MSP50C6xx Mixed-Signal Processor User’s Guide
Important Notice
About This Manual
How to Use This Manual
Notational Conventions
Iii
Csr -a /user/ti/simuboard/utilities
Here is a sample program listing
Notational Conventions
Trademarks
Information About Cautions and Warnings
This book may contain cautions and warnings
Information About Cautions and Warnings
Page
Contents
Contents
Assembly Language Instructions
Peripheral Functions
Code Development Tools
Contentsix
Customer Information
Applications
PLL Performance -27 2-10 Instruction Execution and Timing
Contentsxi
Tables
Tables
Contentsxiii
Xiv
Introduction to the MSP50C6xx
Features of the MSP50C6xx
Features of the MSP50C6xx
Consumer Education
Applications
Industrial
Aids for the Handicapped
Development Device MSP50P614
Development Device MSP50P614
Functional Description for the MSP50C614
Functional Description for the MSP50C614
Functional Description for the MSP50C614
Resistor Trim Oscillator Connections
Crystal Reference Oscillator Connections
Reset Circuit
MSP50C601, MSP50C604, and MSP50C605
MSP50C601, MSP50C604, and MSP50C605
Page
MSP50C6xx Architecture
Architecture Overview
MSP50C6xx Architecture
MSP50C6xx Core Processor Block Diagram
Computational Unit Block Diagram
Multiplier
Computation Unit
Signed and Unsigned Integer Representation
Computation Unit
Computation Unit
Arithmetic Logic Unit
Overview of the Multiplier Unit Operation
Accumulator Block
Overview of the Arithmetic Logic Unit
Points to
AC Register #
Points to Offset
Data Memory Address Unit
Data Memory Address Unit
Data Memory Address Unit
RAM Configuration
Data Memory Addressing Modes
Bit Logic Unit
Program Counter Unit
Program Counter Unit
Memory Map
Memory Organization RAM and ROM
Memory Organization RAM and ROM
Peripheral Communications Ports
C6xx Memory Map not drawn to scale
Summary of MSP50C614’s Peripheral Communications Ports
Reset LOW
Interrupt Vectors
Summary of C614’s Peripheral Communications Ports
Interrupt Name ROM address Event Source Interrupt Priority
ROM Code Security
Address 0x7FFE
Block Protection Word
Write only
True Protection Marker N TM
Protection marker
= the value programmed at TM5 … TM0 true
≡ the binary complement of N TM
= the value programmed at FM5 … FM0 false
Macro Call Vectors
Interrupt Logic
Interrupt Logic
IFR
Bit wide location 00 ← INT number
Interrupt Logic
Interrupt Initialization Sequence
Oscillator Options
Clock Control
PLL Performance
Clock Control
PLL Performance
Clock frequency kHz = Pllm register value + 1 ⋅ 65.536 kHz
Clock Speed Control Register
ClkSpdCtrl register
RTO Oscillator Trim Adjustment
ClkSpdCtrl Value Copied Shaded
Rtrim Register Read Only Applies to MSP50C6xx Device Only
Timer Registers
Timer Registers
Timer Registers
Reduced Power Modes
Reduced Power Modes
Reduced Power Modes
Reduced Power Modes
Programmable Bits Needed to Control Reduced Power Modes
Component Determined
Deeper sleep … relatively less power →
By Controls
Event Determined
Deeper sleep …
Global interrupt enable is SET
Execution Timing
Execution Timing
Peripheral Functions
General-Purpose I/O Ports
I/O
MSP50C614
MSP50C604 MSP50C605
0x14h 0x1Ch 0x24h Possible control values = High-Z Input
Control register address 0x04h†
Peripheral Functions
Dedicated Input Port F
Input Port F
Dedicated Output Port G
Data register address
Totem-Pole Output Port G
Branch on D Port
Internal and External Interrupts
Summary of the interrupts is given in Table
Interrupts
Interrupt Vector Source Trigger Event Priority Comment
Pulse-Density Modulation Rate
Digital-to-Analog Converter DAC
DAC Control and Data Registers
Digital-to-Analog Converter DAC
Overflow bits Least-significant data value Ignored bits
PDM Clock Divider
PDM Clock Divider
Digital-to-Analog Converter DAC
DAC
Example 3-1 -kHz Sampling Rate
Example 3-2 -kHz Sampling Rate
Comparator
INT6 INT7 TIMER1 Enable
Comparator
Interrupt/General Control Register
Interrupt/General Control Register
IntGenCtrl register
Address Bit wide location Low
Interrupt/General Control Register
Hardware Initialization States
Hardware Initialization States
Hardware Initialization States
Bit Bit Name Initialized Value Description
Instruction Set Summary
Assembly Language Instructions
System Registers
Introduction
Top of Stack, TOS
Assembly Language Instructions
System Registers
Postdecrement
Product Low Register PL
Product High Register PH
Accumulators AC0-AC31
Indirect Register R0-R7
Accumulator Pointers AP0-AP3
Bit
Bits 16
Status Register Stat
String Register STR
Function
Status Register Stat
1 MSP50P614/MSP50C614 Instruction Syntax
Instruction Syntax and Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
Addressing Mode Encoding
Bit Opcode
Next a
Rx Bit Description
Addressing Mode Bits and adrs Field Description
Auto Increment and Auto Decrement Modes
MSP50P614/MSP50C614 Addressing Modes Summary
Flag Repeat
Flag addressing mode encoding, flagadrs
Flagadrs
Clocks Words Addressing Operation, † Syntax
Syntax
Immediate Addressing
Example
ADD AP0, 0x1A
MOV *0x012F * 2, *A0
Direct Addressing
Mulr *0x02A1
Memory Operand
Indirect Addressing Syntax
Indirect Addressing
SyntaxOperation
Rx x = 0 Address Memory Operand ++ -- ++R5
MOV A2, *R0
Relative Addressing
*R4++
Movb *R7++, A3
Rx x = 0 Address Index Register R5 Operand
A0, *R3+R5
R6 page register Address Bit positive offset Operand
Rx x = 0 Address Memory Operand
MOV A3, *R6+0x10
TF1, *0x20
Flag Addressing
Or TF2, *R6+0x02
XOR TF1, *R6+0x20
8 Tag/Flag Bits
TF1,*ram1 TF1 bit in Stat is set!?
Possible sources of confusion Consider the following code
Symbol Explanation
10. Symbols and Explanation
Instruction Classification
Instruction Classification
11. Instruction Classification
11. Symbols and Explanation
Next a Accumulator control bits as described in Table
Class Sub- Description
Class Sub Description
Class 1 Instructions Memory and Accumulator Reference
12. Classes and Opcode Definition
14. Class 1a Instruction Description
13. Class 1 Instruction Encoding
C1a ~A~
C1b
C1b Mnemonic Description
15. Class 1b Instruction Description
Class 2 Instructions Accumulator and Constant Reference
17. Class 2a Instruction Description
16. Class 2 Instruction Encoding
C2a Mnemonic Description
Class 3 Instruction Accumulator Reference
18. Class 2b Instruction Description
C2b Mnemonic Description
ADD An ~, An ~, imm16 , next a
20. Class 3 Instruction Description
19. Class 3 Instruction Encoding
Mnemonic Description
Subs An~, An~, An Modified ADD An~, An~, An , next a
SUB a n~, a n~, PH , next a
Zero or be set equal to the sign bit Xsgm dependent
ALU status is modified. String bit causes subtract with
Carry status CF
MOV SV, An~ , next a
PH msbs extended by XM mode bit. Transfer the lower
Is modified
From the offset accumulator A~=1 or accumulator
21. Class 4a Instruction Encoding
Class 4 Instructions Address Register and Memory Reference
23. Class 4b Instruction Description
22. Class 4a Instruction Description
24. Class 4c Instruction Description
25. Class 4d Instruction Description
26. Class 5 Instruction Encoding
Class 5 Instructions Memory Reference
27. Class 5 Instruction Description
Adrs. Transfer status is modified
MOV adrs, TOS
Dressing mode adrs. Transfer status is modified
Stag adrs
Tag bit
28. Class 6a Instruction Encoding
Class 6 Instructions Port and Memory Reference
29. Class 6a Instruction Description
C6a Mnemonic Description
Class 7 Instructions Program Control
30. Class 6b Instruction Description
C6b Mnemonic Description
Vector8
31. Class 7 Instruction Encoding and Description
Jcc
Ccc
32. Class 8a Instruction Encoding
Class 8 Instructions Logic and Bit
34. Class 8b Instruction Description
33. Class 8a Instruction Description
Class 9 Instructions Miscellaneous
C8a Mnemonic Description
36. Class 9a Instruction Description
35. Class 9a Instruction Encoding
37. Class 9b Instruction Description
C9a Mnemonic Description
38. Class 9c Instruction Description
Bit, Byte, Word and String Addressing
39. Class 9d Instruction Description
C9c Mnemonic Description
0000h 0001h 0002h 0040h 0041h Nnnn 17th Bit
Global Flags Relative
Word
0000h MS Byte LS Byte
40. Data Memory Address and Data Relationship
Mode Address Used Data Order Rx Post modify †
Movb A0, *0x0003
MOV A0, *0x0004
Which uses the absolute word memory address
Rflag
MSP50P614/MSP50C614 Computational Modes
MSP50P614/MSP50C614 Computational Modes
41. MSP50P614/MSP50C614 Computational Modes
Computational Setting Resetting Function Mode Instruction
SXM
Example 4.6.2 Sovm
Example 4.6.1 Sovm
Example 4.6.1 SXM
Hardware Loop Instructions
Hardware Loop Instructions
Syntax Operation Limitations
42. Hardware Loops in MSP50P614/MSP50C614
Completion of the BEGLOOP/ENDLOOP block
43. Initial Processor State for String Instructions
String Instructions
Data memory *address = data
Program memory *address = data
Mulapl A0, A0~
44. Lookup Instructions
Lookup Instructions
Lookup Instructions
Instructions Description Data Transfer
MOV An, adrs SUB An MOV An, *An
Special Filter Instructions
Input/Output Instructions
Input/Output Instructions
Xk-2 Xk+2 Xk-1 xk+1 32 or
Special Filter Instructions
Special Filter Instructions
STR,0
0x0104
0x0100 0x0102
0x0106
Go back N words to wrap around
After FIR/COR execution
Important Note About Setting the Stat Register
Firkcoeffs
Coeffarray Samplebuf address
Coeffarray address FIRK/CORK only Program memory FIRK/CORK
FIR/COR only = 0..N
Coeffarray
Samplebuf Coeffarray is stored
Conditionals
Conditionals
Operands
Symbol Meaning
Offset16 ≤
Port4 ≤ Port6 ≤
Clk
Adrsn
Dma n
Flg
Pma n
Offset n
Port n
45. Auto Increment and Decrement
46. Addressing Mode Bits and adrs Field Description
47. Flag Addressing Syntax and BIts
Individual Instruction Descriptions
Individual Instruction Descriptions
Execution
14.1 ADD Add word
See Also
Description
PC PC + Flags Affected
Addb
Opcode
Clock , clk Words , w
Adds Add String
Adds A1, A1~, A1
14.4 Bitwise
A3, *R4
ANDS, ANDB, OR, ORB, ORS, XOR, XORB, Xors
TF2, *0x0020
Src byte PC PC +
Andb Bitwise and Byte
OF, SF, ZF, CF are set accordingly
Clock , clk Word , w
Ands A0, A0~, A0
Ands Bitwise and String
Ands A0, A0~, *R2
Save next instruction address PC +
Begloop Begin Loop
Flags Affected None Opcode
Order to loop N times
Call Unconditional Subroutine Call
RET
TOS
14.9 Ccc
NOP
True condition Not true condition
48. Names for cc
Syntax Alternate Syntax Description
0x2010
CALL, VCALL, RET, Iret
CTF1
Crnbe
Stat flags set by src src1 operation
14.10 CMP Compare Two Words
PC = PC + w
CMPB, CMPS, Jcc, Ccc
CMP R0, R5
CMP R2, 0xfe20
Cmpb R3
Cmpb Compare Two Bytes
PC PC + w Flags Affected
Cmps Compare Two Strings
Cmps A1~
Cmps A2, A2~
14.13 COR Correlation Filter Function
With RPT instruction. See .11 for more detail on the setup
An, *Rx 3nR+2
Rxeven = Rxeven + R5
Sample data. During Cork execution, interrupt is queued
Cork Correlation Filter Function
3n R+2
Xeven = R xeven + R5
Decrement R4 by n 1 or PC first address after Begloop else
Endloop End Loop
Argument, it assumes n =1
BEGLOOP, Inte
~ , next a
Extsgn Sign Extend Word
Copy accumulator sign flag SF to all 16 bits of a n ~
Dest , mod
An~
Extsgns Sign Extend String
100
14.18 FIR FIR Filter Function Coefficients in RAM
Assembly Language Instructions 101
An, *Rx 2nR+2
Rxeven++
102
Firk
Assembly Language Instructions 103
104
Idle Halt Processor
INS, OUT, Outs
14.21 Input From Port Into Word
A2~, 0x3d
IN, OUT, Outs
14.22 INS Input From Port Into String
Assembly Language Instructions 107
Intd Interrupt Disable
STAT.IM
IM is Stat bit PC PC + Flags Affected None Opcode
Inte
Interrupt Enable
INTD, Iret
Clock, clk Word, w With RPT, clk Class
Iret Return From Interrupt
Assembly Language Instructions 109
RCF and RZF affected by post-modification of R
Conditional Jumps
Cc names
Assembly Language Instructions 111
If test condition is false, a NOP is executed
JNZ
See Also JMP, CALL, C cc Example
JE 0x2010, R3++R5
Jtag 0x2010, R2++
Post-modify R x if specified
14.27 JMP Unconditional Jump
See Also Cc, CALL, C cc Example
Instruction Operation
14.28 MOV Move Data Word From Source to Destination
Clock , clk Word , w With RPT , clk Class
XSF, XZF are set accordingly
TF n, cc , R
STR, imm8
MOV adrs, DP
Assembly Language Instructions 117
With some operand types
Example 4.14.28.10 MOV MR, A3, --A
MOVU, MOVT, MOVB, MOVBS, Movs
Example 4.14.28.11 MOV A1~, *A1
Example 4.14.28.12 MOV *0x0200 * 2, R0
Example 4.14.28.15 MOV *0x0200 * 2, R0
Example 4.14.28.13 MOV R1, 0x0200
Transfer R5 to R0 Example
Example 4.14.28.18 MOV *R6 + 8 * 2, DP
Execution An + PH
Movaph Move With Adding PH
MOVAPHS, MOVTPH, MOVTPHS, MOVSPH, Movsphs
Execution + PH
Movaphs Move With Adding PH
Background. See .8 for more details
MOVAPH, MOVTPH, MOVTPHS, MOVSPH, Movsphs
Copy value of unsigned src byte to dest byte
Movb Move Byte From Source to Destination
Movb A0, *R2
Copy data memory byte pointed by R2 to accumulator A0
Movb A0, 0xf2
Movb *R2, A0
Movb R2
TAG bit is set to bit 17th value
Movbs Move Byte String from Source to Destination
Movbs A2, *0x0200
Movbs *0x0200, A2
An ~ , adrs
Movs Move String from Source to Destination
Adrs , An ~
Adrs , *An
Movs A2~
MOVU, MOV, MOVT, MOVB, Movbs
Movs A1, A1~
Movs A1~, A1
MOVSPHS, MOVAPH, MOVAPHS, MOVTPH, Movtphs
Movsph
128
Assembly Language Instructions 129
An second word PH MR contents of adrs
Movsphs Move String With Subtract From PH
Details
PC PC + w Flags Affected None Opcode
Movt
Available
MOVU, MOV, MOVT, MOVB, MOVBS, Movs
TAG bit is set accordingly UM is set to
Movu Move Data Unsigned
MOV, MOVB, MOVT, MOVBS, Movs
Copy the value pointed by R3 to MR
Xxxxxx Xxxx00 Flag Bit
MR/SV An S APn
132
MR * src PC PC + w Flags Affected
14.38 MUL Multiply Rounded
Accumulator pointer if specified
MULR, MULAPL, MULSPL, MULSPLS, MULTPL, MULTPLS, Mulapl
MR * src PC PC + Flags Affected
Mulr Multiply Rounded With No Data Transfer
MULS, MUL, MULAPL, MULSPL, MULSPLS, MULTPL, Multpls
Mulapl
Assembly Language Instructions 135
Length nS+2, where nS is the value in STR register
Muls Multiply String With No Data Transfer
PH,PL MR * src string
PH ,PL MR * src
Mulapl Multiply and Accumulate Result
Background. See .8 for more detail
MULAPLS, MULSPL, MULSPLS, MULTPL, Multpls
MR * src
Mulapls Multiply String and Accumulate Result
MULAPL, MULSPL, MULSPLS, MULTPL, Multpls
Occuring in the background. See .8 for more details
Mulspl Multiply and Subtract PL From Accumulator
MULSPLS, MULTPL, MULTPLS, MULAPL, Mulapls
Syntax Description Mulspl adrs
From dest string
Mulspls Multiply String and Subtract PL From Accumulator
MULSPL, MULTPL, MULTPLS, MULAPL, Mulapls
Syntax Description Mulspls adrs
~ , a n ~ , next a
Multpl Multiply and Transfer PL to Accumulator
Value of src. The 16 MSBs
Multiply MR by data memory word, move PL to a n
Execution PH, PL MR * src PC PC + Flags Affected
Multpls
MULTPL, MULAPL, MULAPLS, MULSPL, Mulspls
Example 4.14.46.2 Multpls A2, A2~
Accumulator
Negac Two’s Complement Negation of Accumulator
NEGACS, SUB, SUBB, SUBS, ADD, ADDB, ADDS, NOTAC, Notacs
Example 4.14.47.1 Negac A3~, A3, --A
Negacs Two’s Complement Negation of Accumulator String
Assembly Language Instructions 143
Dest accumulator string
NEGAC, SUB, SUBB, SUBS, ADD, ADDB, ADDS, NOTAC, Notacs
Execution PC PC +
14.49 NOP No Operation
RPT
NOTACS, AND, ANDB, ANDS, OR, ORB, ORS, XOR, XORB, Xors
Notac One’s Complement Negation of Accumulator
NEGAC, Negacs
Example 4.14.50.1 Notac A3~, A3, --A
Accumulator string
Notacs One’s Complement Negation of Accumulator String
Negacs
A3~
TFn bits in Stat register are set accordingly
14.52 or Bitwise Logical or
Accumulator pointers are allowed with some operand types
Or A0, *R0++R5
ORB, ORS, AND, ANDS, XOR, XORS, NOTAC, Notacs
Or TF1, *R6+0x22
148
Or src
14.53 ORB Bitwise or Byte
Accumulator is affected
OR, ORS, AND, ANDS, XOR, XORS, NOTAC, Notacs
PC + w Flags Affected
14.54 ORS Bitwise or String
OR, ORB, AND, ANDS, XOR, XORS, NOTAC, Notacs
ORS A0, A0~, A0
Address is multipled by 4 to get the actual port address
14.55 OUT
OUTS, IN, INS
Port6 specified in the instruction
Outs Output String to Port
OUT, IN, INS
Port6 , An ~
PC TOS
14.57 RET Return From Subroutine CALL, Ccc
R7 R7 Flags Affected
CALL, i.e., RET followed by a RET should not be allowed
Sflag , Stag , Rtag
Rflag Reset Memory Flag
Example 4.14.58.2 Rflag *R6 +
Resets the fractional mode. Clears FM bit of Stat
Reset Fractional Mode Syntax
14.59 RFM
STAT.FM
Saturation output normal mode
Rovm Reset Overflow Mode
Resets the overflow mode to zero
Stat .OM
If RPT adrs8 Load src to repeat counter
14.61 RPT Repeat Next Instruction
Load imm8 to repeat counter
After execution completes
Stag , Rflag , Sflag
Rtag Reset Tag
Rtag *R6+0x0002
Rtag *R6+0x0003
Assembly Language Instructions 159
14.63 RXM Reset Extended Sign Mode
STAT.XM
SXM
Sflag Set Memory Flag
Address flagadrs only accesses the 17 th bit
Rflag , Stag , Rtag
160
Mode for signed fractional arithmetic
14.65 SFM Set Fractional Mode
Assembly Language Instructions 161
Set fractional mode. Set FM bit of Stat to
PH , PL
14.66 SHL Shift Left
Accumulator. Use Shlac for this purpose
Shls
Its offset. LSB of result is set to zero
Shlac Shift Left Accumulator
Shift accumulator A1 by one bit to the left
Example 4.14.67.2 Shlac A1~, A1, --A
Accumulators in the string
Shlacs Shift Left Accumulator String Individually
164
Example 4.14.69.1 Shlapl A0, *R4++R5
Shlapl Shift Left with Accumulate
Shlapl A2, *R1++
Example 4.14.69.3 Shlapl A1, A1, ++A
Shift data memory string left, add PL to a n
Shlapls Shift Left String With Accumulate
Shift a n ~ string left, addb PL to a n ~
Shls Shift Left Accumulator String to Product
Assembly Language Instructions 167
Execution PH, PL
An~
Example 4.14.72.1 Shlspl A0, *R4++R5
Shlspl Shift Left With Subtract PL
Shlspl A2, *R1++
Example 4.14.72.3 Shlspl A1, A1, ++A
Shlspls Shift Left String With Subtract PL
Assembly Language Instructions 169
NS+3 NR+3
Shift RAM string left, subtract PL from An
Example 4.14.74.1 Shltpl A0, *R4++R5
Shltpl Shift Left and Transfer PL to Accumulator
Shltpl A2, *R1++
Example 4.14.74.3 Shltpl A1, A1, ++A
Receives the same data as PH
Shltpls Shift Left String and Transfer PL to Accumulator
SHLTPL, SHLAPL, SHLAPLS, SHLSPL, Shlspls
Shift the accumulator string A1 by nSV bits to the left
Register
Shrac Shift Accumulator Right
Shift right one bit the accumulator A1
Example 4.14.76.2 Shrac A1~, A1, ++A
Shracs Shift Accumulator String Right
Assembly Language Instructions 173
SHRAC, SHL, SHLS, SHLAPL, SHLAPLS, SHLSPL, SHLSPLS, Shltpl
Shltpls
Output DSP mode
Set Overflow Mode Syntax
Sovm
STAT.OM
RTAG, RFLAG, Sflag
Stag
Stag *0x401
Dest, src , src1 , next a
14.80 SUB Subtract
An ~ , An , adrs , next a
An ~ , An ~ , imm16 , next a
SUB A1, A1~, A1
Example 4.14.80.2 SUB A0, A0, 2, ++A
SUB A3~, A3, *R4
SUB R3, R5
Subtract 0x45 from accumulator A2 byte
Subb Subtract Byte
Subtract 0xF2 from register R3 byte
Syntax Description Subb a n, imm8
Subs Subtract Accumulataor String
Assembly Language Instructions 179
NR+2
Subs A2, A2~, A2
Subs A2, A2, A2~
Subs A3~, A3~, PH
180
Sets extended sign mode status register Stat bit 0 to
14.83 SXM Set Extended Sign Mode
Assembly Language Instructions 181
RXM
Push PC + 0x7F00
Vcall Vectored Call
R7 R7 + Flags Affected
See Also RET, IRET, CALL, C cc Example
XOR src For two operands
14.85 XOR Logical XOR
XOR src For three operands
TAG bit is set accordingly Src is flagadrs
Example 4.14.85.1 XOR A1, A1, 0x13FF
XORB, XORS, AND, ANDS, OR, ORS, ORB, NOTAC, Notacs
Example 4.14.85.2 XOR A0, A0, 2, ++A
Xorb Logical XOR Byte
Assembly Language Instructions 185
XOR, XORS, AND, ANDS, OR, ORS, ORB, NOTAC, Notacs
Dest string
Xors Logical XOR String
XOR, XORB, AND, ANDS, OR, ORS, ORB, NOTAC, Notacs
Xors A2, A2~, A2
PC PC + Flags Affected ZF =
14.88 ZAC Zero Accumulator
Zacs
ZAC A1~, ++A
Zacs Zero Accumulator String
Reset the content of offset accumulator string A1~ to zero
Zero the specified accumulator string
ZAC
Instruction Set Encoding
Assembly Language Instructions 189
Instruction Set Encoding
190
Assembly Language Instructions 191
192
Assembly Language Instructions 193
194
Assembly Language Instructions 195
196
Description True condition Not true condition
Assembly Language Instructions 197
Instruction Set Summary
An~, An~ , next a
Pma16 , Rmod Assembly Language Instructions 199
An~, pma16
An, An~
~, adrs , next a
Adrs, a n~ , next a
An ~, imm16 , next a
MR , imm16 , next a
Adrs, TOS
Assembly Language Instructions 201
STR, adrs
Flagadrs† , TFn
~, a n~ , next a
~ , next a
~ , a n~
Adrs An ~, An ~, imm16 , next a ~, a n~, a n , next a
TFn, flagadrs NR+3 TFn, cc , Rx
An~, An~ , next a NR+3 Assembly Language Instructions 203
An~, An~, pma16
An~, An~, An
~, a n, a n~ , next a
~, a n~
~, a n, a n~
~, a n~, PH
Conditional on RZF=0 and RCF=1 Not condition RZF≠ 0 or RCF≠
Conditional on RCF=1 Not condition RCF=0
Conditional on RZF=1 Not condition RZF=0
Conditional on ZF=0 and SF=1 Not condition ZF≠ Or SF≠
Instruction Set Summay
206Assembly Language Instructions
MC = Pllm value+1 ⋅ 131.07 kHz
208Assembly Language Instructions
209
Language Instructions
Summay
Instruction Set Summay 210Assembly Language Instructions
Code Development Tools
Introduction
Code Development Tools
Pin IDC Connector top view looking at the board
Categories of MSP50Cxx Development Tools
MSP50C6xx Development Tools Guidelines
SDK50P614 kit of 15 MSP50P614s
MSP50C6xx Development Tools Guidelines
SPEECH-EVM†PC50C604†
Tools Definitions
MSP50C6xx Development Tools Guidelines
Software Tools-Definitions
Documentation
MSP50C6xx Code Development Tools
System Requirements
Hardware Tools Setup
Green Target board power
Red MSPSCANPORTI/F power Yellow
Assembler Directives
Assembler
Examples
Assembler
#ELSE see #IF and #IFDEF
An assembly language program
#ELSE
#IF expression Do something here
Do other things here
#ENDIF
#IFNDEF symbol
Example #IFDEF symbol
Assembler
Foreword
Compiler
Compiler
External References
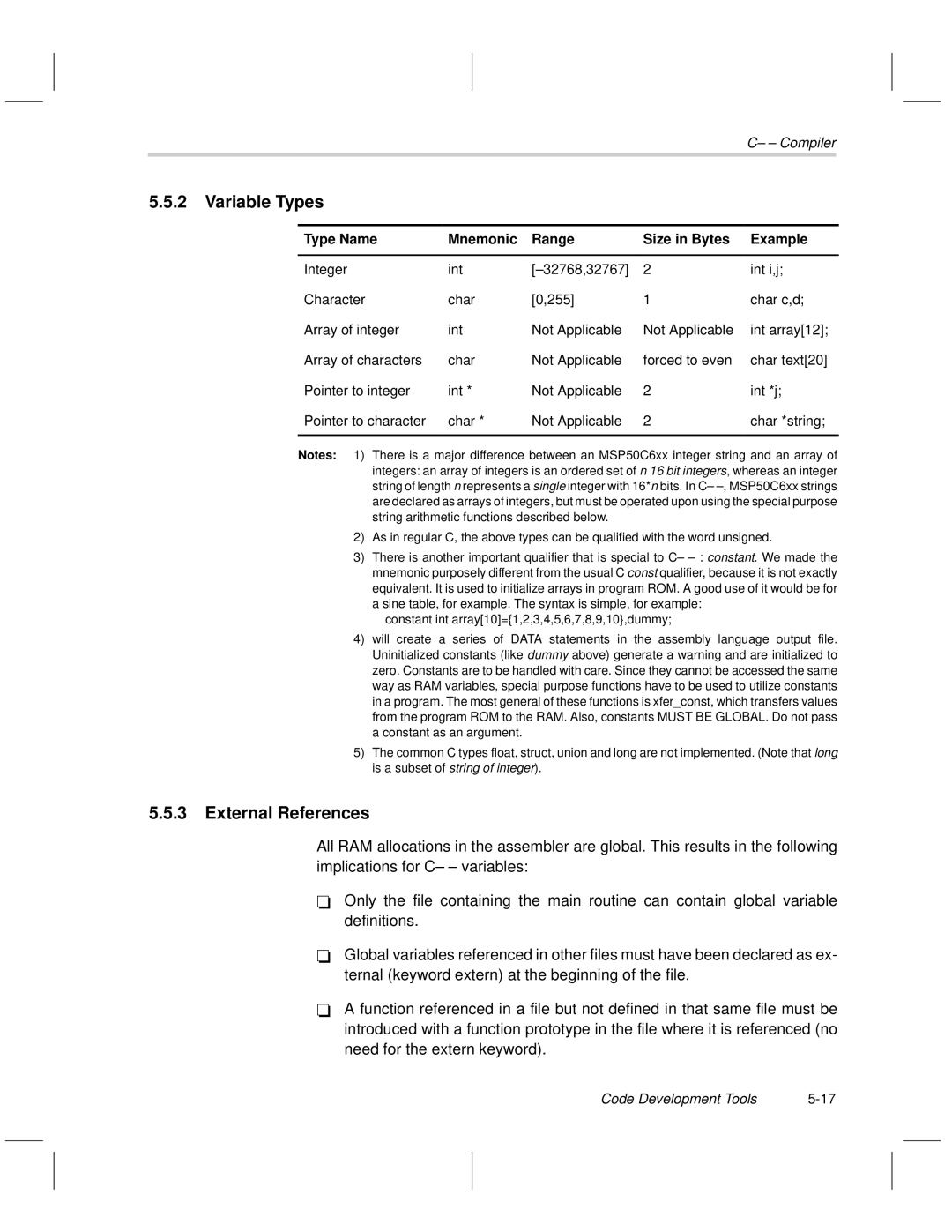
Variable Types
Type Name Mnemonic Range Size in Bytes Example
Directives
Defines a replacement string for a given string
Without Arguments
With Arguments
See #if directive
Include Files
#define STRLENGTHi Major Differences between C and C
Initializations
Function Prototypes and Declarations
RAM Usage
Initialization values are stored in program memory
String Functions
String Functions
Operator can take the following values predefined constants
An example of the use of xferconst is
Constant Functions
Comparisons
Implementation Details
This section is C- specific
Signed comparison of a and b. a is in A0, b is in A0~
Unsigned comparison of a and b. a is in A0, b is in A0~
Assembly Vector
Ult
Ugt
Function Calls
Division
Stack frame has the following structure
Low Address High Address
Cmmfunc bidonint i1,char *i2 is valid, but
Programming Example
On Call
On RET
#include cmmmacr.h
Reserved
Programming Example, C -- With Assembly Routines
Implementation Details
R7Param
Addb R7,2
To C function return in roncoreturn
OldR5 Return Addr Param R7,R5 Stack data
Param R7,R5 Stack data Before call Parameter
Return Addr Param Stack data
To ASM function return
Efficiency
Efficiency
Efficiency
Example 5-1. First Project
Real Time Clock Example
Jrtc.rpj Hmodules
MAINRAM.IRX
Allocated by changing
Efficiency
CMM1.ASM
Allocated as follows
Sixth file, cmm1ram.asm, allocates memory for cmm1.asm
MAIN.CMM
Example 5-2. Second Project C-- With Speech
Util.obj
Celp Celp.irx
Dspvar.irx dsputil.asm getbits.asm speak.asm speak.irx
Isr Tim2isr.asm dacisr.asm J tim1isr.asm
Melp
Tens.qfm
Ampm.qfm
Dsp
Ramendcustomer Ramstartcustomer
New C-- callable functions were declared global
Assembly routines that will be called are declared external
Clock will need to say
Cmmfunc speakHours
Example 5-3. Third Project C-- with an LCD
Lcd Lcd.asm Lcd.irx
Melp.irx Melp.obj
Celp Ampm.qfm Days.qfm Ones.qfm Teens.qfm
External lcdsetio external lcdinit
Case
Efficiency
Beware of Stack Corruption
Beware of Stack Corruption
Reported Bugs With Code Development Tool
Reported Bugs With Code Development Tool
Applications
Application Circuits
Application Circuits
MSP50P614 only 100 kΩ
∝ F 22 pF
3300 pF
Applications6-3
Initializing the MSP50C6xx
Initializing the MSP50C6xx
Applications6-5
File init.asm
JNZ Itsacpart Itsappart
Applications6-7
Getting Started
TI-TALKS Example Code
TI-TALKS Example Code
Creating a New Project
RAM Overlay
RAM Overlay
Applications6-9
Adding Customer Variables
RAM Overlay
Common Problems
Page
Customer Information
Die Bond-Out Coordinates
Mechanical Information
Package Information
Customer Information
Signal and Pad Descriptions for the MSP50C614
Signal and Pad Descriptions for the MSP50C605
Signal and Pad Descriptions for the MSP50C601
Signal and Pad Descriptions for the MSP50C604
Pin QFP Mechanical Information
13 NOM
Extra pin 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Bottom View
13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Bottom view
Bottom View of 120-Pin PGA Package of the MSP50P614
Customer Information Fields in the ROM
Customer Information Fields in the ROM
0x0006 Device number 0x0614
Speech Development Cycle
Speech Specification
Device Production Sequence
Software Design Hardware Design
Device Production Sequence
New Product Release Forms Nprf
Ordering Information
6xx
Code Letter PJM Loopin 100-Pin QFP
New Product Release Forms Nprf
Approval of Prototypes and Authorization to Start Production
NEW Product Release Form for MSP50C604 Option Selection
New Product Release Forms Nprf
NEW Product Release Form for MSP50C605 Option Selection
New Product Release Forms Nprf
NEW Product Release Form for MSP50C601 Option Selection
New Product Release Forms Nprf
Topic
Additional Information
Additional Information
Additional Information