OfficeConnect Isdn LAN Modem
Santa Clara, California
3Com Corporation
Bayfront Plaza
95052-8145
Table of Contents
Hardware Description and Installation
Advanced Configuration
Supplementary Voice Call Services
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Glossary Index 3COM Corporation Limited Warranty
About this Guide
How to Use
Shows where to find specific information in this guide
This Guide
Icon Description
Conventions
List conventions that are used throughout this guide
Convention Description
Introduction
Access to the Internet
Introduction
Applications
Network locally
Access to a Remote Office
A Remote Office
High Performance
Features
Ease of Installation and Use
Connectivity
Bandwidth Management
Remote management using the same Web browser interface
Voice Features
Remote Management
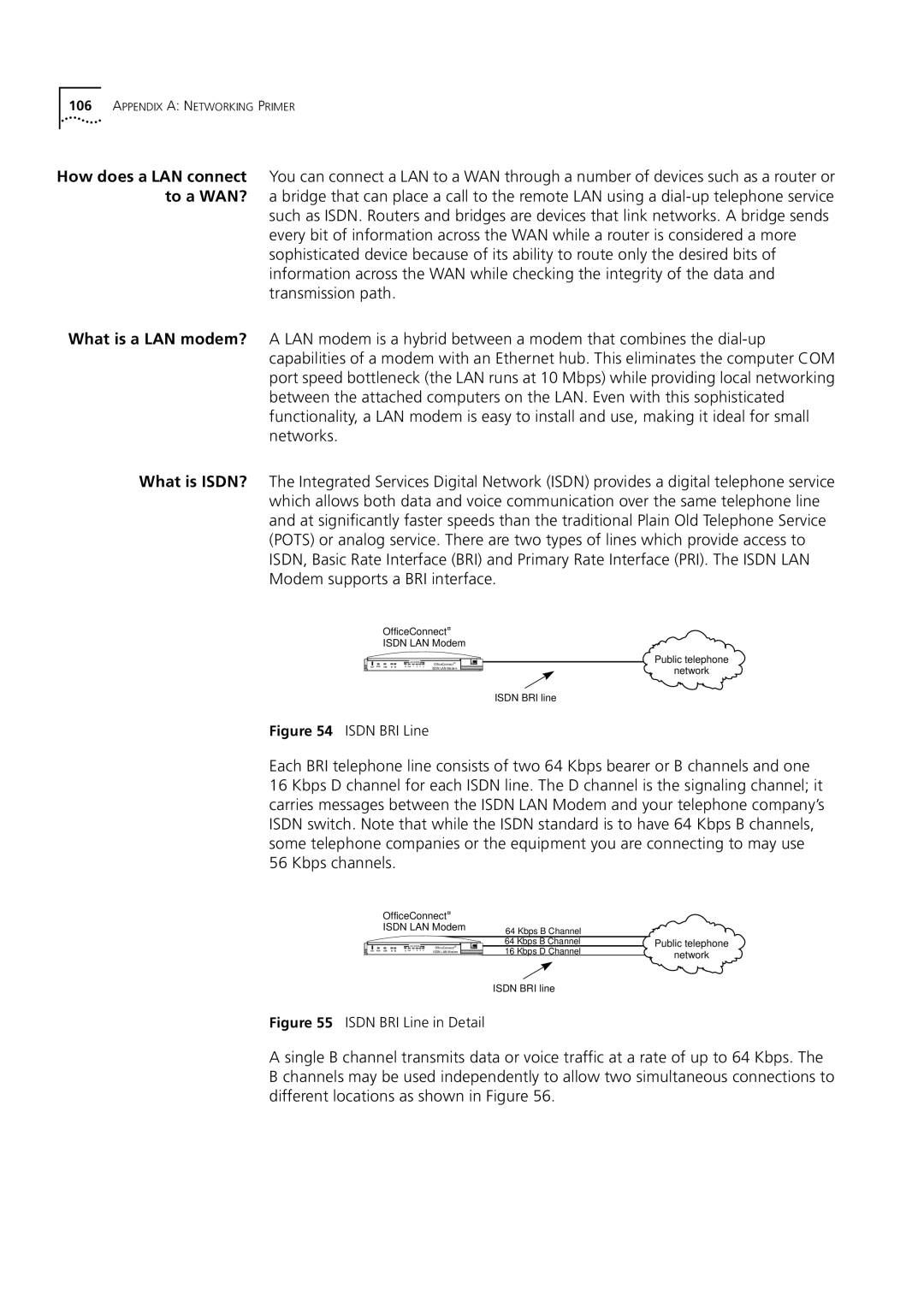
Isdn Standards and Interface
Diagnostics
Warranty
Security
Introduction
Connection Types
Functionality Description
An example of a single connection is shown in Figure
Application Sharing over the LAN
LAN
Location connection to a remote office LAN
Kbps B2
Destination
Translation
Call Routing While No Other Calls Are Connected
Understanding Multilink PPP
What is Multilink PPP?
What is BACP/BAP?
Call Routing While One Call Is Already Connected
Dynamic Bandwidth
Multilink PPP Configuration Options
Understanding
Allocation
Pptp
Understanding VPNs
Network
For Windows Dial-Up Networking Users
Before You Install
Hardware Description Installation
Package Contents
Isdn LAN Modem
Front panel provides the following LEDs
Front Panel LED Description
Color Description
Description
Installing the Isdn LAN Modem
Before You Begin
Installing the Isdn Cable To install the Isdn cable
10BASE-T Ethernet Port
Common scenario, is as follows
10BASE-T Hub-to-Hub Connection
Telephone standard, their operation is not guaranteed
Analog Equipment Connection
Wall Mounting the Isdn LAN Modem
Installing the Power To install the power cable
Cable
Using Rubber Feet and Stacking Clips
Using Stacking Clips
You may be prompted for your installation disks or CD-ROM
Setting UP TCP/IP for Windows Macintosh
TCP/IP Setup Using
Windows 98
Select Network Component Type Dialog Box
TCP/IP Setup Using Windows 98 and Windows 95
You will need your Windows NT 4.0 installation CD-ROM
Have not already set up TCP/IP, do the following
Windows NT
TCP/IP Setup Using Windows NT 4.0
Network Protocols Group Box
TCP/IP Setup Using Mac OS 7.6 or later
From the Network group box, click Network Setup
Select Unlisted or Update Protocol and then click OK
TCP/IP Setup Using Windows 3.11
Setting UP TCP/IP for Windows and Macintosh
Before You Begin
Configuring the Isdn LAN Modem
Typical Configuration
Displayed on your computer
Addresses
For Windows 98 and 95 Users
For Windows NT 4.0 Users
For Macintosh Users
Uncheck Enable Automatic Dhcp Configuration
You are asked to restart your computer Click OK
For Windows 3.11 Users
Configuring the Isdn LAN Modem for the Typical Configuration
Click Continue
Set Password Window
ISP Wizard Window
Click Continue
Click Continue
Main
Isdn LAN Modem WebWizard Main
Isdn LAN Modem Main
Configuring the Isdn LAN Modem
Advanced Configuration
Main configuration page, do the following
When to Select ISP
Direct Connection to an ISP
Setting Up a Connection to the Internet
When to Select Private Network
To an ISP
ISP Service Provider Selection Window
Setting Up Additional Service Providers
Setting Up a Connection to a Remote LAN
Private Network Service Provider Selection Window
Advanced Configuration
Setting Up Additional Service Providers
Editing Service
Provider Profiles
Restricting
Accessing Service Providers
Configuring Your LAN
Workstations from
IP Address and Subnet Mask
Enable Dhcp Server
Enable NetBIOS Filtering
Local Domain Name
Changing Data Call Parameters
Disconnecting a Manual Data Call
Disconnecting an Automatic Data Call
Minimum Call Duration
Connect/Disconnect Threshold for the Second B Channel
Connect Delay
Disconnect Delay
Call Parameters
Default Voice Call Routing Configuration
Addresses
Selective Password
Reserving Dhcp
Protection
Isdn LAN Modem, do the following
Password
Changing Your
OfficeConnect Isdn LAN Modem Isdn Information Sheet
Isdn Parameters Screen
LAN Modem Remotely Following
Configuring the Isdn LAN Modem from a Remote Location
Configuring the Isdn
Via an Isdn Modem
Click TCP/IP Settings
Advanced Configuration
Supplementary Voice Services
Supplementary Voice Call Services
Descriptions of each supplementary voice service follow
Waiting
On port 1 and disabled on port
Call Waiting
Click Isdn Parameters
How Do Do This
Caller ID Date and Time
Caller ID
Go to the Isdn LAN Modem’s main page http//3com.oc.lanmodem
Flexible Calling
Be enabled on your second telephone number as well
To enable or disable Flexible Calling, do the following
Isdn LAN Modem
Received or have placed the first call
Call Conference
Three-Way Calling
Order to activate Call Conference
Through the Isdn LAN Modem
Call Forwarding
Reminder that Call Forwarding is still in effect
Supplementary Voice Call Services
Placing a Call
PLACING, Receiving Disconnecting Calls
Placing Calls
Automatically
Placing a Call Manually
To an Existing Service
Manually
Provider
Placing Multilink PPP
Participating in a
Temporary Call
Calls
Automatically
Disconnecting Data
Calls
Manually
Idle Timeout
Seconds, a second B channel is added, if not already in use
PLACING, Receiving and Disconnecting Calls
Troubleshooting Maintenance
Unauthorized opening of the unit will void the warranty
Instructions to resolve the problem
Monitoring LEDs
LEDs
LED State Possible Cause Solution
B1/B2
Solutions
Evaluating Symptoms
Solutions
Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions Possible Cause
Symptom Possible Cause Solution
For call coming up
To Use two B Channels
Enabled on your Isdn line
Negotiation will not be successful
Information
Isdn LAN Modem Resetting the Isdn LAN Modem
Finding More
Contacting Technical
System
System Statistics Description
Isdn Line Information Description
Information
Call Information
Current Call For This Call Information Type Description
Understanding Last Call Information
For This Call Last Call Information Type Description
Service Provider Information Description
Provider Information
Networking Primer
Example of a LAN
How does a LAN connect to a WAN?
What is a network?
What is an IP Address? What is a Subnet Mask?
Subnet Mask
What is a network?
Appendix a Networking Primer
Using the Custom WEB Browser
Configuration and information Web sites
Internet Explorer
Using Favorites
Installing the Custom
Browser
Isdn LAN Modem Factory C Defaults
Appendix C Isdn LAN Modem Factory Defaults
Power
Refer to for the Isdn LAN Modem specifications
Environmental Operating Range
Year 2000 Compliance
Ordering Isdn Service
EZ-ISDN 1A
This completes the procedure for ordering your Isdn line
Limitations of Isdn Ordering Codes U EZ-ISDN 1, V
Simultaneous Voice Data on the Same Telephone Number
For Siemens Ewsd Switches
Numbers For Lucent Technologies 5ESS Switches
Call Forwarding Variable -- for Call Forwarding
For Nortel DMS-100Switches
Capabilities
Table of Isdn
Ordering Code
Codes for use with the Isdn LAN Modem
Glossary
Channel to call
Firmware IP address
Kbps Layer
Glossary
Glossary
Index
127
UDP
3Com Corporation Limited Warranty
Declaration
Canadian Notice