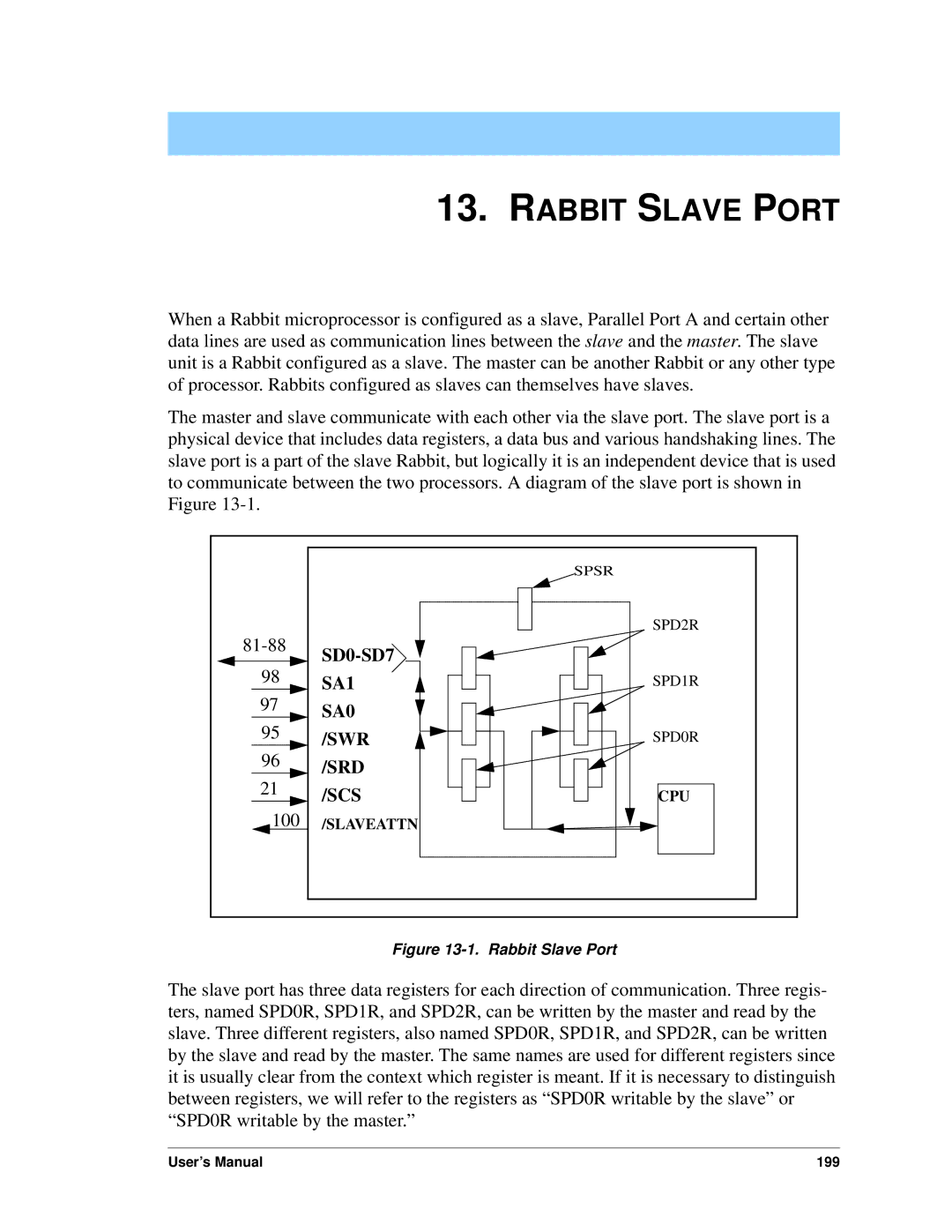
Slave Port
Rabbit
Timers
Auxiliary I/O Bus
Input Capture Channels
PWM
Quadrature Encoder Inputs
Pulse Width Modulation Outputs
Separate Core and I/O Power Pins
Design Standards
Spread Spectrum Clock
Programming Port
Standard Bios
Dynamic C Support for the Rabbit
Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Details on Rabbit Microprocessor Features
Processor Registers
Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Memory Mapping
Addressing Memory Components
Example of Memory Mapping Operation
4shows a memory interface unit
Extended Code Space
Separate I and D Space Extending Data Memory
Use of XPC Segment
Xpc window stack
Using the Stack Segment for Data Storage
Practical Memory Considerations
Data RAM Root Code
User’s Manual
Instruction Set Outline
Load Immediate Data to a Register
Load or Store Data from or to a Constant Address
Load or Store Data Using an Index Register
Other 8-bit loads and stores are the following
Register-to-Register Move
Register Exchanges
Push and Pop Instructions
7 16-bit Arithmetic and Logical Ops
Bool
SBC instruction can also be used to perform a sign extension
Input/Output Instructions
How to Do It in Assembly Language-Tips and Tricks
Zero HL in 4 Clocks
Exchanges Not Directly Implemented
Manipulation of Boolean Variables
Comparisons of Integers
HLB
Atomic Moves from Memory to I/O Space
Interrupt Structure
Interrupt Priority
Effect of Processor Priorities on Interrupts
Processor Priority Effect on Interrupts
Multiple External Interrupting Devices
Privileged Instructions, Critical Sections and Semaphores
Semaphores Using Bit B,HL
Critical Sections
Computed Long Calls and Jumps
Rabbit Capabilities
Precisely Timed Output Pulses
Pulse Width Modulation to Reduce Relay Power
Using Open-Drain Outputs for Key Scan
Open-Drain Outputs Used for Key Scan
Cold Boot
Slave Port
Slave Rabbit As a Protocol Uart
PIN Assignments and Functions
Lqfp Package
Pinout
Mechanical Dimensions and Land Pattern
Same pin dimensions apply along the x axis and the y axis
PC Board Land Pattern for Rabbit 3000 128-pin Lqfp
C D E F G H J K L M
Ball Grid Array Package
Ball and Land Size Dimensions
Design Considerations All dimensions in mm
Key Feature Recommendation
Nominal Ball Tolerance Ball Pitch Nominal Land
BGA Package Outline
Rabbit Pin Descriptions
Rabbit Pin Descriptions
Pin Pin Group Pin Name Direction Function Numbers
Lqfp Tfbga
Vddcore
Bus Timing
Bus Timing Read and Write
Description of Pins with Alternate Functions
Pins With Alternate Functions
PF7 PWM3 AQD2A
Parallel Port x Alternate Functions
Parallel Port x Alternate Functions Control Bits
DC Characteristics
3 Volt DC Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Maximum Rating
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
I/O Buffer Sourcing and Sinking Limit
Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Rabbit Internal I/O Registers
Rabbit 3000 Peripherals and Interrupt Service Vectors
On-Chip Peripheral ISR Starting Address
Register Name Mnemonic Address Reset
Default Values for all the Peripheral Control Registers
Rabbit Internal I/O Registers
Grev
PEB7R
PWM0R
Tbcsr
Sdar
Global ROM Configuration Register
Global RAM Configuration Register
Miscellaneous Functions
Processor Identification
Rabbit Oscillators and Clocks
Global CPU Register
Global Revision Register
Gcpu
Rabbit
Global Control/Status Register
Clock Select Field of Gcsr
Global Control/Status Register
Gcsr
Recommended Delays Set In Gcdr for Clock Doubler
Clock Doubler
Global Clock Double Register
Gcdr
Effect of Clock Doubler
User’s Manual
Clock Spectrum Spreader
Reduction in Peak Spectral Strength from Spectrum Spreader
Chip Select Options for Low Power
Global Power Save Control Register
Address = 0x0D
Short Chip Select Memory Read
Output Pins CLK, STATUS, /WDTOUT, /BUFEN
Global Output Control Register Gocr = 0x0E
Time/Date Clock Real-Time Clock
10. Real-Time Clock RTCxR Data Registers
11. Real-Time Clock Control Register Rtccr adr =
Watchdog Timer
12. Watchdog Timer Control Register Wdtcr adr =
13. Watchdog Timer Test Register Wdttr adr =
System Reset
14. Rabbit 3000 Reset Sequence and State of I/O Pins
Pin Name Direction Reset Low Post-Reset† Recognized by CPU
Rabbit Interrupt Structure
15. Interrupts-Priority and Action to Clear Requests
External Interrupts
External Interrupt Line Logic
16. Control Registers for External Interrupts
Interrupt Vectors INT0 EIR,0x00/INT1 EIR,0x08
Reg Name Reg Address Bits 7,6 Bits 5,4 Bits 3,2 Bits 1,0
Bootstrap Operation
102 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Pulse Width Modulator
Pulse Width LSBs 1st 2nd 3rd 4th
17. PWM LSB x Register
18. PWM MSB x Register
Input Capture
106 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Input Capture Control/Status Register
19. Input Capture Control/Status Register
Iccsr
20. Input Capture Control Register
21. Input Capture Trigger x Register
Iccr
ICT1R
23. Input Capture LSB x Register
22. Input Capture Source x Register
24. Input Capture MSB x Register
Quadrature Decoder
Rejected
Quad Decode Control/Status Register
25. Quadrature Decoder Control/Status Register
Qdcsr
26. Quadrature Decoder Control Register
27. Quadrature Decoder Count Register
Qdcr
QDC1R
114 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Memory Interface and Mapping
Interface for Static Memory Chips
Data Lines Static Address Lines Memory Flash
Rabbit
RAM
Memory-Mapping Unit
Memory Mapping Overview
Processor Memory Mapping Unit Interface Memory Chips
64K
Segment Registers
Segment Size Register
Segment Register Function
Memory Interface Unit
Memory Bank Control Registers
Memory Bank Control Register x MBxCR = 0x014 +
Optional A16, A19 Inversions by Segment /CS1 Enable
MMU Instruction/Data Register Mmidr =
MMU Instruction/Data Register
Mmidr
Memory Timing Control Register MTCR, adr =
MMU Expanded Code Register
Mecr
Memory Timing Control Register
Allocation of Extended Code and Data
Breakpoint/Debug Control Register BDCR, adr = 0x01C
Breakpoint/Debug Control Register
Bdcr
Instruction and Data Space Support
RAM
Use of Physical Memory Separate I & D Space Model
How the Compiler Compiles to Memory
128 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Parallel Ports
Parallel Port a Registers
Parallel Port a
Parallel Port a Data Register Bit Functions
Parallel Port B Registers
Parallel Port B
Parallel Port B Register Bit Functions
Parallel Port C Registers
Parallel Port C
Parallel Port C Register Bit Functions
Parallel Port D
Parallel Port D Registers
PD7
Parallel Port D Control Register adr =
Parallel Port D Register functions
Bits 7 Bits 5 Bits 3 Bits 1
136 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Parallel Port E
PE0
10. Parallel Port E Registers
11. Parallel Port E Register functions
12. Parallel Port E Control Register adr =
13. Parallel Port F Registers
Parallel Port F
14. Parallel Port F Register Functions
Using Parallel Port a and Parallel Port F
15. Parallel Port F Control Register adr = 0x03C
Summary Parallel Port a Parallel Port F
16. Parallel Port G Registers
Parallel Port G
17. Parallel Port G Data Register Functions
Parallel Port G Control Register adr= 0x04C
10. I/O Bank Control Registers
Write data Write strobe T1 Tw T2
Read data Read strobe Chip select strobe
External I/O Timing with 1 wait state
I/O Bank x Control Register
External I/O Register Address Range and Pin Mapping
Control Register Port E Address Pin A1513 Range
148 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Timers
Timer a
Reload Register Operation
Timer a I/O Registers
Timer a I/O Registers
Timer a Control and Status Register
Timer a Capabilities
Tacsr
User’s Manual 153
Timer a Control Register
Timer a Prescale Register
Tacr
Tapr
Practical Use of Timer a
Timer B Registers
Timer B
Register Name Mnemonic Reset Address
Timer B Control and Status Register
Timer B Control Register
Tbcsr
Tbcr
Timer B Count MSB x Registers
10. Timer B Count LSB x Registers
11. Timer B Count MSB Register
12. Timer B Count LSB Register
Using Timer B
160 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Serial Port Signal Name Function
Serial Port Signals
Rabbit Serial Ports
Clka
User’s Manual 163
Signals Shown at Microprocessor Tx Pin
Serial Port Register Layout
User’s Manual 165
Serial Port Registers
Serial Port a Registers
Serial Port B Registers
Serial Port C Registers
Serial Port E Registers
Serial Port D Registers
Serial Port F Registers
Data Register All Ports
Address Register All Ports
10. Long Stop Register All Ports
11. Status Register Asynchronous Mode Only All Ports
Bits Value Description Clocked serial mode only
12. Status Register Clocked Serial Ports A-D only
13. Status Register Hdlc Mode Ports E and F only
Bits Value Description Hdlc mode only
Sacr
14. Serial Port Control Register Ports a and B
Sbcr
15. Serial Port Control Register Ports C and D
Sccr
Address = 0xE4
Sdcr
16. Serial Port Control Register Ports E and F
Secr
Address = 0xCC
Sfcr
17. Extended Register Asynchronous Mode All Ports
18. Extended Register Clocked Serial Mode Ports A-D only
19. Extended Register Hdlc Mode Ports E and F only
Serial Port Interrupt
Transmitter IRQ
Transmit Serial Data Timing
Receive Serial Data Timing
Serial Port Synchronization
Clock Polarities Supported in Clocked Serial Mode
Clocked Serial Ports
User’s Manual 183
184 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Clocked Serial Timing With Internal Clock
Clocked Serial Timing
Clocked Serial Timing with External Clock
Valid
Synchronous Communications on Ports E and F
Last Byte Bit Pattern Valid Data Hits
User’s Manual 189
190 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
User’s Manual 191
Serial Port Software Suggestions
Push AF IOI LD A,SCSR
Controlling an RS-485 Driver and Receiver
Transmitting Dummy Characters
Using a Serial Port to Generate a Periodic Interrupt
Transmitting and Detecting a Break
Parity, Extra Stop Bits with 7-Data-Bit Characters
Parity, Extra Stop Bits with 8-Data-Bit Characters
Stop bit Start bit Data bits 9th bit low
Stop bit
Rabbit-Only Master/Slave Protocol
Supporting 9th Bit Communication Protocols
Data Framing/Modbus
User’s Manual 197
198 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Rabbit Slave Port
SRD SCS
Slave Port Read Cycle
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum
Following table explains the parameters used in Figure
Slaveattn PB7
Typical Connection Slave Rabbit to Master Rabbit
Hardware Design of Slave Port Interconnection
Slave Port Registers
Slave Port Registers
Register Mnemonic Internal Address External Address
Slave Port Control Register Spcr adr =
Bit Bits 6,5 Bit 3,2 Bits 1,0 Write Only Read Only
Slave Applications
Applications and Communications Protocols for Slaves
Slave Port Status Register Spsr adr =
Master-Slave Messaging Protocol
208 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Rabbit 3000 Clocks
Rabbit 3000 Main Oscillator Circuit
Low-Power Design
EMI Control
Power Supply Connections and Board Layout
Using the Clock Spectrum Spreader
Spread Spectrum Enable/Disable Register
Spread Spectrum Mode Select
GCM0R
GCM1R
214 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
AC Timing Specifications
Memory Access Time
Access Enable Access MHz
Memory Requirements at 3.3 V, -40C to +85C, Adr Bus 60 pF
VDD
Data and Clock Delays VDD ±10%, Temp, -40C-+85C maximum
Normal Strong 30 pF 60 pF 90 pF No dbl/dbl
CSx
Memory Write Time Delays
Memory Read Time Delays
Time Delay Output Capacitance 30 pF 60 pF 90 pF
CLK A190 CSx WEx D70
Example
Clock Doubler Max-Min Clock Low Times
222 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
16.2 I/O Access Time
Bufen
I/O Read Time Delays
I/O Write Time Delays
Further Discussion of Bus and Clock Timing
Clock Doubler and Memory Timing
Maximum Clock Speeds
Maximum Clock Speeds at 3.3 V Preliminary
Conditions Commercial Ratings Industrial Ratings
Period Frequency
External Oscillator Buffer
Power and Current Consumption
User’s Manual 229
Rabbit 3000 System Current vs. Frequency at 3.3
11. Sleepy Mode Current Consumption
Current Consumption Mechanisms
Sleepy Mode Current Consumption
Memory Current Consumption
Battery-Backed Clock Current Consumption
Current is negligible for V 1.14
Reduced-Power External Main Oscillator
Voltage Current incl built-in buffer
Bios
Rabbit Bios and Virtual Driver
Bios Services
Bios Assumptions
Watchdog Timer Support
Virtual Driver
Periodic Interrupt
User’s Manual 239
240 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Power Management Support
Other Rabbit Software
Using Library Functions
Using Assembly Language
Reading and Writing I/O Registers
Shadow Registers
Updating Shadow Registers
Interrupt While Updating Registers
Atomic Instruction
Write-only Registers Without Shadow Registers
Timer and Clock Usage
Non-atomic Instructions
Format of the structure used is the following
246 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Rabbit Instructions
Summary
Spreadsheet Conventions
Flag Description
Symbols
Rabbit Z180 Meaning
Load Immediate Data
Load & Store to Immediate Address
19.3 8-bit Indexed Load and Store
19.4 16-bit Indexed Loads and Stores
19.5 16-bit Load and Store 20-bit Address
Register to Register Moves
Stack Manipulation Instructions
Exchange Instructions
19.9 16-bit Arithmetic and Logical Ops
19.10 8-bit Arithmetic and Logical Ops
ADD A,HL
19.11 8-bit Bit Set, Reset and Test
19.12 8-bit Increment and Decrement
19.13 8-bit Fast a Register Operations
19.14 8-bit Shifts and Rotates
Instruction Prefixes
Block Move Instructions
Control Instructions Jumps and Calls
Miscellaneous Instructions
Privileged Instructions
Following instructions are privileged
Differences Rabbit VS. Z80/Z180 Instructions
Z80/Z180 Instructions Dropped Rabbit Instructions to Use
IOI and IOE I Column Symbol Key
Flag Register Key
Rabbit Z180 Meaning
Z V C
EX AF,AF
LD A,BC
LDP HL,IX
RRA
268 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Appendix A. the Rabbit Programming Port
Programming Port PIN Assignments
Use of the Programming Port as a Diagnostic/Setup Port
Alternate Programming Port
Suggested Rabbit Crystal Frequencies
Non-Stock Crystals
Appendix B. Rabbit 3000 Revisions
274 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
User’s Manual 275
Discussion of Fixes and Improvements
Table B-1. Summary of Rabbit 3000 Improvements and Fixes
Rabbit Description 3000 3000A
IL1T/IZ1T IL2T/IZ2T
Table B-2. Reset State of New Rabbit 3000A I/O Registers
Rabbit Internal I/O Registers
Iuer
Rabbit Register Name Mnemonic 3000 3000A Address Reset
Peripheral and ISR Address
On-Chip Peripheral Address Range ISR Starting Address
User’s Manual 281
Revision-Level ID Register
Table B-5. Rabbit 3000 Revision Identification Information
Processor Revision Package
Gcpu Grev
System/User Mode
Memory Protection
Table B-6. Write Protect Control Register
Write Protect Control Register
Wpcr
Write Protect Low Register
Table B-7. Write Protect Low Register
Wplr
Table B-8. Write Protect High Register
Table B-9. Write Protect Segment x Register
Wphr
Wpsar
Table B-10. Write Protect Segment x Low Register
Write Protect Segment x Low Register
Wpsalr
Wpsblr
Table B-11. Write Protect Segment x High Register
Write Protect Segment x High Register
Wpsahr
Wpsbhr
Stack Protection
Figure B-2. Simple Stack Protection Layout
Table B-13. Stack Low Limit Register
Table B-12. Stack Limit Control Register
Table B-14. Stack High Limit Register
RAM Segment Relocation
Table B-15. RAM Segment Register
RAM Segment Register
Ramsr
Secondary Watchdog Timer
Table B-16. Watchdog Timer Control Register-Updated
Table B-17. Secondary Watchdog Timer Register
Wdtcr
New Opcodes
Table B-18. New Rabbit 3000 Opcodes
Instruction Bytes Clks Operation
New UMA/UMS Opcodes
Table B-19. Rabbit 3000 Revision Block Copy Opcode Effects
New Block Copy Opcodes
Source Destination
IOI/IOE
Expanded I/O Memory Addressing
Table B-20. MMU Instruction/Data Register
External I/O Improvements
Table B-21 Bank x Control Register
Short Chip Select Timing for Writes
Table B-22. Global Power Save Control Register
Address = 0x000D
Table B-23. Global Control/Status Register
Clock Select and Power Save Modes
Table B-24. Clock Select Field of Gcsr
Short Chip Select Timing
Figure B-3. Short Chip Select Timing CLK/8, Read Operation
Figure B-4. Short Chip Select Timing CLK/6, Read Operation
Figure B-6. Short Chip Select Timing CLK/2, Read Operation
Figure B-7. Short Chip Select Timing 2 kHz, Read Operation
Figure B-9. Short Chip Select Timing 8 kHz, Read Operation
Figure B-11. Short Chip Select Timing 32 kHz, Read Operation
Figure B-12. Short Chip Select Timing CLK/8, Write Operation
Figure B-13. Short Chip Select Timing CLK/6, Write Operation
Figure B-15. Short Chip Select Timing CLK/2, Write Operation
Figure B-16. Short Chip Select Timing 2 kHz, Write Operation
Figure B-18. Short Chip Select Timing 8 kHz, Write Operation
310 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
Pulse Width Modulator Improvements
Figure B-21. PWM Interrupt and Output Timing
Table B-25. PWM LSB 0 Register
Table B-26. PWM LSB 1 Register
PWM LSB 0 Register
PWM LSB 1 Register
Address = 0x008C
Table B-27. PWM LSB 2 and 3 Registers
Address = 0x008E
Quadrature Decoder Improvements
Table B-28. Quadrature Decoder Control Register
Table B-29. Quadrature Decoder Count High Register
QDC1HR
User’s Manual 315
Pins with Alternate Functions
Serial Ports E/F
System Mode User Mode
Appendix C. SYSTEM/USER Mode
Table C-1. Differences Between System and User Modes
Table C-2. New System/User Mode Opcodes
System/User Mode Opcodes
Instruction Bytes Clk Operation Priv
System/User Mode Registers
Table C-3. System/User Mode I/O Registers
Table C-4. I/O Addresses Inaccessible in User Mode
Register Name Mnemonic Address
Figure C-1. Interrupt Handing in System/User Mode
Interrupts
Peripheral Interrupt Prioritization
Table C-5. Interrupts-Priority and Action to Clear Requests
Using the System/User Mode
Memory Protection Only
Mixed System/User Mode Operation
Figure C-3. System/User Mode Setup for Mixed Operation
Figure C-4. System/User Mode Setup for Operating System
Complete Operating System
Appendix D. Rabbit 3000A Internal I/O Registers
Table D-1 Rabbit 3000A Internal I/O Registers
Table D-1. Rabbit 3000A Internal I/O Registers
0x03C0 00000000 Serial Port E User Enable Register
0x006A Xxxxxxxx Port D Bit 3 Register
0x0082 00000000 Bank 3 Control Register
0x0098 Xx000000 Interrupt 1 Control Register
0x00D1 Xxxxxxxx Serial Port B Long Stop Register
334 Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor
User’s Manual 335
Page
Index
Numerics
Memory A16, A19 inversions /CS1
PWL2R, PWL3R
200