Chapter 1 Cisco Analog Telephone Adaptor Overview
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Overview
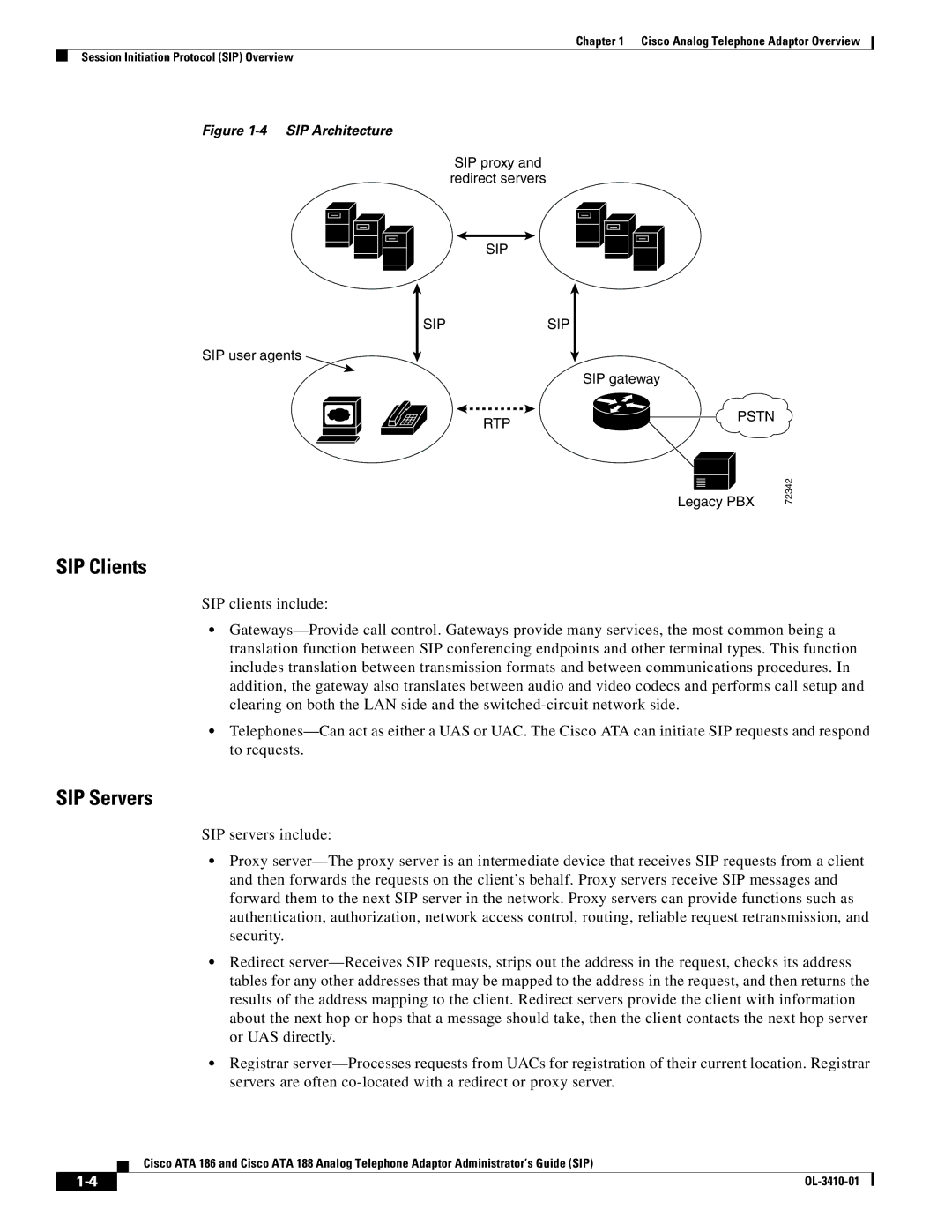
Figure 1-4 SIP Architecture
SIP proxy and redirect servers
SIP
SIP user agents
SIP |
| SIP |
|
|
| SIP gateway |
|
| RTP | PSTN |
|
|
|
| |
|
| Legacy PBX | 72342 |
|
|
|
SIP Clients
SIP clients include:
•
•
SIP Servers
SIP servers include:
•Proxy
•Redirect
•Registrar
Cisco ATA 186 and Cisco ATA 188 Analog Telephone Adaptor Administrator’s Guide (SIP)
| ||
|