Management Guide
Page
TigerSwitch 10/100/1000 Management Guide
Page
Contents
Page
Iii
Page
Command Line Interface
Page
Vii
Viii
Contents
Page
Contents
Xii
Appendix B Troubleshooting
Appendix a Software Specifications
Glossary Index
Xiii
Xiv
Tables
Xvi
Xvii
Xviii
Xix
Figures
Figures
Xxi
Xxii
Feature Description
Key Features
Key Features
Introduction
Description of Software Features
Description of Software Features
Introduction
Description of Software Features
Function Parameter Default
System Defaults
System Defaults
Client Enabled
System Defaults Function Parameter
Sntp
Configuration Options
Connecting to the Switch
Required Connections
Initial Configuration
Console Connection
Basic Configuration
Remote Connections
Manual Configuration
Setting Passwords
Setting an IP Address
Dynamic Configuration
Enabling Snmp Management Access
Trap Receivers
Configuring Access for Snmp Version 3 Clients
Saving Configuration Settings
Managing System Files
Initial Configuration
Using the Web Interface
Configuring the Switch
Home
Navigating the Web Browser Interface
Panel Display
Configuration Options Action
Button
Revert Apply Help
System System Information
Main Menu
Main Menu Description
ACL
Configuration Allows ports to dynamically join trunks
116
STA
122
Class-of-service value
Current Table
131
Configuration Settings Igmp Filter/Throttling Trunk
Query Igmp Filter Configuration
Configuration Settings
152
183
Dhcp Snooping 186 Configuration
Cache
185
Field Attributes
Displaying System Information
CLI Specify the hostname, location and contact information
Displaying Switch Hardware/Software Versions
Main Board
Management Software
Switch Information
Web Click System, Switch Information
Displaying Bridge Extension Capabilities
Bridge Extension Configuration
Command Attributes
Setting the Switch’s IP Address
CLI Enter the following command
Manual IP Configuration
Dhcp IP Configuration
Using DHCP/BOOTP
Managing Firmware
Enabling Jumbo Frames
Copy Firmware
Downloading System Software from a Server
11 Deleting Files
Saving or Restoring Configuration Settings
12 Downloading Configuration Settings for Startup
Downloading Configuration Settings from a Server
13 Setting the Startup Configuration Settings
Console Port Settings
14 Console Port Settings
Telnet Settings
15 Enabling Telnet
Displaying Log Messages
Configuring Event Logging
Error resource exhausted
System Log Configuration
CLI This example shows the event message stored in RAM
Logging Levels
17 System Logs
Remote Log Configuration
18 Remote Logs
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
19 Enabling and Configuring Smtp
Renumbering the System
Resetting the System
Configuring Sntp
Setting the System Clock
23 Setting the System Clock
Setting the Time Zone
Simple Network Management Protocol
Setting Community Access Strings
Access Mode
Specifying Trap Managers and Trap Types
24 Configuring Snmp Community Strings
Enabling Snmp Agent Status
25 Configuring IP Trap Managers
CLI This example sets an SNMPv3 engine ID
Configuring SNMPv3 Management Access
Setting the Local Engine ID
CLI This example specifies a remote SNMPv3 engine ID
Configuring SNMPv3 Users
Specifying a Remote Engine ID
Configuring the Switch
29 Configuring SNMPv3 Users
30 Configuring Remote SNMPv3 Users
Configuring Remote SNMPv3 Users
Topology Change Timer immediately
Configuring SNMPv3 Groups
Supported Notification Messages
Subsequent to its election
Rmon Events
SNMPv2 Traps
PD Powered Device. This notification is
Private Traps SwPowerStatus 6.1.4.1.202.20.68.2.1.0.1
Mode PethPsePortPower 6.1.4.1.202.20.68.2.1.0.1
ChangeTrap SwIpFilterRejectTrap 6.1.4.1.202.20.68.2.1.0.1
31 Configuring SNMPv3 Groups
32 Configuring SNMPv3 Views
Setting SNMPv3 Views
Configuring User Accounts
User Authentication
33 Access Levels
Command Usage
Configuring Local/Remote Logon Authentication
Tacacs Settings
Radius Settings
34 Authentication Settings
User Authentication
Https System Support Web Browser Operating System
Configuring Https
Replacing the Default Secure-site Certificate
Configuring the Secure Shell
User Authentication
SSH server includes basic settings for authentication
Configuring the SSH Server
Generating the Host Key Pair
37 SSH Host-Key Settings
Configuring Port Security
38 Configuring Port Security
Configuring 802.1X Port Authentication
802.1X protocol provides client authentication
Displaying 802.1X Global Settings
CLI This example shows the default global setting for
Configuring 802.1X Global Settings
CLI This example enables 802.1X globally for the switch
Web Click Security, 802.1X, Information
Authorized
Configuring Port Settings for
41 802.1X Port Configuration
Consoleconfig#interface ethernet 1/2
Parameter Description
Displaying 802.1X Statistics
802.1X Statistics
CLI This example displays the 802.1X statistics for port
Access Control Lists
Configuring Access Control Lists
CLI This example creates a standard IP ACL named david
Setting the ACL Name and Type
Configuring an Extended IP ACL
Configuring a Standard IP ACL
Configuring the Switch
45 Configuring Extended IP ACLs
Configuring a MAC ACL
This switch supports ACLs for ingress filtering only
Binding a Port to an Access Control List
47 Configuring ACL Port Binding
Filtering IP Addresses for Management Access
48 Creating an IP Filter List
CLI This example allows Snmp access for a specific client
Port Configuration
Displaying Connection Status
Field Attributes Web
Basic Information
Configuration
Web Click Port, Port Information or Trunk Information
Current Status
Configuring Interface Connections
50 Port/Trunk Configuration
Creating Trunk Groups
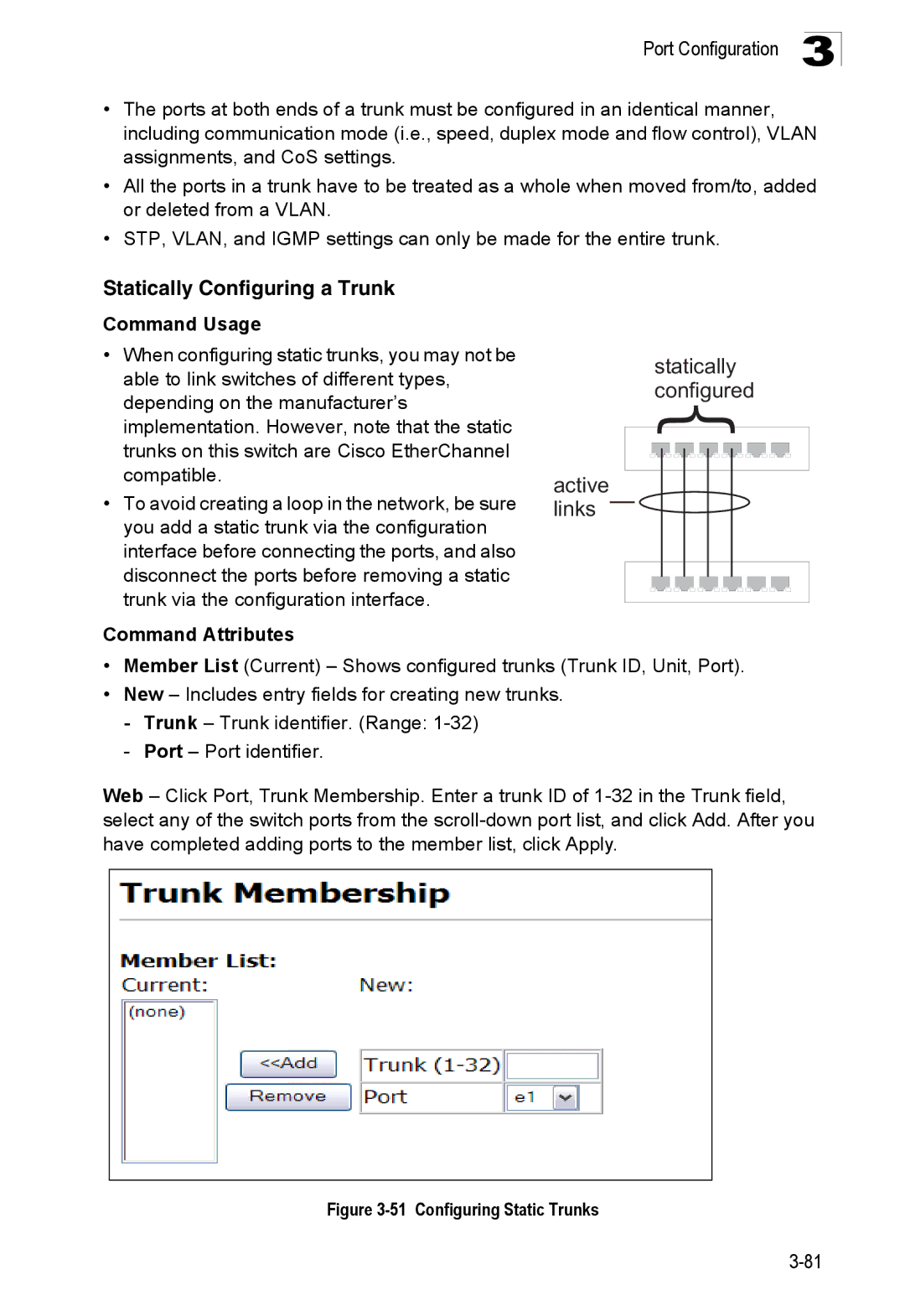
51 Configuring Static Trunks
Statically Configuring a Trunk
131
Enabling Lacp on Selected Ports
52 Lacp Trunk Configuration
Dynamically Creating a Port Channel
Configuring Lacp Parameters
53 Lacp Port Configuration
You can display statistics for Lacp protocol messages
Displaying Lacp Port Counters
Lacp Port Counters
Field Description
CLI The following example displays Lacp counters
54 Lacp Port Counters Information
Lacp Internal Configuration Information
Displaying Lacp Settings and Status for the Local Side
55 Lacp Port Internal Information
Lacp Neighbor Configuration Information Field Description
Displaying Lacp Settings and Status for the Remote Side
Setting Broadcast Storm Thresholds
57 Port Broadcast Control
58 Mirror Port Configuration
Configuring Port Mirroring
Rate Limit Configuration
Configuring Rate Limits
Showing Port Statistics
Etherlike Statistics
10 Port Statistics
Rmon Statistics Drop Events
Or alignment error Received Bytes
Resources Jabbers
Formed Oversize Frames
60 Port Statistics
CLI This example shows statistics for port
Address Table Settings
Setting Static Addresses
Displaying the Address Table
61 Configuring a Static Address Table
62 Configuring a Dynamic Address Table
CLI This example sets the aging time to 300 seconds
Spanning Tree Algorithm Configuration
Changing the Aging Time
Spanning Tree Algorithm Configuration
104
Displaying Global Settings
64 Displaying Spanning Tree Information
Global settings apply to the entire switch
Configuring Global Settings
Root Device Configuration
Basic Configuration of Global Settings
Configuration Settings for Mstp
Configuration Settings for Rstp
65 Configuring Spanning Tree
Displaying Interface Settings
112
CLI This example shows the STA attributes for port
66 Displaying Spanning Tree Port Information
Configuring Interface Settings
CLI This example sets STA attributes for port
67 Configuring Spanning Tree per Port
Configuring Multiple Spanning Trees
68 Configuring Multiple Spanning Trees
MST Instance ID Instance identifier to configure. Default
Displaying Interface Settings for Mstp
69 Displaying Mstp Interface Settings
Configuring Interface Settings for Mstp
121
CLI This example sets the Mstp attributes for port
Vlan Configuration
Ieee 802.1Q VLANs
Assigning Ports to VLANs
124
Forwarding Tagged/Untagged Frames
Enabling or Disabling Gvrp Global Setting
CLI This example enables Gvrp for the switch
Displaying Current VLANs
Command Attributes Web
Displaying Basic Vlan Information
73 Displaying Current VLANs Command Attributes CLI
175
Creating VLANs
CLI This example creates a new Vlan
Adding Static Members to VLANs Vlan Index
130
Adding Static Members to VLANs Port Index
75 Configuring a Vlan Static Table
Configuring Vlan Behavior for Interfaces
77 Configuring VLANs per Port
Configuring Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling
Layer 2 Flow for Packets Coming into a Tunnel Access Port
Layer 2 Flow for Packets Coming into a Tunnel Uplink Port
General Configuration Guidelines for QinQ
Configuration Limitations for QinQ
78 802.1Q Tunnel Status
Enabling QinQ Tunneling on the Switch
Adding an Interface to a QinQ Tunnel
CLI This example sets the switch to operate in QinQ mode
79 Tunnel Port Configuration
45-1
Enabling Private VLANs
Configuring Private VLANs
CLI This example enables private VLANs
Protocol VLANs
Configuring Uplink and Downlink Ports
Protocol Vlan Group Configuration
82 Protocol Vlan Configuration
Configuring Protocol Vlan Interfaces
Setting the Default Priority for Interfaces
Class of Service Configuration
Layer 2 Queue Settings
CLI This example assigns a default priority of 5 to port
Port Priority Configuration
Mapping CoS Values to Egress Queues
11 Mapping CoS Values to Egress Queues
Priority Level Traffic Type
12 CoS Priority Levels
Background
Spare
Enabling CoS
Selecting the Queue Mode
87 Queue Mode
Setting the Service Weight for Traffic Classes
Selecting IP Precedence/DSCP Priority
Layer 3/4 Priority Settings
Mapping Layer 3/4 Priorities to CoS Values
13 Mapping IP Precedence
Mapping IP Precedence
90 Mapping IP Precedence Priority Values
14 Mapping Dscp Priority Values
Mapping Dscp Priority
IP Dscp Value CoS Value
10, 12, 14 18, 20, 22 26, 28, 30, 32, 34 38, 40
92 IP Port Priority Status
Mapping IP Port Priority
93 IP Port Priority
Quality of Service
Class map is used for matching packets to a specified class
Configuring Quality of Service Parameters
Configuring a Class Map
Class Map
Class Configuration
Match Class Settings
94 Configuring Class Maps
Policy Map
Policy Configuration
Creating QoS Policies
Policy Options
Policy Rule Settings Class Settings
95 Configuring Policy Maps
Attaching a Policy Map to Ingress Queues
96 Service Policy Settings
Layer 2 Igmp Snooping and Query
Multicast Filtering
Configuring Igmp Snooping and Query Parameters
Enabling Igmp Immediate Leave
97 Igmp Configuration
98 Igmp Immediate Leave
Displaying Interfaces Attached to a Multicast Router
99 Displaying Multicast Router Port Information
Specifying Static Interfaces for a Multicast Router
100 Static Multicast Router Port Configuration
Displaying Port Members of Multicast Services
101 IP Multicast Registration Table
Assigning Ports to Multicast Services
102 Igmp Member Port Table
Igmp Filtering and Throttling
103 Enabling Igmp Filtering and Throttling
Enabling Igmp Filtering and Throttling
Configuring Igmp Filtering and Throttling for Interfaces
104 Igmp Filter and Throttling Port Configuration
Configuring Igmp Filter Profiles
105 Igmp Profile Configuration
Multicast Vlan Registration
General Configuration Guidelines for MVR
Configuring Global MVR Settings
Displaying MVR Interface Status
106 MVR Global Configuration
107 MVR Port Information
Web Click MVR, Port or Trunk Information
108 MVR Group IP Information
Displaying Port Members of Multicast Groups
MVR Vlan
Configuring MVR Interface Status
Assigning Static Multicast Groups to Interfaces
Web Click MVR, Port or Trunk Configuration
Configuring General DNS Service Parameters
Configuring Domain Name Service
111 DNS General Configuration
238
Configuring Static DNS Host to Address Entries
112 DNS Static Host Table
113 DNS Cache
Displaying the DNS Cache
Dhcp Snooping
Web Click Dhcp Snooping, Configuration
Dhcp Snooping Configuration
Dhcp Snooping Information Option Configuration
Dhcp Snooping Vlan Configuration
Enables Dhcp snooping on the specified Vlan
CLI This example first enables Dhcp Snooping for Vlan
Trust Status Enables or disables port as trusted
Dhcp Snooping Port Configuration
Dhcp Snooping Binding Information
117 Dhcp Snooping Port Configuration
Web Click Dhcp Snooping, Dhcp Snooping Binding Information
IP Source Guard Port Configuration
IP Source Guard
119 IP Source Guard Port Configuration
Static IP Source Guard Binding Configuration
Dynamic IP Source Guard Binding Information
120 Static IP Source Guard Binding Configuration
Web Click IP Source Guard, Dynamic Information
Switch Clustering
122 Cluster Member Choice
Cluster Configuration
Adds Candidate switches to the cluster as Members
Cluster Member Configuration
Web Click Cluster, Configuration
Cluster Member Information
Web Click Cluster, Member Configuration
Displays current cluster Member switch information
126 Cluster Candidate Information
Cluster Candidate Information
Accessing the CLI
Using the Command Line Interface
Telnet Connection
Command Completion
Entering Commands
Getting Help on Commands
Keywords and Arguments
Showing Commands
Using Command History
Negating the Effect of Commands
Understanding Command Modes
Partial Keyword Lookup
Command Modes
Exec Commands
Consoleconfig-if# 120
Configuration Commands
Configuration Modes Command Prompt
Keystroke Function
Command Line Processing
Command Line Processing
Command Groups Description
Command Groups
Line Commands Function Mode
Line Commands
Line
Login
Username 4-25 password
Password
Syntax Password 0 7 password no password
No password is specified
Exec-timeout
Timeout login response
Syntax Password-thresh threshold no password-thresh
Password-thresh
Syntax Exec-timeout seconds no exec-timeout
Syntax Silent-time seconds no silent-time
Silent-time
Databits
Syntax Parity none even odd no parity
Parity
Syntax Databits 7 8 no databits
Stopbits
Speed
Syntax Speed bps no speed
Syntax Stopbits 1
Show line
Disconnect
Syntax Disconnect session-id
Syntax Show line console vty
Enable
General Commands
To show all lines, enter this command
General Commands Function Mode
Disable Enable password
Disable
Enable
Level
Show history
Configure
End
Reload
This example shows how to quit a CLI session
This command exits the configuration program
Exit
Quit
Prompt
System Management Commands
Device Designation Commands
User Access Commands Function Mode
User Access Commands
Hostname
Username
Guest Admin
Enable password
10 Default Login Settings Username Access-level Password
Management
IP Filter Commands
11 IP Filter Commands Function Mode
All addresses
Show management
12 Web Server Commands Function Mode
Web Server Commands
Default Setting Command Mode
Ip http port
Syntax No ip http secure-server Default Setting
Syntax No ip http server Default Setting
Ip http server
Ip http secure-server
13 Https System Support Web Browser Operating System
Ip http secure-port
Ip http secure-port4-31 Copy tftp https-certificate
Portnumber The UDP port used for HTTPS. Range
14 Telnet Server Commands Function Mode
Telnet Server Commands
Ip telnet port
Ip http secure-server4-30
Syntax No ip telnet server Default Setting
Secure Shell Commands
15 SSH Commands Function Mode
Ip telnet server
Copy tftp public-key
Ip ssh server
Syntax No ip ssh server Default Setting
Syntax Ip ssh timeout seconds no ip ssh timeout
Ip ssh timeout
Exec-timeout4-13 show ip ssh
Ip ssh crypto host-key generate 4-38 show ssh
Ip ssh server-key size
Ip ssh authentication-retries
Key-size- The size of server key. Range 512-896 bits
Bits
Ip ssh crypto host-key generate
Delete public-key
Syntax Delete public-key username dsa rsa
Syntax Ip ssh crypto host-key generate dsa rsa
Ip ssh save host-key
Ip ssh crypto zeroize
Syntax Ip ssh crypto zeroize dsa rsa
Syntax Ip ssh save host-key dsa rsa
Show ip ssh
This command displays the current SSH server connections
Show ssh
Ip ssh crypto host-key generate
Syntax Show public-key user username host
Show public-key
Terminology
Console#show public-key host Host
17 Event Logging Commands Function Mode
Event Logging Commands
Syntax No logging on Default Setting
Logging on
18 Logging Levels
Flash errors level 3 RAM warnings level 6
Logging history
Logging facility
Logging host
Syntax No logging host hostipaddress
Hostipaddress The IP address of a syslog server
Clear logging
Logging trap
Syntax Logging trap level no logging trap
Syntax Clear logging flash ram
19 show logging flash/ram display description
Show logging
Syntax Show logging flash ram sendmail trap
Logging trap command
Facility command
Syntax Show log flash ram login tail
Show log
21 Smtp Alert Commands Function Mode
Smtp Alert Commands
Logging sendmail host
Following example shows sample messages stored in RAM
Syntax Logging sendmail level level
Logging sendmail level
Logging sendmail destination-email
Logging sendmail source-email
Syntax No logging sendmail source-email email-address
This example will set the source email john@acme.com
Show logging sendmail
Syntax No logging sendmail Default Setting
Logging sendmail
22 Time Commands Function Mode
Time Commands
Syntax No sntp client Default Setting
Sntp client
Sntp server 4-54 sntp poll 4-55 show sntp
Sntp server
Syntax Sntp server ip1 ip2 ip3
Sntp client 4-53 sntp poll 4-55 show sntp
Show sntp
Sntp poll
Syntax Sntp poll seconds no sntp poll
Sntp client
Calendar set
Clock timezone
Syntax
Calendar set hour min sec day month year month day year
Show startup-config
System Status Commands
This command displays the system clock
23 System Status Commands Function Mode
Command Line Interface
Show running-config4-59
Show running-config
Show startup-config4-57
Show users
This command displays system information
Show system
Show version
24 Frame Size Commands Function Mode
Frame Size Commands
Jumbo frame Enables support for jumbo frames
Syntax No jumbo frame Default Setting
25 Flash/File Commands Function Mode
Flash/File Commands
Copy
Copy
Flash/File Commands
Following example shows how to download a configuration file
Delete
This command deletes a file or image
Delete unit filename
Dir Delete public-key4-38
Dir
Syntax Dir unit boot-rom config opcode filename
26 File Directory Information
Column Heading Description
Boot system
Whichboot
Syntax whichboot unit
Syntax Boot system unit boot-romconfig opcode filename
Authentication Sequence
Authentication Commands
Dir 4-68 whichboot
27 Authentication Commands Command Group Function
Local
Authentication login
Username for setting the local user names and passwords
Authentication enable
Radius Client
29 Radius Client Commands Function Mode
Show radius-server Shows the current Radius settings
Retransmit Command Mode
Default Setting Auth-port
Radius-server host
Radius-server port
Syntax Radius-server key keystring no radius-server key
Radius-server key
Radius-server retransmit
Show radius-server
Radius-server timeout
TACACS+ Client
30 Tacacs Commands Function Mode
Tacacs-server host
Tacacs-server port
Syntax Tacacs-server key keystring no tacacs-server key
Tacacs-server key
Show tacacs-server
31 Port Security Commands Function Mode
Port Security Commands
Status Disabled Action None Maximum Addresses
Interface Configuration Ethernet
Command Usage
32 802.1X Port Authentication Command Function Mode
802.1X Port Authentication
Syntax No dotx system-auth-control Default Setting
Dot1x system-auth-control
Default Command Mode
Dot1x default
Dot1x max-req
Dot1x port-control
Single-host
Dot1x operation-mode
Force-authorized
Dot1x timeout quiet-period
Dot1x re-authenticate
Dot1x re-authentication
Dot1x timeout tx-period
Dot1x timeout re-authperiod
Statistics Displays dot1x status for each port
Show dot1x
Syntax Show dot1x statistics interface interface
Reauthentication State Machine
Authenticator State Machine
State Current state including initialize, reauthenticate
Backend State Machine
Command Line Interface
33 Access Control Lists Command Groups Function
Access Control List Commands
Access Control Lists
34 IP ACLs Command Function Mode
Access-list ip
Syntax No access-list ip standard extended aclname
IP ACLs
Access-list ip
Permit, deny Ip access-group4-93 show ip access-list4-93
Syntax No permit deny any source bitmask host source
Standard ACL
Extended ACL
Any destination address-bitmask host destination
Source-port sport end destination-port dport end
Ip access-group
Show ip access-list
Syntax Show ip access-list standard extended aclname
Syntax No ip access-group aclname
This command shows the ports assigned to IP ACLs
Show ip access-group
Show ip access-list4-93
35 MAC ACL Commands Function Mode
Access-list mac
Syntax No access-list mac aclname
Permit, deny Mac access-group4-98 show mac access-list4-97
Permit, deny MAC ACL
This command displays the rules for configured MAC ACLs
Show mac access-list
Syntax Show mac access-list aclname
Permit, deny Mac access-group4-98
Show mac access-group
Mac access-group
Syntax Mac access-group aclname
Show mac access-list4-97
Show access-group
Show access-list
36 ACL Information Command Function Mode
ACL Information
37 Snmp Commands Function Mode
Snmp Commands
Show snmp
Syntax No snmp-server Default Setting
Snmp-server
Snmp-server community
Snmp-server location
Snmp-server contact
Syntax Snmp-server contact string no snmp-server contact
Syntax Snmp-server location text no snmp-server location
Host Address None Notification Type Traps
Snmp-server host
Snmp Version UDP Port
Issue authentication and link-up-down traps
Snmp-server enable traps
Snmp-server enable traps
Snmp-server engine-id
Show snmp engine-id
This command shows the Snmp engine ID
This example shows the default engine ID
Snmp-server view
Defaultview includes access to the entire MIB tree
Examples
This view includes MIB-2
Show snmp view
This command shows information on the Snmp views
Snmp-server group
39 show snmp view display description
Consoleconfig#snmp-server group r&d v3 auth write daily
Show snmp group
40 show snmp group display description
Snmp-server user
114
41 show snmp user display description
This command shows information on Snmp users
Show snmp user
42 Interface Commands Function Mode
Interface Commands
Interface
Port-channel channel-idRange
Syntax Description string no description
Description
Speed-duplex
Negotiation 4-118 capabilities
Syntax No negotiation Default Setting
Negotiation
Capabilities 4-119speed-duplex4-117
Following example configures port 11 to use autonegotiation
Capabilities
Negotiation 4-118speed-duplex4-117 flowcontrol
Syntax No flowcontrol Default Setting
Flowcontrol
Shutdown
Syntax No shutdown Default Setting
Port-channel channel-idRange Default Setting
Switchport broadcast packet-rate
Clear counters
Syntax Clear counters interface
Show interfaces status
This command displays the status for an interface
Following example clears statistics on port
Syntax Show interfaces status interface
Show interfaces counters
This command displays interface statistics
Syntax Show interfaces counters interface
Shows the counters for all interfaces
Shows all interfaces
Show interfaces switchport
Syntax Show interfaces switchport interface
43 Interfaces Switchport Statistics
44 Mirror Port Commands Function Mode
Mirror Port Commands
Port monitor
Interface ethernet unit/port source port
Following shows mirroring configured from port 6 to port
This command displays mirror information
Show port monitor
Syntax Show port monitor interface
Gigabit Ethernet 1000 Mbps
Rate Limit Commands
Rate-limit
46 Link Aggregation Commands
Link Aggregation Commands
135
123
Guidelines for Creating Trunks
Channel-group
General Guidelines
Dynamically Creating a Port Channel
Following example creates trunk 1 and then adds port
Syntax No lacp Default Setting
Lacp
32768
Lacp system-priority
Lacp admin-keyEthernet Interface
Interface Configuration Port Channel
Lacp admin-key Port Channel
Show lacp
This command displays Lacp information
Lacp port-priority
47 show lacp counters display description
Port Channel all
Type
LACPDUs Illegal Pkts
48 show lacp internal display description
50 show lacp sysid display description
49 show lacp neighbors display description
51 Address Table Commands Function Mode
Address Table Commands
Mac-address-table static
Action
Mac-address- MAC address Mask Bits to match in the address
Clear mac-address-table dynamic
Show mac-address-table
Sort Sort by address, vlan or interface
Mac-address-table aging-time
Show mac-address-table aging-time
52 Spanning Tree Commands Function Mode
Spanning Tree Commands
Syntax No spanning-tree Default Setting
Spanning-tree mode
Spanning tree is enabled
Spanning-tree
Spanning-tree forward-time
Spanning-tree hello-time
Spanning-tree priority
Spanning-tree max-age
Long method
Spanning-tree pathcost method
This command limits the maximum transmission rate for BPDUs
Spanning-tree mst-configuration
Spanning-tree transmission-limit
Count The transmission limit in seconds. Range
Mst vlan
MST Configuration
Mst priority
No mst instanceid vlan vlan-range
Name
Switch’s MAC address
Syntax Name name
Name Name of the spanning tree
Max-hops
Revision
Syntax Revision number
Max-hopshop-number
Syntax No spanning-tree spanning-disabled Default Setting
Spanning-tree spanning-disabled
This example disables the spanning tree algorithm for port
Spanning-tree cost
Priority The priority for a port. Range 0-240, in steps
Spanning-tree port-priority
Syntax No spanning-tree portfast Default Setting
Syntax No spanning-tree edge-port Default Setting
Spanning-tree edge-port
Spanning-tree portfast
Auto
Spanning-tree link-type
Spanning-treeedge-port4-156
Spanning-tree mst cost
Spanning-tree mst port-priority4-159
Spanning-tree mst port-priority
Spanning-tree protocol-migration
Port-channel channel-idRange Command Mode
Show spanning-tree
Syntax Spanning-tree protocol-migration interface
Mstp
Show spanning-tree mst configuration
Gvrp and Bridge Extension Commands
Vlan Commands
53 VLANs Command Groups Function
54 Gvrp and Bridge Extension Commands Function Mode
Show bridge-ext
Syntax No bridge-ext gvrp Default Setting
Bridge-ext gvrp
Show gvrp configuration
Switchport gvrp
Syntax No switchport gvrp Default Setting
Syntax Show gvrp configuration interface
Show garp timer
Garp timer
55 Editing Vlan Groups Command Function Mode
Syntax Show garp timer interface
Editing Vlan Groups
Vlan database
Vlan Database Configuration
By default only Vlan 1 exists and is active
Vlan
Show vlan
56 Configuring Vlan Interfaces Command Function Mode
Configuring Vlan Interfaces
Interface vlan
Interface vlan
Switchport acceptable-frame-types4-171
Switchport mode
All ports are in hybrid mode with the Pvid set to Vlan
Switchport ingress-filtering
Switchport acceptable-frame-types
Switchport mode
All frame types
Switchport native vlan
Switchport allowed vlan
No VLANs are included in the forbidden list
Switchport forbidden vlan
Show vlan
57 Show Vlan Commands Function Mode
Displaying Vlan Information
58 Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling Commands Function Mode
Configuring Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling
General Configuration Guidelines for QinQ
Dot1q-tunnel system-tunnel-control
Show dot1q-tunnel4-178 Show interfaces switchport
Switchport dot1q-tunnel mode
Related Commands
Switchport dot1q-tunnel tpid
This command displays information about QinQ tunnel ports
Show dot1q-tunnel
Pvlan
Switchport dot1q-tunnel mode
59 Private Vlan Commands Function Mode
No private VLANs are defined
This command displays the configured private Vlan
Show pvlan
60 Protocol-based Vlan Commands Function Mode
Configuring Protocol-based VLANs
Protocol-vlan protocol-group Configuring Groups
No protocol groups are mapped for any interface
Protocol-vlan protocol-group Configuring Interfaces
No protocol groups are configured
Syntax Show protocol-vlan protocol-group group-id
Show protocol-vlan protocol-group
Show interfaces protocol-vlan protocol-group
Priority Commands Layer
Priority Commands
61 Priority Commands Command Groups Function
62 Priority Commands Layer Function Mode
Syntax Queue mode strict wrr no queue mode
Queue mode
Switchport priority default
Queue bandwidth
Queue bandwidth weight1...weight4 no queue bandwidth
Weights 1, 2, 4, 8 are assigned to queues 0-3 respectively
Queue cos-mapqueueid cos1 ... cosn no queue cos-map
63 Default CoS Values to Egress Queues
Queue cos-map
Following example shows how to change the CoS assignments
Show queue mode
This command shows the current queue mode
Show queue bandwidth
This command shows the class of service priority map
Priority Commands Layer 3
64 Priority Commands Layer 3 Function Mode
Show queue cos-map
65 IP Dscp to CoS Vales IP Dscp Value CoS Value
Syntax No map ip dscp Default Setting
Map ip dscp dscp-value cos cos-value no map ip dscp
Syntax Show map ip dscp interface
This command shows the IP Dscp priority map
Show map ip dscp
Quality of Service Commands
199 Input of a particular interface Show class-map
66 Quality of Service Commands Function Mode
198 Service-policy
Match
Class-map
Syntax No class-map class-map-namematch-any
Show class map
No policy-mappolicy-map-name
Class Map Configuration
Policy-map
No class class-map-name
Policy Map Configuration
Class
Set
Policy Map Class Configuration
Drop out-of-profile packets
Police
Syntax No police rate-kbpsburst-byteexceed-action drop set
Syntax No service-policy input policy-map-name
Service-policy
Show class-map
Syntax Show class-map class-map-name
Show policy-map interface
Show policy-map
Show policy-mappolicy-map-name class class-map-name
Displays all policy maps and all classes
Igmp Snooping Commands
Multicast Filtering Commands
67 Multicast Filtering Commands Command Groups Function
68 Igmp Snooping Commands Function Mode
Following example enables Igmp snooping
Syntax No ip igmp snooping Default Setting
Ip igmp snooping
Ip igmp snooping vlan static
Syntax No ip igmp snooping leave-proxy Default Setting
Following configures the switch to use Igmp Version
Ip igmp snooping version
Ip igmp snooping leave-proxy
Interface Configuration Vlan
Syntax No ip igmp snooping immediate-leave Default Setting
This command shows the Igmp snooping configuration
Ip igmp snooping immediate-leave
Show mac-address-table multicast
Following shows the current Igmp snooping configuration
This command shows known multicast addresses
69 Igmp Query Commands Layer Function Mode
Igmp Query Commands Layer
Syntax No ip igmp snooping querier Default Setting
Ip igmp snooping querier
Ip igmp snooping query-interval
Following shows how to configure the query count to
Times
Ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time4-208
Ip igmp snooping router-port-expire-time
Seconds The report delay advertised in Igmp queries. Range
Ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time
70 Static Multicast Routing Commands Function Mode
Static Multicast Routing Commands
Ip igmp snooping vlan mrouter
Syntax No ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-idmrouter interface
Show ip igmp snooping mrouter
Displays multicast router ports for all configured VLANs
Syntax Show ip igmp snooping mrouter vlan vlan-id
Multicast router port types displayed include Static
71 Igmp Filtering and Throttling Commands Function Mode
Igmp Filtering and Throttling Commands
Syntax No ip igmp filter Default Setting
213
Ip igmp profile
Syntax Permit deny Default Setting
Permit, deny
Syntax No ip igmp profile profile-number
Syntax No ip igmp filter profile-number
Range
No range low-ip-address high-ip-address
Syntax Ip igmp max-groups number No ip igmp max-groups
Ip igmp max-groups
Show ip igmp filter
Ip igmp max-groups action
Syntax Ip igmp max-groups action replace deny
Syntax Show ip igmp filter interface interface
Show ip igmp throttle interface
Show ip igmp profile
Syntax Show ip igmp profile profile-number
Syntax Show ip igmp throttle interface interface
72 Multicast Vlan Registration Commands Function Mode
Multicast Vlan Registration Commands
Port Port number. Range Port-channelchannel-id Range
219
No mvr group ip-address count vlan vlan-id
Command Line Interface Mvr Global Configuration
Multicast Filtering Commands Mvr Interface Configuration
220
73 show mvr display description
Show mvr
Syntax Show mvr interface interface members ip-address
Members
74 show mvr interface display description
75 show mvr members display description
76 IP Interface Commands Function Mode
IP Interface Commands
Ip address
224
Syntax Ip default-gateway gateway no ip default-gateway
Ip default-gateway
Gateway IP address of the default gateway
Following example defines a default gateway for this device
This command displays the settings of an IP interface
This command submits a Bootp or Dhcp client request
Ip dhcp restart
Show ip interface
This command has no default for the host
Ip default-gateway4-224
Show ip redirects
Ping
Ip source-guard
IP Source Guard Commands
77 IP Source Guard Commands Function Mode
Syntax Ip source-guard sip sip-macno ip source-guard
No configured entries
This example enables IP source guard on port
Ip source-guard binding
No ip source-guard binding mac-addressvlan vlan-id
Show ip source-guard
This command shows the source guard binding table
Show ip source-guard binding
Ip source-guard4-227 ip dhcp snooping Ip dhcp snooping vlan
78 Dhcp Snooping Commands Function Mode
Dhcp Snooping Commands
Syntax No ip dhcp snooping Default Setting
Ip dhcp snooping
232
This example enables Dhcp snooping for Vlan
This example enables Dhcp snooping globally for the switch
Ip dhcp snooping vlan
Ip dhcp snooping vlan 4-233 ip dhcp snooping trust
Ip dhcp snooping trust
Syntax No ip dhcp snooping trust Default Setting
Ip dhcp snooping information option
This example enables MAC address verification
Ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address
Replace
This example enables the Dhcp Snooping Information Option
Ip dhcp snooping information policy
79 Switch Cluster Commands Function Mode
Switch Cluster Commands
Show ip dhcp snooping
Show ip dhcp snooping binding
Displays current cluster Candidates in the network 242
Syntax No cluster Default Setting
Cluster
Syntax No cluster commander Default Setting
Cluster commander
Cluster ip-pool
Syntax Cluster ip-pool ip-addressno cluster ip-pool
Syntax Rcommand id member-id
Rcommand
Member-id- The ID number of the Member switch. Range
Cluster member
This command shows the current switch cluster members
This command shows the switch clustering configuration
Show cluster
Show cluster members
Show cluster candidates
Software Features
Appendix a Software Specifications
Groups 1, 2, 3, 9 Statistics, History, Alarm, Event
Management Features
Standards
Igmp RFC 1112 IGMPv2 RFC 2236 RADIUS+ RFC
Management Information Bases a
Management Information Bases
Software Specifications
Symptom Action
Table B-1 Troubleshooting Chart
Using System Logs
Boot Protocol Bootp
Access Control List ACL
Class of Service CoS
Differentiated Services Code Point Service Dscp
Generic Attribute Registration Protocol Garp
Garp Vlan Registration Protocol Gvrp
Generic Multicast Registration Protocol Gmrp
Group Attribute Registration Protocol Garp
Igmp Query
Igmp Snooping
Internet Group Management Protocol Igmp
In-Band Management
Port Authentication
Multicast Switching
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service Radius
Network Time Protocol NTP
Simple Network Management Protocol Snmp
Secure Shell SSH
Simple Network Time Protocol Sntp
Spanning Tree Algorithm STA
XModem
Virtual LAN Vlan
Numerics
Index
Index
Gateway, default 3-14,4-224
Index-3
Index-4
Page
Technical Support