Cisco EtherSwitch Service Modules Feature Guide
Network Configuration Examples
Table 6 | Providing Network Services (continued) | |
|
| |
Network Demands | Suggested Design Methods | |
|
| |
High demand on network redundancy | • Use switch stacks, where all stack members are eligible stack masters in case of | |
and availability to provide always on | stack master failure. All stack members have synchronized copies of the saved and | |
running configuration files of the switch stack. | ||
|
| • |
|
| • Use Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) for cluster command EtherSwitch |
|
| service module and router redundancy. |
|
| • Use VLAN trunks, |
|
| balancing on the uplink ports so that the uplink port with a lower relative port cost |
|
| is selected to carry the VLAN traffic. |
|
| |
An evolving demand for IP telephony | • Use QoS to prioritize applications such as IP telephony during congestion and to | |
|
| help control both delay and jitter within the network. |
|
| • Use internal interfaces that support at least two queues per port to prioritize voice |
|
| and data traffic as either high- or |
|
| Cisco EtherSwitch service module supports at least four queues per port. |
|
| • Use voice VLAN IDs (VVIDs) to provide separate VLANs for voice traffic. |
|
|
|
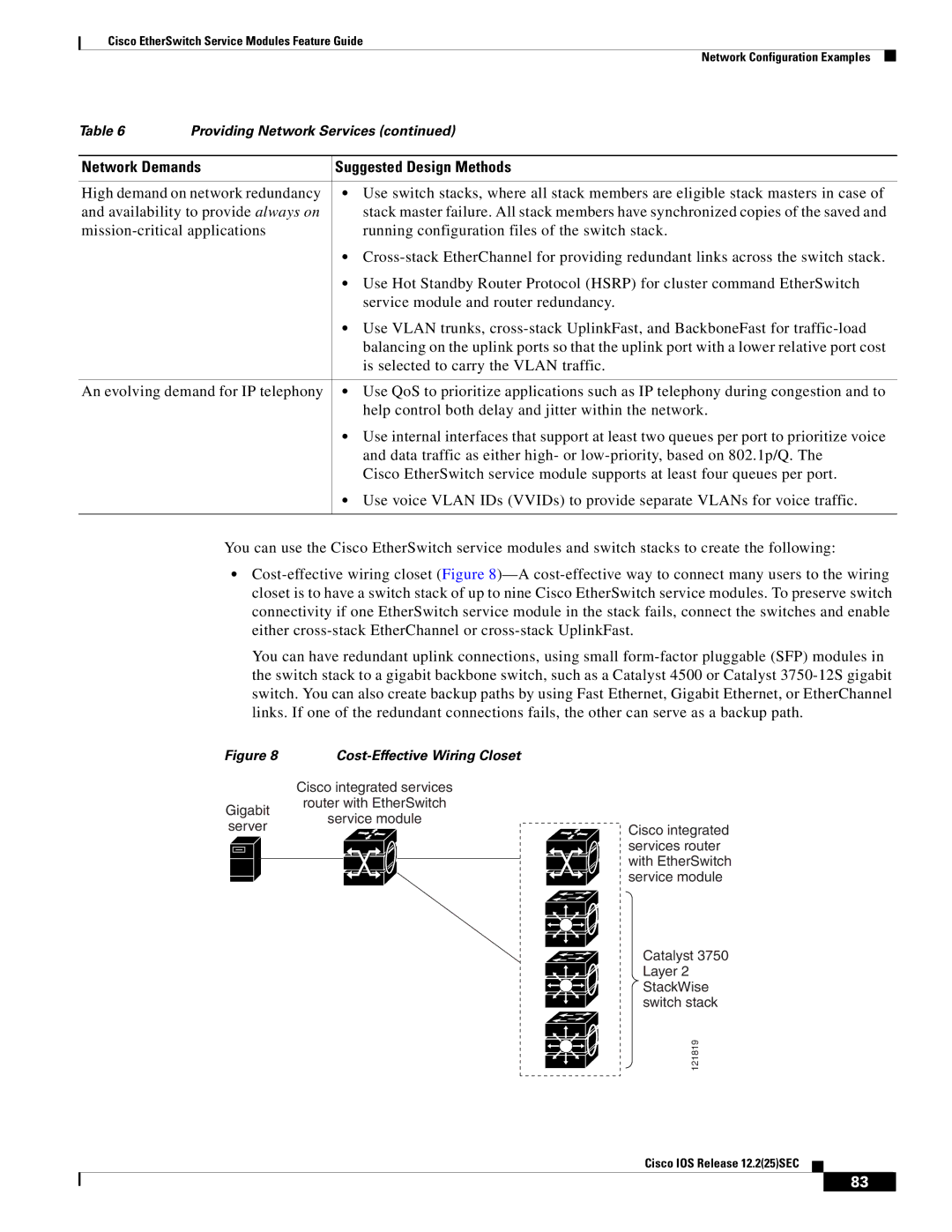
You can use the Cisco EtherSwitch service modules and switch stacks to create the following:
•
You can have redundant uplink connections, using small
Figure 8 |
| |
| Cisco integrated services | |
Gigabit | router with EtherSwitch | |
service module | ||
server | ||
Cisco integrated | ||
| services router | |
| with EtherSwitch | |
| service module |
Catalyst 3750 Layer 2 StackWise switch stack
121819
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)SEC
83