Parameter Guide
■FILTER
Here are the
Page08: FILTER
A: Type FILTER TYPE | [24LPF...12HPF] |
Select the filter type.
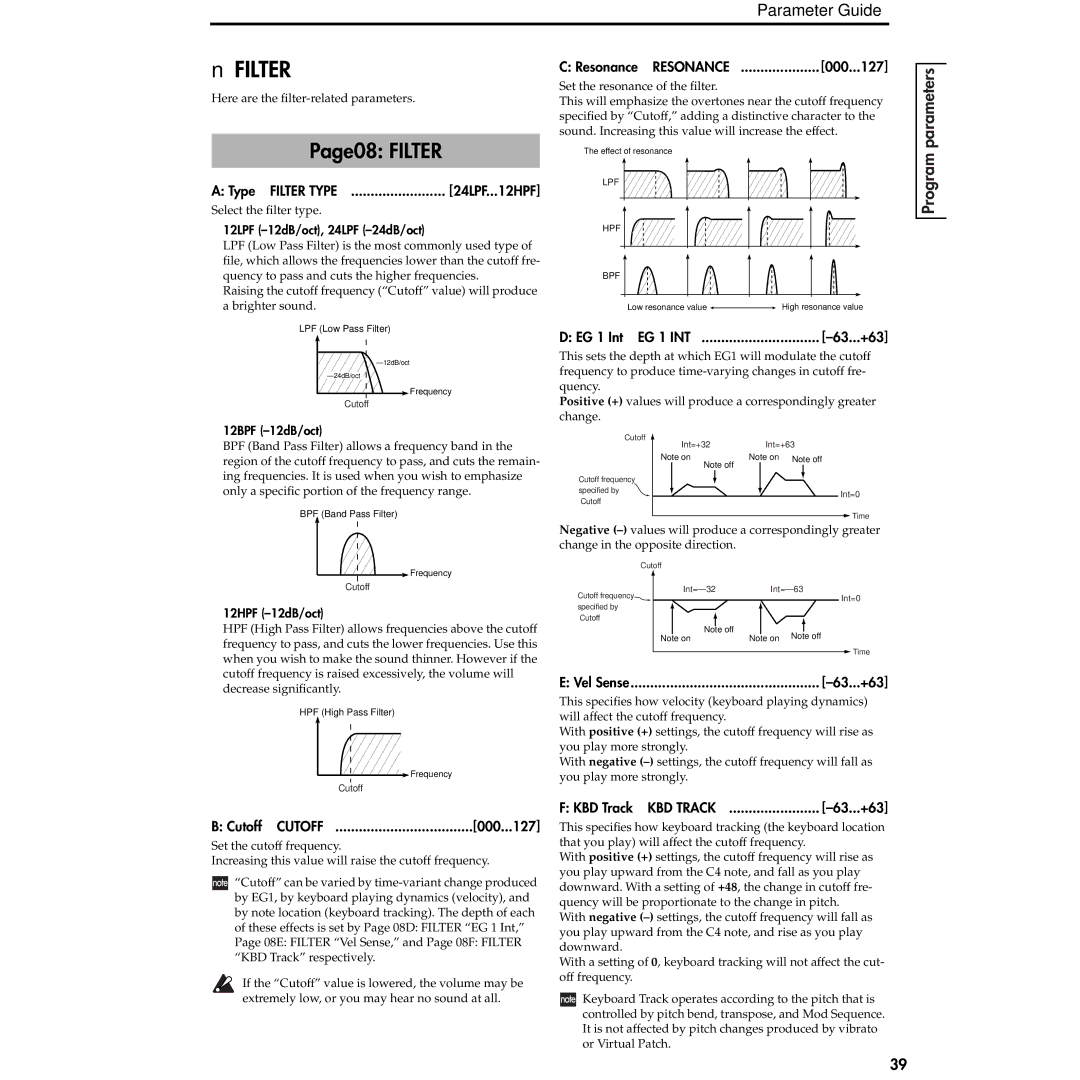
12LPF (–12dB/oct), 24LPF (–24dB/oct)
LPF (Low Pass Filter) is the most commonly used type of file, which allows the frequencies lower than the cutoff fre- quency to pass and cuts the higher frequencies.
Raising the cutoff frequency (“Cutoff” value) will produce a brighter sound.
LPF (Low Pass Filter)
![]() Frequency
Frequency
Cutoff
C: Resonance RESONANCE | [000...127] |
Set the resonance of the filter.
This will emphasize the overtones near the cutoff frequency specified by “Cutoff,” adding a distinctive character to the sound. Increasing this value will increase the effect.
The effect of resonance
LPF
HPF
BPF
Low resonance value |
| High resonance value |
| ||
D: EG 1 Int EG 1 INT |
| |
This sets the depth at which EG1 will modulate the cutoff frequency to produce
Positive (+) values will produce a correspondingly greater
Program parameters
12BPF (–12dB/oct)
BPF (Band Pass Filter) allows a frequency band in the region of the cutoff frequency to pass, and cuts the remain- ing frequencies. It is used when you wish to emphasize only a specific portion of the frequency range.
BPF (Band Pass Filter)
change.
Cutoff
Cutoff frequency specified by ![]() “Cutoff”
“Cutoff”
| Int=+32 |
| Int=+63 | ||
Note on | Note on Note off | ||||
| Note off |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Int=0
![]() Time
Time
![]() Frequency
Frequency
Cutoff
12HPF (–12dB/oct)
HPF (High Pass Filter) allows frequencies above the cutoff frequency to pass, and cuts the lower frequencies. Use this when you wish to make the sound thinner. However if the cutoff frequency is raised excessively, the volume will decrease significantly.
HPF (High Pass Filter)
![]() Frequency
Frequency
Cutoff
Negative
Cutoff |
|
|
|
| ||||
Cutoff frequency |
|
| ||||||
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
| Int=0 | |||
specified by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
“Cutoff” |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| Note off |
|
|
|
| ||
Note on Note off | ||||||||
| Note on | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Time | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
E: Vel Sense |
|
| ||||||
This specifies how velocity (keyboard playing dynamics) will affect the cutoff frequency.
With positive (+) settings, the cutoff frequency will rise as you play more strongly.
With negative
B: Cutoff CUTOFF | [000...127] |
Set the cutoff frequency.
Increasing this value will raise the cutoff frequency.
![]()
![]() “Cutoff” can be varied by
“Cutoff” can be varied by
If the “Cutoff” value is lowered, the volume may be extremely low, or you may hear no sound at all.
F: KBD Track KBD TRACK |
|
This specifies how keyboard tracking (the keyboard location that you play) will affect the cutoff frequency.
With positive (+) settings, the cutoff frequency will rise as you play upward from the C4 note, and fall as you play downward. With a setting of +48, the change in cutoff fre- quency will be proportionate to the change in pitch.
With negative
With a setting of 0, keyboard tracking will not affect the cut- off frequency.
![]() Keyboard Track operates according to the pitch that is controlled by pitch bend, transpose, and Mod Sequence. It is not affected by pitch changes produced by vibrato or Virtual Patch.
Keyboard Track operates according to the pitch that is controlled by pitch bend, transpose, and Mod Sequence. It is not affected by pitch changes produced by vibrato or Virtual Patch.
39