Chapter 2 SRG50 overview 23
Local mode
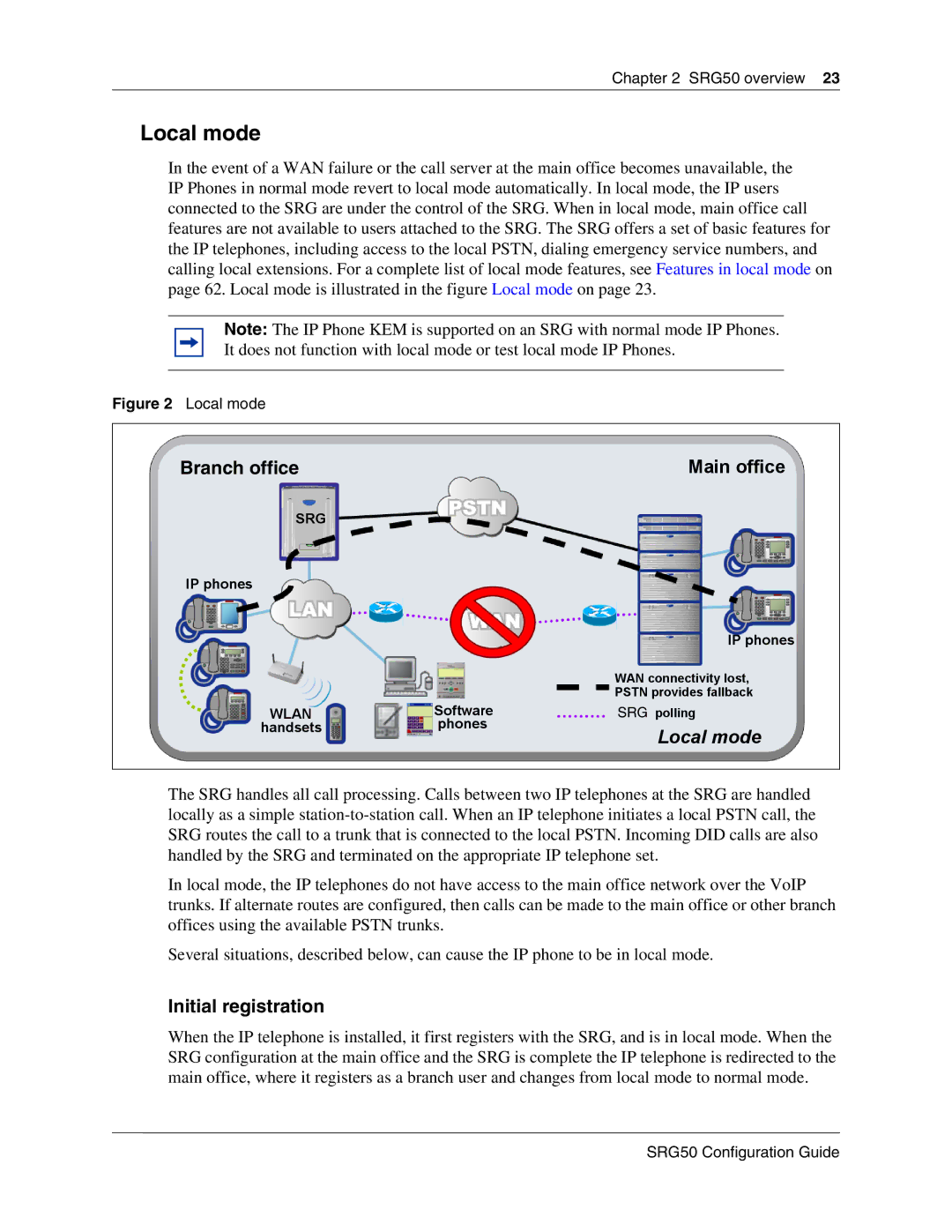
In the event of a WAN failure or the call server at the main office becomes unavailable, the IP Phones in normal mode revert to local mode automatically. In local mode, the IP users connected to the SRG are under the control of the SRG. When in local mode, main office call features are not available to users attached to the SRG. The SRG offers a set of basic features for the IP telephones, including access to the local PSTN, dialing emergency service numbers, and calling local extensions. For a complete list of local mode features, see Features in local mode on page 62. Local mode is illustrated in the figure Local mode on page 23.
Note: The IP Phone KEM is supported on an SRG with normal mode IP Phones. It does not function with local mode or test local mode IP Phones.
Figure 2 Local mode
Branch office | Main office |
SRG
IP phones
IP phones
|
| WAN connectivity lost, |
|
| PSTN provides fallback |
WLAN | Software | SRG polling |
handsets | phones | Local mode |
|
|
The SRG handles all call processing. Calls between two IP telephones at the SRG are handled locally as a simple
In local mode, the IP telephones do not have access to the main office network over the VoIP trunks. If alternate routes are configured, then calls can be made to the main office or other branch offices using the available PSTN trunks.
Several situations, described below, can cause the IP phone to be in local mode.
Initial registration
When the IP telephone is installed, it first registers with the SRG, and is in local mode. When the SRG configuration at the main office and the SRG is complete the IP telephone is redirected to the main office, where it registers as a branch user and changes from local mode to normal mode.