INSTALLATION
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
To prevent dangerous electric shock, other equipment to which this engine driven welder supplies power must:
a)Be grounded to the frame of the welder using a grounded type plug.
b)Be double insulated.
WARNING
Do not ground the machine to a pipe that carries explo- sive or combustible material.
When this welder is mounted on a truck or trailer, its frame must be securely connected to the metal frame of the vehicle. When connected to premises wiring such as that in a home or shop, the welder frame must be connected to the system earth ground. See further connection instructions in the section entitled Standby Power Connections as well as the article on ground- ing in the latest U.S. National Electrical Code and the local code.
In general, if the machine is to be grounded, it should be connected with a #8 or larger copper wire to a solid earth ground such as a metal water pipe going into the ground for at least ten feet and having no insulated joints, or to the metal framework of a building which has been effectively grounded. The U.S. National Electrical Code lists a number of alternate means of grounding electrical equipment. A machine grounding
stud marked with the ![]() ground symbol is provided on the front of the welder.
ground symbol is provided on the front of the welder.
WELDING OUTPUT CABLES
With the engine off, connect the electrode and work cables to the output terminals. The welding process dictates the polarity of the electrode cable. These con- nections should be checked periodically and tightened with a wrench.
Table A.1 lists recommended cable sizes and lengths for rated current and duty cycle. Length refers to the distance from the welder to the work and back to the welder. Cable diameters are increased for long cable lengths to reduce voltage drops. Avoid coiling long cables on the machine when welding.
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
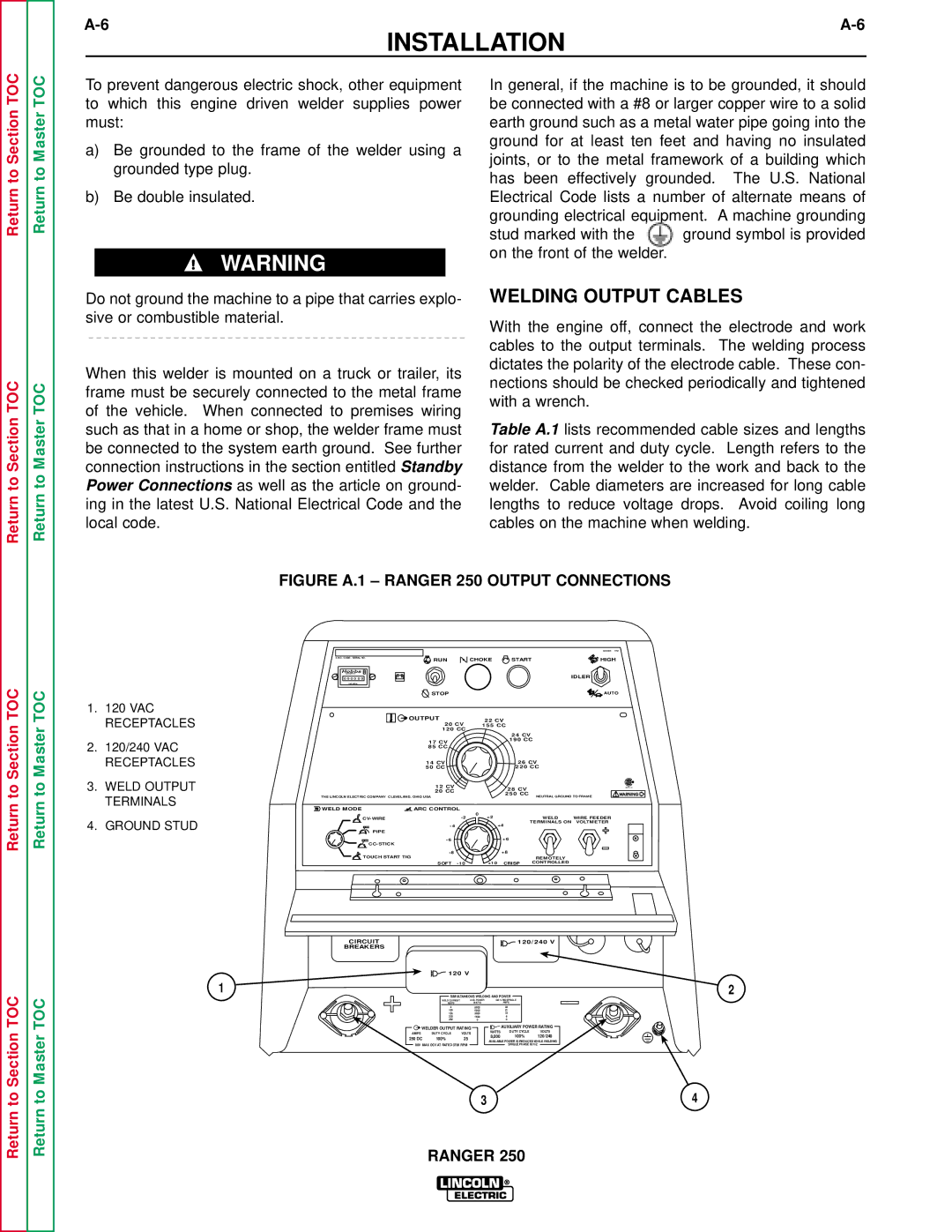
FIGURE A.1 – RANGER 250 OUTPUT CONNECTIONS
|
|
|
|
| G3668 VM |
| K NO.- CODE - SERIAL NO. | RUN | CHOKE | START | HIGH |
|
| ||||
| Hobbs |
|
|
|
|
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
|
|
| IDLER |
|
| STOP |
|
| AUTO |
1. 120 VAC |
|
|
|
|
|
RECEPTACLES |
| OUTPUT | 155 CC |
| |
|
| 20 CV | 22 CV |
| |
|
| 120 CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 24 CV |
|
2. 120/240 VAC |
| 17 CV |
| 190 CC |
|
|
|
|
| ||
| 85 CC |
|
|
| |
RECEPTACLES |
| 50 CC |
| 220 CC |
|
|
| 14 CV |
| 26 CV |
|
3. WELD OUTPUT |
| 20 CC |
| 28 CV |
|
|
| 12 CV |
|
|
|
TERMINALS | THE LINCOLN ELECTRIC COMPANY CLEVELAND, OHIO USA |
| 250 CC |
| |
| NEUTRAL GROUND TO FRAME | ||||
WELD MODE | ARC CONTROL |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
| 0 |
|
|
4. GROUND STUD | +2 | WELD | WIRE FEEDER | ||
PIPE |
|
| TERMINALS ON VOLTMETER | ||
| +4 |
| |||
|
| +6 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| +8 |
| |
| TOUCH START TIG |
| REMOTELY |
| |
|
| SOFT | +10 | CRISP CONTROLLED |
|
CIRCUIT |
|
|
| 120/240 V | ||
BREAKERS |
|
|
|
|
| |
| 120 V |
|
|
| ||
1 | SIMULTANEOUS WELDING AND POWER | 2 | ||||
| WELD CURRENT | AUX. POWER | 240 V. RECEPTACLE |
| ||
| AMPS | WATTS |
| AMPS |
| |
| 0 | 8000 |
| 33 |
| |
| 100 | 5000 |
| 21 |
| |
| 150 | 3000 |
| 13 |
| |
| 200 | 1500 |
| 6 |
| |
| 250 | 0 |
| 0 |
| |
WELDER OUTPUT RATING |
| AUXILIARY POWER RATING | ||||
AMPS | DUTY CYCLE | VOLTS | WATTS | DUTY CYCLE | VOLTS | |
250 DC | 100% | 25 | 8,000 | 100% | 120/240 | |
AVAILABLE POWER IS REDUCED WHILE WELDING | ||||||
|
|
| ||||
80V MAX OCV AT RATED 3700 RPM |
| SINGLE PHASE 60 HZ |
| |||
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 | |