Text Part Number OL-2159-05
Corporate Headquarters
Copyright 2001-2003, Cisco Systems, Inc All rights reserved
Iii
N T E N T S
Navigating Using the Map Windows
Native Vlan ID
WEP Not Set on the Wireless Phone
Vii
Settings on the Authenticator Configuration
Viii
Event Notifications Setup
Setting Up Administrator Authorization
Snmp Setup
Ssid
Xii
Xiii
Audience and Scope
Organization
Xiv
Conventions
Tip Means the following are useful tips
Cisco.com
Related Publications
Obtaining Documentation
Xvi
Documentation CD-ROM
Ordering Documentation
Documentation Feedback
Xvii
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco TAC Website Opening a TAC Case
TAC Case Priority Definitions
Xviii
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
A P T E R
Overview
Key Features
Roaming Client Devices
Quality of Service Support
Management Options
These documents are available on Cisco.com
What is QoS?
Limitations and Restrictions
Related Documents
Vlan Support
What is a VLAN?
Incorporating Wireless Devices into VLANs
Vlan Example
Level of Access
Root Unit on a Wired LAN
Network Configuration Examples
Access Points as Root Units on a Wired LAN
Repeater Unit that Extends Wireless Range
Access Point as Repeater
Central Unit in an All-Wireless Network
Using the Management Interfaces
Button/Link Description
Using the Web-Browser Interface
Using the Web-Browser Interface for the First Time
Using the Management Pages in the Web-Browser Interface
Map Window with Network Ports Pages Expanded
Navigating Using the Map Windows
Preparing to Use a Terminal Emulator
Using the Command-Line Interface
Setting Up the Terminal Emulator
Changing Settings with the CLI
Connecting the Serial Cable
Function Description
Selecting Pages and Settings
Applying Changes to the Configuration
Using Snmp
Using a Telnet Session
Supported MIBs
Radio Configuration and Basic Settings
Express Setup
Basic Settings
MAC Address
Entering Basic Settings
Express Setup page contains the following settings
System Name
Default Gateway
Configuration Server Protocol
Default IP Address
Default IP Subnet Mask
Root-Unit Access Points
Radio Network Optimization Optimize Radio Network For
Security Setup Link
Radio Network Compatibility Ensure Compatibility With
Radio Configuration
Snmp Admin. Community
Entering Identity Information
Settings on the AP Radio Identification
Service Set ID Ssid
Primary Port Settings
Default IP Address
Default IP Subnet Mask
Entering Radio Hardware Information
Leap Password
Allow Broadcast Ssid to Associate?
Settings on the AP Radio Hardware
AP Radio Hardware page contains the following settings
Data Rates
Enable World Mode
Max. RTS Retries
Transmit Power
Frag. Threshold
RTS Threshold
Restrict Searched Channels
Default Radio Channel
Search for Less-Congested Radio Channel
Receive Antenna and Transmit Antenna
Entering Advanced Configuration Information
AP Radio Advanced Page for Internal Radio
Packet Forwarding
Settings on the AP Radio Advanced
AP Radio Advanced pages contain the following settings
Requested Status
Ssid For Use By Infrastructure Stations
Default Multicast Address Filters
Maximum Multicast Packets/Second
Radio Cell Role
Classify Workgroup Bridges as Network Infrastructure
Use Aironet Extensions
Ethernet Encapsulation Transform
Quality of Service Setup Link
Vlan Setup Link
Require Use of Radio Firmware
Broadcast WEP Key rotation interval sec
Advanced Primary Ssid Setup Link
Preferred Access Points
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
Radio Preamble
Radio Modulation
Non-Root Mobility
Ethernet Configuration
Entering Ethernet Hardware Information
Settings on the Ethernet Identification
Speed
Settings on the Ethernet Hardware
Ethernet Hardware page contains the following settings
Loss of Backbone Connectivity Ssid
Loss of Backbone Connectivity # of Secs
Loss of Backbone Connectivity Action
Ethernet Advanced page contains the following settings
Settings on the Ethernet Advanced
Default Unicast and Multicast Address Filters
Optimize Ethernet for
Default Unicast Address Filter
Always Unblock Ethernet When STP is Disabled
OL-2159-05
Configuring VLANs
Entering Vlan Information
Settings on the Vlan Setup
Vlan setup page contains the following settings
Vlan 802.1Q Tagging
802.1Q Encapsulation Mode
Maximum Number of Enabled Vlan IDs
Vlan Summary Status Link
Vlan Name
Vlan Security Policy
Single Vlan ID which allows Unencrypted packets
Optionally allow Encrypted packets on the unencrypted Vlan
TKIP/MIC
Native Vlan Configuration
Broadcast Domain Segmentation
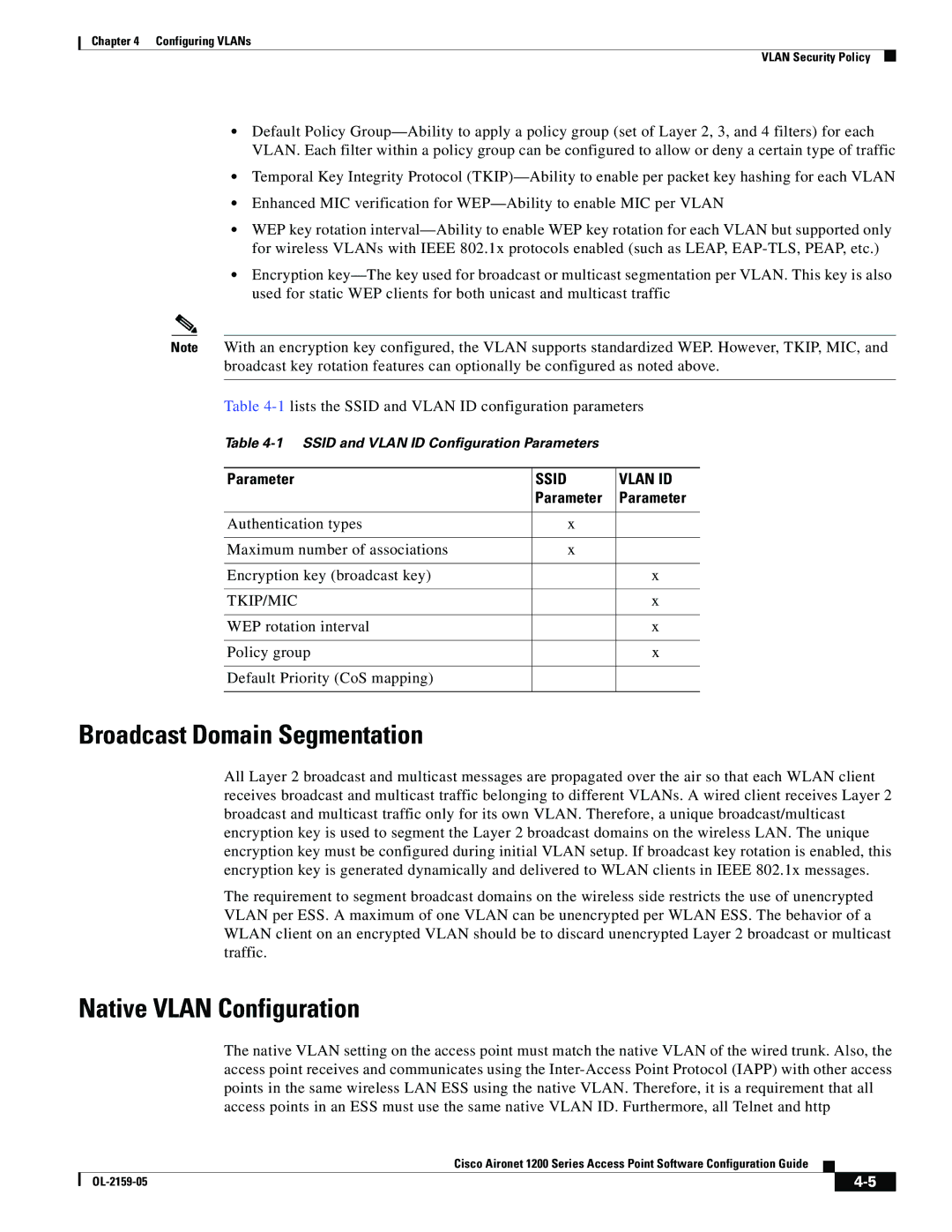
Parameter
Deployment of Infrastructure and Non infrastructure Devices
Primary and Secondary SSIDs
Vlan ID
RADIUS-Based Vlan Access Control
Vlan
Criteria for Deploying Wireless VLANs
Wireless Vlan Deployment Example
5shows the wireless Vlan deployment scenario described above
Creating the Native Vlan
Using the Configuration Screens
Obtaining and Recording Vlan ID and Setup Information
Creating and Configuring VLANs on the Access Point
Vlan Setup
Vlan ID #1 Setup
Creating the Full- and Part-Time VLANs
Creating the Guest Vlan
Creating the Maintenance Vlan
Creating and Configuring the SSIDs
AP Radio Internal Service Sets
Configuring VLANs Wireless Vlan Deployment Example
Enabling Vlan 802.1Q Tagging and Identifying the Native Vlan
11 AP Radio Service Sets
Creating an Ssid for Infrastructure Devices
Guidelines for Wireless Vlan Deployment
OL-2159-05
Configuring Filters and QoS
Protocol Filtering
Filter Setup
Enter a descriptive filter set name in the Set Name field
Creating a Protocol Filter
Filter Set
Enabling a Protocol Filter
Address Filters
MAC Address Filtering
Creating a MAC Address Filter
AP Radio Advanced
AP Radio Primary Ssid
QoS Configuration
Generate Qbss Element
Settings on the Quality of Service Setup
Use Symbol Extensions
Traffic Category
Applying QoS
By Station
Send Igmp General Query
10 Protocol Filters Setup
12 Vlan ID
By Vlan
By Filter
13 Filters Priority Setting
By Dscp Value
By CoS Value
17 Vlan Setup
Wireless QoS Deployment Example
18 Vlan ID #xx
WEP Not Set on the Wireless Phone
WEP Set on the Wireless Phone
20 AP Radio Internal Service Sets
21 AP Radio Internal Service Sets
OL-2159-05
Configuring Proxy Mobile IP
Introduction to Mobility in IP
Proxy Mobile IP
Mobile IP Explained
Nomadic Approach
Mobile Approach
Mobile IP Environment
Mobile IP Traffic Pattern
Proxy Mobile IP Explained
Before Deploying Proxy Mobile IP
Components of a Proxy Mobile IP Network
Issues to Consider While Deploying Proxy Mobile IP
Agent Discovery
How Proxy Mobile IP Works
Home Agent Subnet Mask
Subnet Map Exchange
Tunneling
Registration
Proxy Mobile IP Security
Proxy Mobile IP Setup
General
Proxy Mobile IP Setup
Authoritative AP n
Authentication Server
Settings on the Proxy Mobile IP General
Enable Proxy Mobile IP
Settings on the Authenticator Configuration
Local SA Bindings
Settings on the Local SA Bindings
Statistics
Settings on the Proxy Mobile IP Statistics
MN IP Addresses
Authentication Failures for HA
Authentication Failures for FA
Active AAP
View Subnet Map Table
Configuring Proxy Mobile IP
Settings on the Subnet Map Table
Configuring Proxy Mobile IP on Your Wired LAN
11 a Sample Network
13 AP Radio Internal Service Sets
15 Proxy Mobile IP General
17 Subnet Map Table
18 Authenticator Configuration
20 Network Configuration Screen for an Access Point Client
22 Passed Authentication Screen
Configuring Other Settings
Entering Time Server Settings
Server Setup
Settings on the Time Server Setup
Boot Server Setup page contains the following settings
Entering Boot Server Settings
Settings on the Boot Server Setup
Dhcp Multiple-Offer Timeout sec
Configuration Server Protocol
Use Previous Configuration Server Settings
Bootp Server Timeout sec
Option Definition
Dhcp Requested Lease Duration min
Dhcp Minimum Lease Duration min
Dhcp Client Identifier Type
Dhcp Class Identifier
Settings on the Web Server Setup
Web Server Setup page contains the following settings
Dhcp Client Identifier Value
Http Port
Default Help Root URL
Default Web Root URL
Allow Non-Console Browsing
Domain Name System
Entering Name Server Settings
Settings on the Name Server Setup
Default Domain
Domain Name Servers
Entering FTP Settings
Settings on the FTP Setup
FTP Setup page contains the following settings
Routing Setup
Routing Setup page contains the following settings
Entering Routing Settings
New Network Route Settings
Association Table Filters
Association Table Display Setup
Installed Network Routes list
Configuring Other Settings Association Table Display Setup
Fields to Show
Settings on the Association Table Filters
Stations to Show
Primary Sort
Association Table Advanced
Packets To/From Station
Bytes To/From Station
Association Table Advanced
Settings on the Association Table Advanced
Maximum Number of Forwarding Table Entries
Rogue AP Alert Timeout minutes
Handle Station Alerts as Severity Level
Maximum number of bytes stored per Station Alert packet
Default Activity Timeout seconds Per Device Class
Event Notification Setup
Event Display Setup
Settings on the Event Display Setup
Severity Level Description
How should time generally be displayed?
How should Event Elapsed non-wall-clock Time be displayed?
Severity Level at which to display events
Event Handling Setup
10 The Event Handling Setup
Maximum number of bytes stored per Alert packet
Settings on the Event Handling Setup
Disposition of Events
Handle Station Events as Severity Level
Purge Trace Buffer
Event Notifications Setup
Clear Alert Statistics
Snmp Trap Community
Settings on the Event Notifications Setup
Should Notify-Disposition Events generate Snmp Traps?
Snmp Trap Destination
Ieee Snmp Traps Should Generate the Following Notifications
Should Syslog Messages use the Cisco Emblem Format?
Syslog Destination Address
Syslog Facility Number
Security Setup
Levels of Security
Encrypting Radio Signals with WEP
Security Overview
Network Authentication Types
Additional WEP Security Features
Sequence for EAP Authentication
Wired LAN Client
Sequence for Open Authentication
Combining MAC-Based, EAP, and Open Authentication
Protecting the Access Point Configuration with User Manager
Setting Up WEP
Transmit? Key Contents
Key Access Point Associated Device
Not set
Snmp Variable WEP Full WEP Off
Enabling Additional WEP Security Features
Using Snmp to Set Up WEP
Enabling Message Integrity Check MIC
AP Radio Advanced Page for Internal Radio
Enabling Temporal Key Integrity Protocol Tkip
Enabling Broadcast WEP Key Rotation
Setting Up Open or Shared Key Authentication
Enabling EAP on the Access Point
Setting Up EAP Authentication
Firmware Version Draft 802.1x-2001
Access Point EAP Settings for Various Client Configurations
Enabling EAP in Cisco Secure ACS
Click Add New Access Server
Setting a Session-Based WEP Key Timeout
Setting Up a Repeater Access Point As a Leap Client
AP Radio Identification Page for Internal Radio
Enabling MAC-Based Authentication on the Access Point
Setting Up MAC-Based Authentication
11 Authenticator Configuration
Security Setup Setting Up MAC-Based Authentication
12 AP Radio Advanced
Authenticating Client Devices Using MAC Addresses or EAP
Enabling MAC-Based Authentication in Cisco Secure ACS
Leap
Summary of Settings for Authentication Types
Authentication Types Required Settings
EAP-TLS, EAP-MD5
Attribute ID Description
Radius Attributes Sent by the Access Point
VSA attribute Nas-location Vlan-id Auth-algo-type
Acct-Delay-Time
Acct-Session-Id
Acct-Authentic
Acct-Terminate-Cause
Setting Up Backup Authentication Servers
Setting Up Administrator Authorization
Creating a List of Authorized Management System Users
14 Security Setup
16 User Management Window
Click Apply. You are returned to the User Information
Setting up Centralized Administrator Authentication
Click User Information. The User Information page appears
Click Add New User. The User Management window appears
18 Authenticator Configuration
System Flow Notes
Authorization Parameters
Network Management
Browsing to Network Devices
Using the Association Table
Setting the Display Options
Station
Using Station Pages
Station Identification and Status
Information on Station Pages
From Station Information
Rate, Signal, and Status Information
To Station Information
Performing a Ping
Performing Pings and Link Tests
Hops and Timing Information
Click Link Test
Performing a Link Test
Clearing and Updating Statistics
Using the Network Map Window
Deauthenticating and Disassociating Client Devices
Using Cisco Discovery Protocol
MIB for CDP
Settings on the CDP Setup
Port Assignments
Assigning Network Ports
Settings on the Port Assignments
Enabling Wireless Network Accounting
Accounting Setup
Settings on the Accounting Setup
Attribute Definition
Accounting Attributes
Radiusipadr
OL-2159-05
10-1
Managing Firmware and Configurations
10-2
Full Update of the Firmware Components
Updating Firmware
Updating with the Browser from a Local Drive
10-3
Selective Update of the Firmware Components
10-4
Updating from a File Server
10-5
Update All Firmware From File Server
10-6
Update Firmware From File Server
10-7
Retrieving Firmware and Web Page Files
10-8
Distributing Firmware
10-9
Distributing a Configuration
10-10
Limiting Distributions
10-11
Downloading the Current Configuration
10-12
Uploading a Configuration
Uploading from a Local Drive
Uploading from a File Server
10-13
Resetting the Configuration
10-14
Restarting the Access Point
11-1
Management System Setup
11-2
Snmp Setup
Settings on the Snmp Setup
11-3
Using the Database Query
Settings on the Database Query
11-4
Console and Telnet Setup
Changing Settings with the Database Query
11-5
Settings on the Console/Telnet
Using Secure Shell
11-6
12-1
Special Configurations
12-2
Setting Up a Repeater Access Point
12-3
12-4
12-5
Using Hot Standby Mode
12-6
12-7
12-8
13-1
Sections in this chapter include
13-2
Using Diagnostic Pages
Network Diagnostics
Selections on the Network Diagnostics
13-3
Radio Diagnostics Tests
13-4
Vlan Summary Status
SSIDs Int, Mod
13-5
Network Ports
13-6
Identifying Information and Status
Data Received
13-7
Data Transmitted
Ethernet Port
13-8
Configuration Information
Receive Statistics
13-9
AP Radio
Transmit Statistics
AP Radio Port
13-10
13-11
13-12
Display Options
13-13
Display Settings
Event Log
13-14
Log Headings
Saving the Log
Event Log Summary
13-15
Using Command-Line Diagnostics
Command Information Displayed
13-16
Entering Diagnostic Commands
13-17
Diagnostic Command Results
Eapdiag1on
13-18
Eapdiag2on
Vxdiagarpshow
13-19
13-20
Vxdiagcheckstack
13-21
Vxdiaghostshow
13-22
Vxdiagi
13-23
Vxdiagipstatshow
13-24
Vxdiagmemshow
13-25
Vxdiagmuxshow
13-26
Vxdiagrouteshow
13-27
Vxdiagtcpstatshow
13-28
Reserving Access Point Memory for a Packet Trace Log File
Tracing Packets
Vxdiagudpstatshow
13-29
Tracing Packets for Specific Devices
13-30
Tracing Packets for Ethernet and Radio Ports
Viewing Packet Trace Data
Packets Stored in a Log File
13-31
Checking the Top Panel Indicators
Packets Displayed on the CLI
13-32
Message Ethernet Status Radio Meaning Type Indicator
13-33
Finding an Access Point by Blinking the Top Panel Indicators
13-34
Checking Basic Settings
EAP Authentication Requires Matching 802.1x Protocol Drafts
WEP Keys
13-35
Firmware Version Draft
13-36
Resetting to the Default Configuration
13-37
13-38
Channels, Power Levels, and Antenna Gains
Regulatory Domains
Channels
Ieee 802.11a
Ieee 802.11b
Maximum Power Levels and Antenna Gains
Americas -A 100 Eirp maximum 13.5 Emea -E MW Eirp maximum
Maximum Power Level mW
Regulatory Domain Antenna Gain dBi Maximum Power Level mW
Regulatory Domain With 6-dBi Antenna Gain
Regulatory Domain Antenna Gain dBi Maximum Power Level mW
OL-2159-05
Protocol Filter Lists
ISO Designator
Protocol
Smtp
UDP XNS-IDP ISO-TP4 ISO-CNLP Cnlp
Vines
SVP
POP2
Tftp
Http
Tsap
RIP
Cmot
BGP
IRC
RFE
Radius
CVS
Event Log Messages
With a timestamp, messages look like this example
Default Format
Message Formats
Cisco Emblem Format
Logalert
Loginfo
Syslog Severity Emblem Severity
Logemerg
Reason
Message Descriptions
Possible Cause or
Severity Event Description Mnemonic Recommended Action
Host
Device
IfDescr
Newaddr
Srchost
Srchost to port ifDescr
Desthost length pktLen
Reqlen bytes
Desthost on port ifDescr
IfDescr error= errornum
Packet from srchost to desthost
From srchost to desthost on port
IfDescr error=erronum
For procedure on port ifDescr
Srchost to desthost on port
Srchost on port ifDescr
Desthost
Version
Srchost to desthost of unknown
Prtrarpip
Sysreboot
Rebootinf
Admin
Port device
Status
PktLen
IfDescr errno=errno
Ethercon
ENC WEP
Unenc
Xidexp
Media port
Frame
Frame bytes
Unit
Username Failed
Username
Port devName unit
Hstndbyeth
1XVER
Hstndbyen
Assoclost
Nulses
Instkey
Acctcon
Amngrreq
Open
Norbuf
Nosbuf
Noaserv
VlanID
IfIndex Awcmib
IfIndex MIB
Taskstarted
Nomibdkey
Badsize
Taskfailed
SsidIdx
Statuses and Reasons
Appendix C Event Log Messages Statuses and Reasons
OL-2159-05
IN-1
Numerics
Dtim
CDP MIB
Dhcp
CLI
IN-3
IN-4
Ethernet Locate unit by flashing LEDs
Radio traffic
IN-5
Pspf
IN-6
SSH
Vlan
IN-7
Warm restart
IN-8