April
Operating System and Version Tru64 Unix Version 5.0A
Compaq Computer Corporation Houston, Texas
Page
Contents
1.2.1
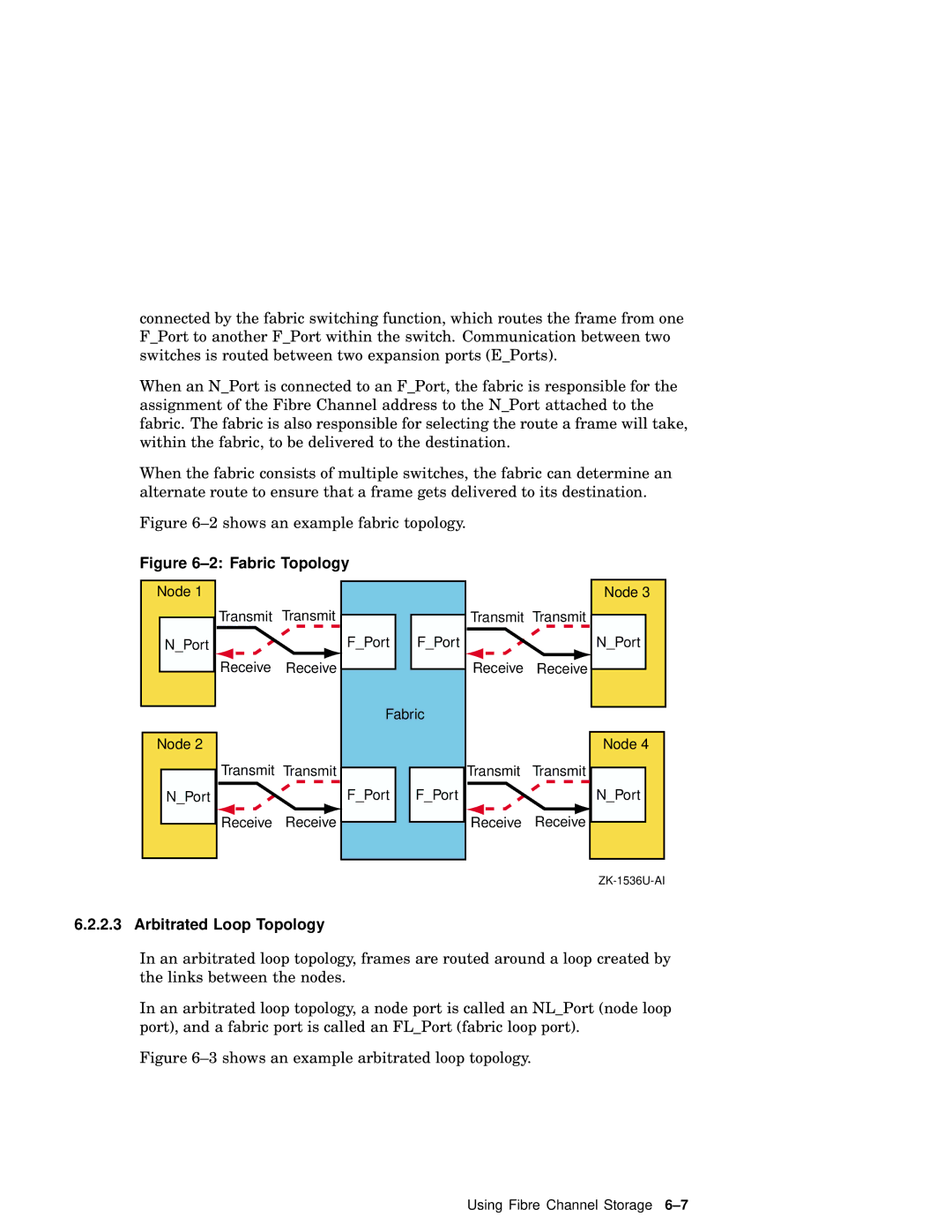
Using Fibre Channel Storage
Setting Up the Memory Channel Cluster Interconnect
2.2
Preparing ATM Adapters
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
10.1
11.2.1.2
10-1
Figures
Worldwide ID to Disk Name Conversion Table Index Examples
Xii Contents
Tables
12 and Figure
10-4
Page
Organization
Audience
Related Documents
TZ89 DLT Series Tape Drive User’s Guide
Mail
Reader’s Comments
Cat
Conventions
Cluster
TruCluster Server Product
Introduction
Overview of the TruCluster Server Hardware Configuration
Memory Requirements
Disks Needed for Installation
Minimum Disk Requirements
1.1 Tru64 Unix Operating System Disk
Clusterwide Disks
Member Boot Disk
Quorum Disk
Generic Two-Node Cluster
Member System
Growing a Cluster from Minimum Storage to a Nspof Cluster
8Introduction
Minimum Two-Node Cluster with UltraSCSI BA356 Storage Unit
10Introduction
Two-Node Cluster with Two UltraSCSI DS-BA356 Storage Units
12Introduction
DiskMember System
Memory
Creating a Nspof Cluster
Nspof Cluster using HSZ70s in Multiple-Bus Failover Mode
Kgpsa
18Introduction
Memory Channel Restrictions
TruCluster Server Member System Requirements
2Hardware Requirements and Restrictions
Fibre Channel Requirements and Restrictions
AlphaServer Number of KGPSA-BC Adapters Supported
AlphaServer Systems Supported for Fibre Channel
Hardware Requirements and Restrictions
Scsi Bus Adapter Restrictions
KZPSA-BB Scsi Adapter Restrictions
KZPBA-CB Scsi Bus Adapter Restrictions
RAID Array Controller Restrictions
Disk Device Restrictions
RAID Controller Scsi IDs
RAID Controller Number of Scsi IDs Supported
Scsi Signal Converters
Scsi Cables
DS-DWZZH-03 and DS-DWZZH-05 UltraSCSI Hubs
Supported Scsi Cables
Cable Connector Pins Configuration Use Density
Supported Scsi Terminators and Trilink Connectors
Scsi Terminators and Trilink Connectors
Page
Page
Shared Scsi Bus Configuration Requirements
Scsi Bus Performance
Transmission Methods
Scsi Bus Versus Scsi Bus Segments
Data Path
Scsi Bus Device Identification Numbers
Bus Speed
Scsi Bus Speeds
Scsi Bus Length
Terminating the Shared Scsi Bus when Using UltraSCSI Hubs
Scsi Bus Segment Length
Scsi Bus Bus Speed Maximum Cable Length
UltraSCSI Hubs
Vhdci Trilink Connector H8861-AA
DS-DWZZH-03 Description
Using a Dwzzh UltraSCSI Hub in a Cluster Configuration
DS-DWZZH-05 Description
DS-DWZZH-05 Configuration Guidelines
Disk Drivesa Personality Moduleb c
DS-DWZZH UltraSCSI Hub Maximum Configurations
Disk Drives a Personality Module b c
DS-DWZZH-05 Fair Arbitration
DS-DWZZH-05 Address Configurations
DS-DWZZH-05 Rear View
Scsi Bus Termination Power
DS-DWZZH-05 Indicators
Installing the DS-DWZZH-05 UltraSCSI Hub
Preparing the UltraSCSI Storage Configuration
Page
Page
Page
KZPBA-CB ID 6 T
H8863-AA Vhdci terminatorb
Callout Number Description
Page
Page
KZPBA-CB ID DS-DWZZH-03
HSZ80
Page
Page
Cluster interconnects
Planning Your TruCluster Server Hardware Configuration
To increase You can
Planning Your Configuration
Obtaining the Firmware Release Notes
TruCluster Server Hardware Installation
Step Action Refer to
Configuring TruCluster Server Hardware
Configuring TruCluster Server Hardware
Page
Cluster Administration
Example 4-1 Displaying Configuration on an AlphaServer DS20
Displaying KZPBA-CB Adapters with the show Console Commands
TIG
P00 show device
Example 4-2 Displaying Devices on an AlphaServer DS20
Example 4-4 Displaying Devices on an AlphaServer
Example 4-3 Displaying Configuration on an AlphaServer
Example 4-4 Displaying Devices on an AlphaServer 8200
Displaying Console Environment Variables and Setting
P00show pk
P00show isp
Setting the KZPBA-CB Scsi ID
Example 4-7 Setting the KZPBA-CB Scsi Bus ID
KZPBA-CB Termination Resistors
JA1
Setting Up the Memory Channel Cluster Interconnect
MC1 and MC1.5 Jumper Configuration
Setting the Memory Channel Adapter Jumpers
If hub mode is Jumper Example
1 MC1 and MC1.5 Jumpers
MC2 Jumper Configuration
2 MC2 Jumpers
JumperDescriptionExample
Jumper Description Example
VH0 Pins 2 to
MC2 Linecard Jumper Configurations
Installing the Memory Channel Adapter
Installing the Memory Channel Hub
Installing the MC2 Optical Converter in the Member System
Installing the MC1 or MC1.5 Cables
Installing the Memory Channel Cables
Connecting MC1 Link Cables in Standard Hub Mode
Connecting MC1 or MC1.5 Link Cables in Virtual Hub Mode
Connecting Memory Channel Adapters to Hubs
Installing the MC2 Cables
10Setting Up the Memory Channel Cluster Interconnect
Running Memory Channel Diagnostics
12Setting Up the Memory Channel Cluster Interconnect
Ctrl/C
Example 5-1 Running the mccable Test
Page
Using Fibre Channel Storage
Procedure for Installation Using Fibre Channel Disks
Boot genvmunix
Basic Fibre Channel Terminology
Fibre Channel Overview
NLPort
Fibre Channel Topologies
Fabric
Point-to-Point
Arbitrated Loop Topology
Fabric Topology
Hub
HSG80
10Using Fibre Channel Storage
Multiple-Bus Nspof Configuration Number
Dsgga
Zoning
Zoning and Cascaded Switches
A Simple Zoned Configuration
Cascaded Switches
Installing and Setting Up the Fibre Channel Switch
Installing and Configuring Fibre Channel Hardware
Installing the Switch
Using the Switch Front Panel
Managing the Fibre Channel Switches
18Using Fibre Channel Storage
Press Enter. You can change your mind and not reboot
Admin ipAddrSet
Logging Into the Switch with a Telnet Connection
Setting the Switch Name via Telnet Session
Telnet Session Default User Names for Fibre Channel Switches
Return
Installing the Kgpsa PCI-to-Fibre Channel Adapter Module
Setting the KGPSA-BC or KGPSA-CA to Run on a Fabric
P00 wwidmgr -show adapter
Obtaining the Worldwide Names of Kgpsa Adapters
You can use the wwidmgr -show adapter command as follows
Set this Cacheups
Use the command set failover copy =
HSG80 show connection
Example 6-1 Determine HSG80 Connection Names
30Using Fibre Channel Storage
Obtaining the Worldwide Names of HSG80 Controller
32Using Fibre Channel Storage
Configuring the HSG80 Storagesets
HSG80 RUN Config
Example 6-2 Setting up the Mirrorset
HSG80 Show CROOT-MIR
36Using Fibre Channel Storage
HSG80 show d131
38Using Fibre Channel Storage
Using Fibre Channel Storage
Setting the Device Unit Number
Converting Storageset Unit Numbers to Disk Names
File System
P00 wwidmgr -clear all P00 show wwid
42Using Fibre Channel Storage
P00 wwidmgr -quickset -udid
44Using Fibre Channel Storage
P00 show wwid
Example 6-4 Sample Fibre Channel Device Names
Setting the bootdefdev Console Environment Variable
Using Fibre Channel Storage
48Using Fibre Channel Storage
Install the Base Operating System
Resetting the bootdefdev Console Environment Variable
For member system 1 boot disk
Determining /dev/disk/dskn to Use for a Cluster Installation
# hwmgr -get attribute -a name -a devbasename more
Installing the TruCluster Server Software
54Using Fibre Channel Storage
Using Fibre Channel Storage
HSG80 SET Nofailover HSG80 SET Multibusfailover COPY=THIS
Console is in diagnostic mode
Initialize the console
# /usr/sbin/emxmgr -m emx0
# emxmgr -t emx1
Using the emxmgr Utility Interactively
# emxmgr
Using Fibre Channel Storage
Page
ATM Overview
Preparing ATM Adapters
2Preparing ATM Adapters
Emulated LAN Over an ATM Network
Installing ATM Adapters
Verifying ATM Fiber Optic Cable Connectivity
PHY
ATM Switch Indicator Comments
ATMworks Adapter LEDs
ATMworks Adapter LEDs
Network LED Module LED Description
Preparing the TZ88 for Shared Bus Usage
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
TZ88N-VA Scsi ID Switches
Setting the TZ88N-VA Scsi ID
TZ88N-VA Switch Settings
Scsi ID Selection Switches
Cabling the TZ88N-VA
Cabling the TZ88N-TA
Setting the TZ88N-TA Scsi ID
Preparing the TZ89 for Shared Scsi Usage
Setting the DS-TZ89N-VW Scsi ID
DS-TZ89N-VW Switch Settings
DS-TZ89N-VW Scsi ID Switches
Cabling the DS-TZ89N-VW Tape Drives
Cabling the DS-TZ89N-TA Tape Drives
Setting the DS-TZ89N-TA Scsi ID
Compaq 20/40 GB DLT Tape Drive
Setting the Compaq 20/40 GB DLT Tape Drive Scsi ID
Compaq 20/40 GB DLT Tape Drive Rear Panel
Cabling the Compaq 20/40 GB DLT Tape Drive
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Hardware Components Used to Create the Configuration Shown
Setting the TZ885 Scsi ID
Preparing the TZ885 for Shared Scsi Usage
Cabling the TZ885 Tape Drive
14Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Preparing the TZ887 for Shared Scsi Bus Usage
Setting the TZ887 Scsi ID
TZ887 DLT MiniLibrary Rear Panel
Cabling the TZ887 Tape Drive
Cabling a Shared Scsi Bus with a TZ887
Setting the TL891 or TL892 Scsi ID
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Cabling the TL891 or TL892 MiniLibraries
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
22Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Preparing the TL890 DLT MiniLibrary Expansion Unit
1 TL890 DLT MiniLibrary Expansion Unit Hardware
Preparing the DLT MiniLibraries for Shared Scsi Bus Usage
Cabling the DLT MiniLibraries
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
10 TL890 and TL892 DLT MiniLibraries on Shared Scsi Buses
Configuring a Base Module as a Slave
DLT0 Idle DLT1 Idle Loader Idle
Setting the TL890/TL891/TL892 Scsi ID
Powering Up the DLT MiniLibrary
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
TL894 Default Scsi ID Settings
Setting TL894 Robotics Controller and Tape Drive Scsi IDs
1 TL894 Robotic Controller Required Firmware
Scsi Device Scsi Address
Scsi ID
32Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
3 TL894 Tape Library Internal Cabling
11 TL894 Tape Library Four-Bus Configuration
34Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Connecting the TL894 Tape Library to the Shared Scsi Bus
12 Shared Scsi Buses with TL894 in Two-Bus Mode
36Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
TL895 Default Scsi ID Settings
Setting the TL895 Tape Library Scsi IDs
1 TL895 Robotic Controller Required Firmware
Scsi Device
3 TL895 Tape Library Internal Cabling
13 TL895 Tape Library Internal Cabling
Upgrading a TL895
Connecting the TL895 Tape Library to the Shared Scsi Bus
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Communications with the Host Computer
MUC Switch Functions
MUC Switch Functions
Setting the MUC Scsi ID
Switch Function
Tape Drive Scsi IDs
TL893 Default Scsi IDs
TL896 Default Scsi IDs
Scsi Port Device Default Scsi ID
14 TL893 Three-Bus Configuration
15 TL896 Six-Bus Configuration
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
11.1 TL881 and TL891 DLT MiniLibraries Overview
16 Shared Scsi Buses with TL896 in Three-Bus Mode
11.1.2 TL881 and TL891 MiniLibrary Rackmount Components
11.1.1 TL881 and TL891 DLT MiniLibrary Tabletop Model
11.1.3 TL881 and TL891 Rackmount Scalability
11 DLT MiniLibrary Part Numbers
DLT MiniLibrary Part Numbers
52Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Setting the Standalone MiniLibrary Tape Drive Scsi ID
Cabling the TL881 or TL891 DLT MiniLibrary
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
56Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
17 TL891 Standalone Cluster Configuration
328215-00X, BN21K, or BN21L cable c
Cabling the Rackmount TL881 or TL891 DLT MiniLibrary
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
18 TL881 DLT MiniLibrary Rackmount Configuration
Configuring a Base Unit as a Slave to the Expansion Unit
Powering Up the TL881/TL891 DLT MiniLibrary
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
General Overview
Compaq ESL9326D Enterprise Library
Order Number Number of Tape Drives
12.2 ESL9326D Enterprise Library Overview
12.3.3 ESL9326D Enterprise Library Internal Cabling
Library Electronics and Tape Drive Scsi IDs
Scsi ID
68Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Configuring a Shared Scsi Bus for Tape Drive Use
Page
Page
Types of Scsi Bus Signal Converters
Using Scsi Bus Signal Converters
Dwzza and Dwzzb Signal Converter Termination
Using the Scsi Bus Signal Converters
DS-BA35X-DA Termination
Standalone Scsi Signal Converter
Terminating the Shared Scsi Bus
DS-BA35X-DA Personality Module Switches
Page
BN21W-0B Y Cable
Overview of Disk Storage Shelves
HD68 Trilink Connector H885-AA
1 BA350 Storage Shelf
Non-UltraSCSI BA356 Storage Shelf
2 BA356 Storage Shelf
Page
BA356 Internal Scsi Bus
UltraSCSI BA356 Storage Shelf
BA356 Jumper and Terminator Module Identification Pins
Page
Preparing a BA350 Storage Shelf for Shared Scsi Usage
Preparing a BA356 Storage Shelf for Shared Scsi Usage
Connecting Storage Shelves Together
Connecting a BA350 and a BA356 for Shared Scsi Bus Usage
BA350 and BA356 Cabled for Shared Scsi Bus Usage
Connecting Two BA356s for Shared Scsi Bus Usage
10 Two BA356s Cabled for Shared Scsi Bus Usage
Connecting Two UltraSCSI BA356s for Shared Scsi Bus Usage
Page
11 Two UltraSCSI BA356s Cabled for Shared Scsi Bus Usage
BN37A cable a
Hardware Components Used for Configuration Shown in Figure
Page
KZPSA-BB ID HSZ50
Cabling an HSZ20 in a Cluster using External Termination
Page
Page
BN21K or BN21L cableb
Hardware Components Used in Configuration Shown in Figure
DS-DWZZH-05
Page
Page
Step Action Refer to
Page
PCI-to-SCSI Storage
Kzpsa PCI-to-SCSI
Installing a KZPSA-BB or KZPBA-CB Using External Termination
Power down the member system. Install
Step Action Refer to
P00 show config
Example 10-1 Displaying Configuration on an AlphaServer
Example 10-2 Displaying Devices on an AlphaServer
Example 10-1 Displaying Configuration on an AlphaServer 4100
Example 10-3 Displaying Configuration on an AlphaServer
Example 10-2 Displaying Devices on an AlphaServer 4100
Example 10-4 Displaying Devices on an AlphaServer
P00show pk
Qlogic ISP1020 devices KZPBA-CBs as isp0 and isp1 with disks
P00 show isp
Example 10-8 Setting the KZPBA-CB Scsi Bus ID
Example 10-9 Setting KZPSA-BB Scsi Bus ID and Speed
Updating the KZPSA-BB Adapter Firmware
KZPSA-BB and KZPBA-CB Termination Resistors
UPD update pkb0
Page
User Device Name Dskn Or Disk Unit Define Iden Tifier
Table A-1 Converting Storageset Unit Numbers to Disk Names
Page
Index-1
TL893, 8-40 TL896, 8-40
Index-2
Show Thiscontroller
Index-3
TL891, 8-48 DS-BA356
Index-4
Topology, 6-5, 6-61 file
Index-5
See KGPSA, KZPBA-CB, KZPSA-BB
Index-6
KZPSA-BB
Index-7
See also signal converters
Index-8
See cables requirement
Index-9
SBB
Index-10
Cabling, 8-44
Index-11
Page
Name Order Number
How to Order Tru64 Unix Documentation
Page
TruCluster Server
Reader’s Comments
Spit Brook RD Nashua NH