MASTER-K 120S series
Safety Instructions
Design Precautions
Not doing so could cause a malfunction, failure or drop
Poor connection could cause an input or output failure
Not doing so could result in erroneous operation
Such debris could cause fire, damage, or erroneous operation
Not doing so can cause a malfunction
Doing so could cause electric shock or erroneous operation
Not doing so could cause poisonous pollution or explosion
Revision History
Contents
Power Supply / CPU
Communication I/F Module ················· 4
Input and Output Modules
Usage of Various Functions
100
104
Installation and Wiring
Communication Function
Maintenance
Troubleshooting
General
Guide to Use This Manual
Features
Terminology
Kglwin
FAM
RTC
Output Contact
Overall Configuration
Basic system
Expansion
G7L-CUEB, G7L-CUEC
System Configuration Cnet I/F system
Communications system
MASTER-K120S
MASTER-K120SMASTER-K120S
1n Communications system
MASTER-K120S G7L-CUEB
RS-232C ⇔ RS-422 Converter
G7L-CUEC
Product Functional Model
Product Functional Block
Main Unit
CPU
Main Unit Standard type
Main Unit Economic type
Expansion Modules
General Specifications
General Specifications
Main Unit
PWR LED
RUN LED
LED
1 60-points main unit Standard
Name Description
2 40-points main unit Standard
3 30-points main unit Standard
4 20-points main unit Standard
5 30-points main unit Economic
7 14-points main unit Economic
Names of Parts 6 20-points main unit Economic
8 10-points main unit Economic
1 20points I/O Module
Expansion I/O Module
2 10points I/O Module
Names of Parts 3 8points I/O Module
Special Module
1 A/D·D/A Combination Module
Names of Parts 2 D/A Conversion Module
G7F-DA2I
Names of Parts Analog timer Module
RTD Input Module
Cnet I/F Module
Communication I/F Module
Fnet I/F Module
Names of Parts Pnet I/F Module
Option Module
DeviceNet I/F Module
Power Supply Specifications
Standard Type
Economic Type
DR/DRT/DT60U
CPU Specifications
Items Specifications Remarks
D0000 ~ D4999 Data register Operation modes
RUN, STOP, PAUSE, Debug
Items Specifications
JOG
K7M-DR10UE K7M-DR14UE K7M-DR20UE K7M-DR30UE
Power Supply / CPU Economic Type
RUN, STOP, Pause
Modbus protocol support RS-232C 1port Cnet I/F Function
Remarks Dedicated protocol support
User defined protocol support RS-485 1 port
Operation Processing Method
Operation Processing
Cyclic operation
Operation Processing at Momentary Power Failure Occurrence
Momentary power failure within 10 ms
Momentary power failure exceeding 10 ms
Interrupt operation method
Power Supply / CPU Scan Time
Scan Watchdog Timer
Setting range of watchdog 10 ~ 6,000msunit 10ms
Expression for scan time
On delay timer
Power Supply / CPU Timer Processing
Off delay timer
Integral timer
Monostable timer
Retriggerable timer
Power Supply / CPU Counter Processing
Up counter CTU
Down counter CTD
Up-down counter
Ring counter
Maximum counting speed
OFF
T1 + T2
Program
Program Execution Procedure
Classifications of Program
Interrupt Programs
Scan program
Interrupt program
Usage of interrupt program
Process driven interrupt
Parameter setting Time driven interrupt
HSC driven interrupt
Error Classification
Error Handling
Operation mode at error occurrence
Power Supply / CPU
RUN Mode
Processing when the operation mode is changed
Operation processing contents
Operation Modes
Power Supply / CPU Stop mode
Pause mode
Processing when the operation mode changes
Debug modeStandard type only
Operation Mode Change
Operation mode change methods
Debug operation conditions
Operation method
Mode change Remote operation
Functions
Self-diagnosis
Power Supply / CPU 2 I/O Force On/Off function
Forced I/O setting method
Power Supply / CPU
Special data register for forced I/O
Force on/ off Processing timing and method
Power Supply / CPU Direct I/O Operation function
System error history
Special data register for error history
Clear error data
Memory Configuration
I/O Address Allocation
O No. allocation method
Built-in Cnet Selection Switch
ROM Mode
Structure
Usage
Power Supply / CPU
External Memory Module
Installation connector
Saving the user’s program on the external memory module
Run the PLC with a program of external memory module
RTC Module
Read RTC data
Read RTC data from Kglwin
Following message box will be displayed
Write RTC data
Date expression
Number Date Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday
Saturday
Input and Output Specification
Input / Output Specifications
Opening/shutting of electric current
Digital Input Specification
Specification
Circuit diagram
Main unit
Input wiring
DC24VDC24V
Example of external devices
Current
PNP
Voltage
Input and Output Specification Expansion Module
Specifications
Model Expansion Module Specification
It’s the same with the one for the main unit
Main unit Relay Output
Digital Output Specification
K7M-DRT40U
Circuit
Economic type Model Main Unit Specifications
Internal Circuit Relay
Output wiring
DC5V DC24V
AC110/220V
DC24V DC24V
Model Main Unit Specifications
K7M-DRT/DT20U K7M-DRT/DT30U K7M-DRT/DT40U K7M-DRT/DT60U
P40,P41 24V Internal Circuit
P42,P43 Internal Circuit 24V
DC12V/24V
… …
It’s the same with the output circuit of the main unit
AC110/220V DC5V/24V AC110/220V
DC12/24V
Model Expansion Module Specifications G7E-TR10A
Refer to 7.2 ‘Special Functions’ for the special modules
Performance Specifications
Input specification
Built-in Functions
High-speed counter function
Names of wiring terminals
Input pulse Preset input
COM0
Input Common Input common terminal
Wiring instructions
External interface circuit
Wiring example
Pulse Generator
Voltage output pulse generator
Open collector output pulse generator
InstructionHSCST
Hscast
High speed counter Available device
Flag Instruction
Parameter Setting
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions
Programming example
Remark
Using method
Usage of Various Functions Pulse Catch Function
Usage
Minimum input pulse width
Remark
Usage of Various Functions Input Filter Function
External input signal Scan program
Usage of Various Functions External Interrupt Function
Minimum processing time
Function
For the details , refer to Kglwin manual
Introduction
Manipulation Value
Kp is too large
MV = KpTi Edt
System response when a long integration time given
MV = Kp ⋅ Td dEdt
Example of integral windup
Perform the auto tuning operation
Where, h sampling period
PID8
Perform the PID operation
Usage of Various Functions
ENP ENI END
Usage of Various Functions
DigitalOutput = Temp.⋅10 +
Tse +1
Instruction
PID8
PID Control Instruction Available device
Flag
PID Auto Tuning Available device
PID8AT
KGL-WIN
Program Example
TPR
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions
Error code list
D4980
Performance specification
Usage of Various Functions 1 A/D·D/A Combination module
G7F-ADHA G7F-ADHB
Voltage DC 0 ∼10V
Names of parts and functions
Explain about names of parts and functions G7F-ADHA
① RUN LED
Voltage Input Current Input
G7F-ADHB
Right current input
Left voltage input
Analog output terminal Voltage output Current output
4000
Wiring
O converstion characteristics
Analog input characteristics Voltage input
Analog output characteristics Voltage output
Program example
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions 2 A/D Conversion module
Remark
① RUN LED
Be sure to use two-core twisted shield wire
Analog/Digital conversion characteristics
Program example
Program
Usage of Various Functions 3 D/A Conversion module
G7F-DA2I G7F-DA2V
③ ①
Parameter setting
Scaling function
Digital/Analog conversion characteristics
G7F-DA2I ~20mA output
Program example
Usage of Various Functions Analog timer
Name Contents Indicate the operating status the G7F-AT2A
Off DC 5V power off or the G7F-AT2A module fault
On normal operating
Usage of Various Functions
Name Contents
Explain about names of parts and functions
Parameter setting Digital conversion value register
Error code D4880 ∼D4885
BD bC bB BA b9 b8 b7 b6 B5 b4 b3 b2 B1 b0 D4880
CH1 CH0
Temperature conversion characteristics
Digital conversion value
4000 2000
6000
No wiring Shield wire
Type Wire
Burn-out detection function
Wire resistance ≤10 Ω
RTD input module
P0000
P0040 ~ P004F
Main unit input contact P000 ~ P023
Items Specification
Specification
Positioning FunctionDRT/DT type only
Output SpecificationP40, P41
Names of wiring terminal
Internal circuit and wiring example
COM1
Parameter setting
Setting Incremental End Single 000 100
Usage of Various Functions Positioning function
Positioning function
Speed Control Uniform Speed Operation
Please refer to the ‘7.3.4 Instruction’ for details
Operation pattern
Operation methods are as follows Remark
Step No. can be assigned within 1 ~ Items of parameter
Absolute End Single
Operation Mode End Operation
Start command Posist
Example End operation Speed
Absolute End Single 10,000 50,000 20,000 30,000 40,000
Keep Operation
Absolute Keep Single 10,000 50,000 20,000 End 30,000 40,000
Continuous Operation
Absolute Continuous Single 10,000 50,000 End 20,000
Operation Method Repeat Operation
Positioning start
Positioning stop
Return to OriginPOSORG Rising edge ↑
Origin Detection when Approximate origin turns off
Origin return method
This is the method using the approximate origin signal only
Origin Detection by approximate origin
Speed Override CommandPOSSOR Rising edge ↑
JOG Operation Posjog Level input
External Input Stroke High/Low Limit
Point
Error and Output Prohibition
Positioning parameter
Bias Speed
Backlash Compensation Amount
Speed Limit
Origin return parameter
② Origin return-Low speed
Dwell Time
DOG
Positioning parameter
Operation Mode is divided into following three kinds
Usage of Various Functions
Usage of Various Functions Instructions
Positioning Indirect startPOSIST
Posist
Positioning Indirect Start Instruction Available device
JOG OperationPOSJOG
Positioning Indirect Start Available device Instruction
Posctr
Positioning Control InstructionPOSCTR
Control instruction designation
Current position preset Posprs
Current position preset Instruction Available device
Preset value designation
Posprs
PWM
PWM output PWM
SV1 SV2
Posvel
Speed control operation Posvel
Speed control operation Instruction Available device
Speed override Possor
Possor
Speed override instruction Instruction Available device
Ch. for speed override0~1 SV Speed 5 ~ 100,000pps
Positioning direct startPOSDST
Posdst
Posorg
Return to originPOSORG
Return to origin Instruction Available device
Flag list
Usage of Various Functions Flag list and Error codes
Device Function Description
101
Error Condition
Error code
Corrective action Code
103
H48
Wiring with stepping motor driverDC
Wiring with stepping motor driver DC
Wiring with servo motor driverMR-J2/J2S-A
K7M-DRT**U
Wiring with Servo motor driverFDA-5000 AC Servo Driver
SSR
Communication Functions
Dedicated Protocol Communication
Introduction
Communication Functions System configuration method
Connecting system configuration link between MASTER-K’s
Pmulgis
PMU
Pin assignment and direction Pin no Signal
Communication Functions Frame Structure
Base Format
EOT BCC
Sequence of command frame
ETX BCC
Communication Functions List of commands
Communication Functions Data type
PX000, %MX000, %LX000, %KX000, %CX000, %TX000, %FX000 Byte
Communication Functions Execution of commands
Individual reading of deviceRrSS
Response format ACK response
Response format NAK response
Continuous readingRrSB of device
Wordw
EOT
Blocksetting can be repeated up to max blocks Explanation
Individual writing of deviceWwSS
NAK
H00FF EOT BCC
Continuous writing of deviceWwSB
H10
Format name Header Station
Monitor registerX##
RSS
Blockmax blocks ② Continuous reading of device
RSB
H06 H3130 H5878 H3039 H03
RSS
Monitor executionY##
Command Registration Error code Tail
Reading PLC StatusRST
Mode Bit Local Remote Connection
Pause Debug
3041 5272 5354 31313332
G7E-DR10A
Parameter setting
Cuec
Communication Functions
Flag related with operating status
Normal
RUN Pause Debug
Example
Protocol Mode
④ Set parameters as the following table Communication Method
Communication Functions
Communication Functions
Communication Functions Error code
Error code Error type Error condition and causes Treatment
Setting Communications Parameter
Parameter Setting
User Defined Protocol Communication
Setting frame
VTH0B
Communication Functions
FFH0C CRH0D SOH0E
XOR
SUM
MUL
Communication Functions
Type setting
Kinds Value of sum check Last transmitting frame
Ascii Type Hex Type 05 31 32 33 34 04 30
Ascii Type Hex Type 05 31 32 33 34 04 36
Communication Functions
Communication Functions Instruction
User defined communication instructionSNDCOM
Example of program
Sndcom
Example of Usage
Communication Functions
Communication Functions
Communication Functions
Setting and program of slave station
Communication Functions
Communication Functions
Communication Functions
Communication Functions
Basic Specification
Ascii mode
RTU mode
Modbus Protocol Communication
Address area
Function code area
Data area
LRC Check/CRC Check area
Size of using data
Function code types and memory mapping
Modbus addressing rules
H5000 Area Areacurrent value area H6000
Map of wiring
Parameters Setting
Setting communication parameter
PLC
Modbus communication instructionMODCOM
Communication Functions Instruction and example
Modcom
Remark
Example program
Coil Status
Input
Communication Functions
Sending Data
No Protocol Communication
Receiving Data
Parameter setting
Error flag turns on, when designating area is over
Communication Functions Instructions
No protocol receiveDRCV
Drcv
No protocol sendDSND
Dsnd
Communication Functions Examples
Communication Parameter Setting
Program
Remote connection
Remote connection and communication I/F module
Remote connection by built-in Cnet I/F
Remote connection by modem
Remote connection by Fnet I/F module
Master Slave Wiring Example RS-422 I/F
Usage of G7L-CUEB
Usage of G7L-CUEC
OFF Must be off
Wiring Example RS-485 I/F
Usage of G7L-FUEA/RUEA
RDB SDA SDB SG
Master Slave
Usage of G7L-PBEA/DBEA
Installation
Installation Environment
Precautions during installing
Environment requirements
Power consumption block diagram of PLC systems
Power consumption of each part
Power Input Supply
Part
Handling Instructions
Main unit or Expansion Module handling instructions
Mounting instructions
OUT
Output part
COM OUT
100mm or more
Heat generating device
Installation and Wiring Connection of expansion module
Wiring
Power Supply Wiring
Power Main circuit Device
※ T1,T2 constant voltage transformer
Input and Output Devices Wiring
Input
Installation and Wiring Grounding
Cable Specifications for wiring
Daily Inspection
Maintenance and Inspection
LED ERR LED
Periodic Inspection
10-2
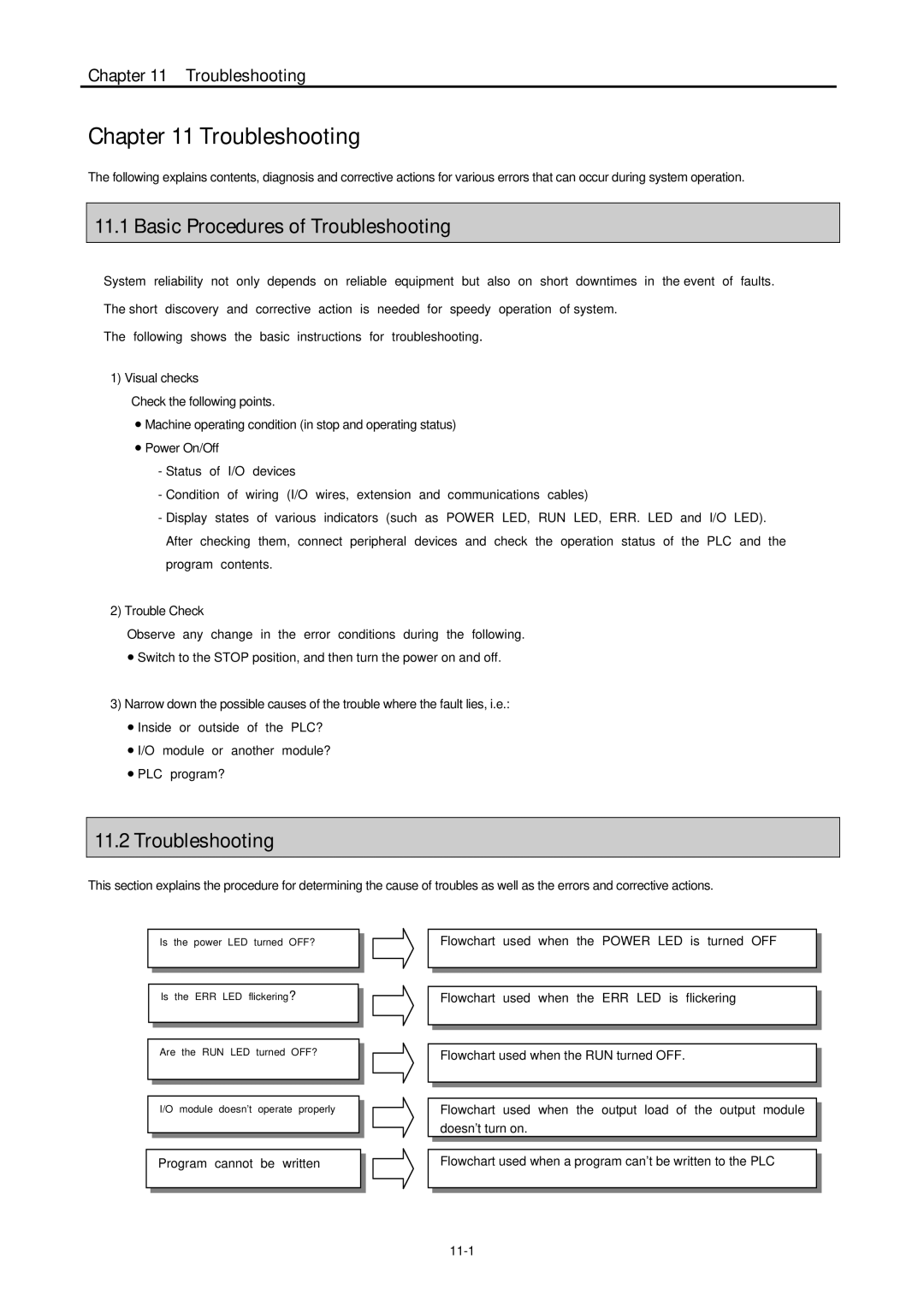
Basic Procedures of Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Yes
Kglwin
Contact the nearest service center
Turn the power unit off and on Is RUN LED off?
11-4
Measure the voltage of power supply in P40
11-5
11-6
11-7
Troubleshooting Questionnaire
Troubleshooting Examples
Input circuit troubles and corrective actions
Output circuit troubles and corrective actions
11-10
Transistor 1/3 to 1/5 rated current flow Destroyed
Surge current of 10 times or more when turned on
11-11
Error code List
11-12
Error CPU state Message Cause Corrective Actions Code
11-13
Appendix 1 System Definitions
Option
Editor option
Appendix 1 System Definitions
Basic Parameters
Special relay F
Appendix 2 Flag List
Always Off
Operation error flag
Operation error flag Latch
Overflow error flag
Relay Function F0040 to F005F
Internal relay M
Data relay D
App2-4
App2-5
App2-6
App2-7
Clock data Relay Description
App2-8
Extension module
Appendix 3 External Dimensions
Standard type 95 105 App3-1
Appendix 3 External Dimensions