Chapter 1 Cisco Analog Telephone Adaptor Overview
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Overview
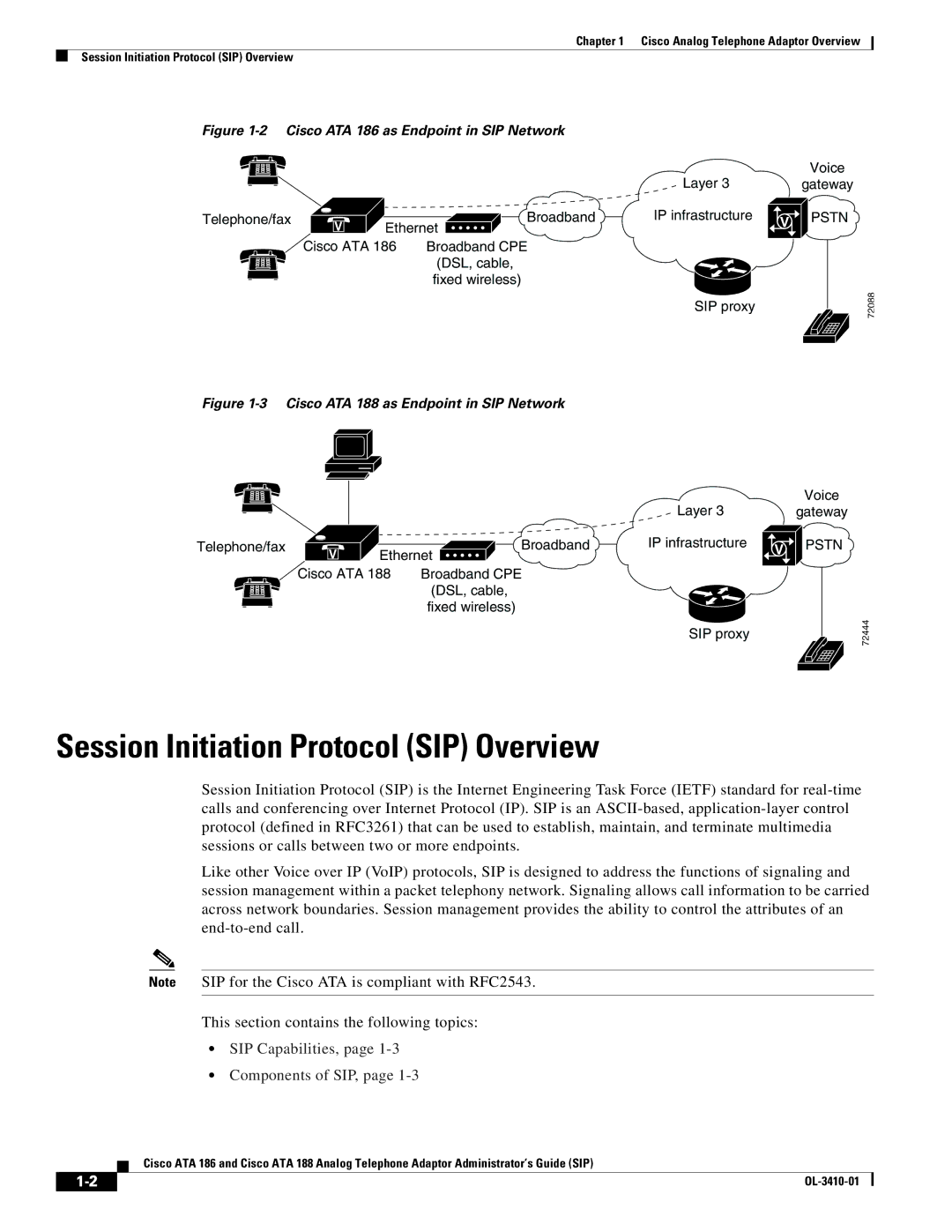
Figure 1-2 Cisco ATA 186 as Endpoint in SIP Network
|
|
|
| Layer 3 |
Telephone/fax | V |
| Broadband | IP infrastructure |
| Ethernet |
| ||
| Cisco ATA 186 | Broadband CPE |
| |
|
|
| (DSL, cable, |
|
|
|
| fixed wireless) |
|
SIP proxy
Voice
gateway
V | PSTN |
|
72088
Figure 1-3 Cisco ATA 188 as Endpoint in SIP Network
|
|
|
| Layer 3 |
Telephone/fax | V |
| Broadband | IP infrastructure |
| Ethernet |
| ||
| Cisco ATA 188 | Broadband CPE |
| |
|
|
| (DSL, cable, |
|
|
|
| fixed wireless) |
|
SIP proxy
Voice
gateway
V | PSTN |
|
72444
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Overview
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard for
Like other Voice over IP (VoIP) protocols, SIP is designed to address the functions of signaling and session management within a packet telephony network. Signaling allows call information to be carried across network boundaries. Session management provides the ability to control the attributes of an
Note SIP for the Cisco ATA is compliant with RFC2543.
This section contains the following topics:
•SIP Capabilities, page 1-3
•Components of SIP, page 1-3
Cisco ATA 186 and Cisco ATA 188 Analog Telephone Adaptor Administrator’s Guide (SIP)
| ||
|