ASCII and EBCDIC Characters
Appendix F ASCII and EBCDIC Characters
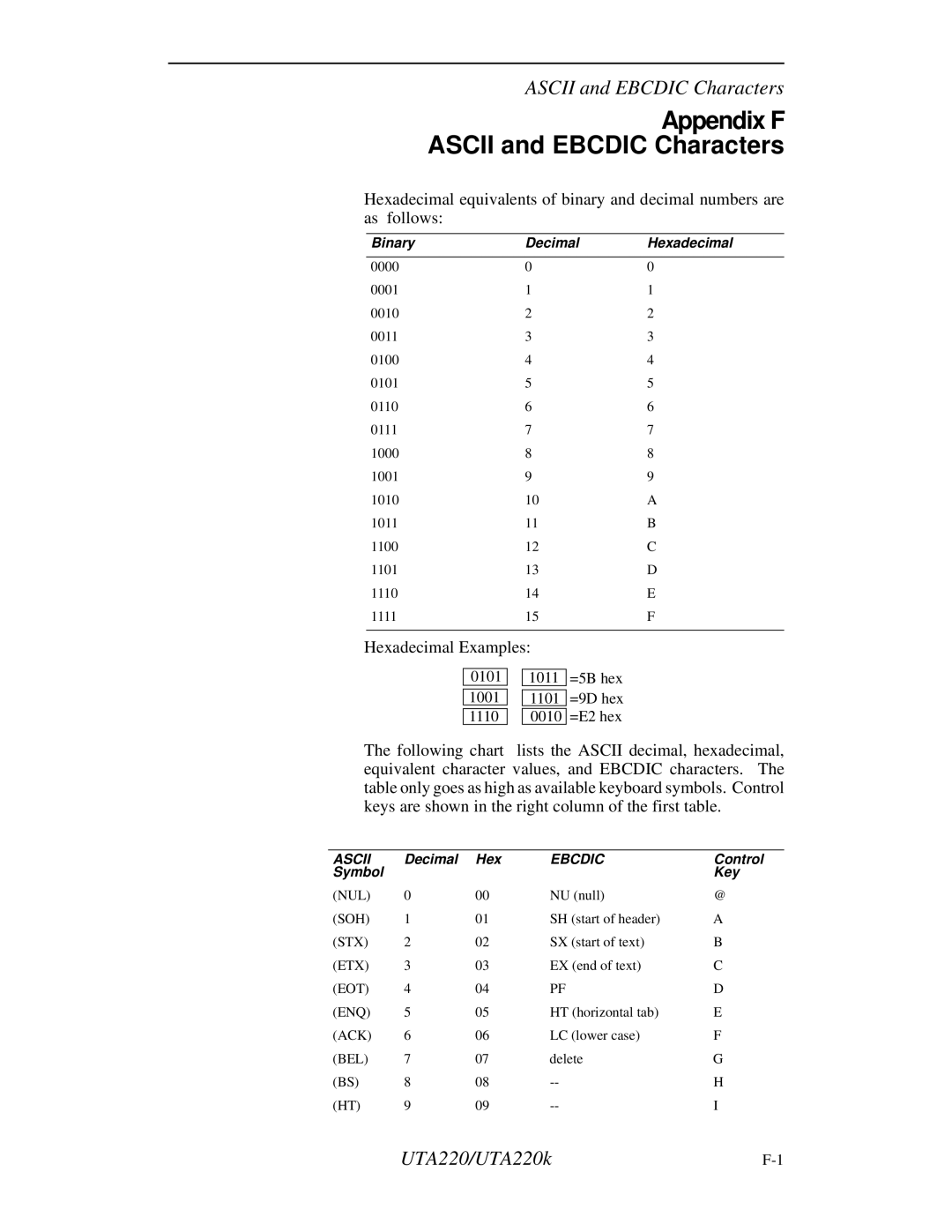
Hexadecimal equivalents of binary and decimal numbers are as follows:
Binary | Decimal | Hexadecimal |
|
|
|
0000 | 0 | 0 |
0001 | 1 | 1 |
0010 | 2 | 2 |
0011 | 3 | 3 |
0100 | 4 | 4 |
0101 | 5 | 5 |
0110 | 6 | 6 |
0111 | 7 | 7 |
1000 | 8 | 8 |
1001 | 9 | 9 |
1010 | 10 | A |
1011 | 11 | B |
1100 | 12 | C |
1101 | 13 | D |
1110 | 14 | E |
1111 | 15 | F |
|
|
|
Hexadecimal Examples:
0101
1001
1110
1011
1101
0010
=5B hex =9D hex =E2 hex
The following chart lists the ASCII decimal, hexadecimal, equivalent character values, and EBCDIC characters. The table only goes as high as available keyboard symbols. Control keys are shown in the right column of the first table.
ASCII | Decimal | Hex | EBCDIC | Control |
Symbol |
|
|
| Key |
(NUL) | 0 | 00 | NU (null) | @ |
(SOH) | 1 | 01 | SH (start of header) | A |
(STX) | 2 | 02 | SX (start of text) | B |
(ETX) | 3 | 03 | EX (end of text) | C |
(EOT) | 4 | 04 | PF | D |
(ENQ) | 5 | 05 | HT (horizontal tab) | E |
(ACK) | 6 | 06 | LC (lower case) | F |
(BEL) | 7 | 07 | delete | G |
(BS) | 8 | 08 | H | |
(HT) | 9 | 09 | I |
UTA220/UTA220k |