Indoor Units
Model No Outdoor Units
…In a Room
For safe installation and trouble-free operation, you must
…In Moist or Uneven Locations
…In an Area with High Winds
Check of Density Limit
Precautions for Installation Using New Refrigerant
Configuration and characteristics of cylinders
Contents
Tentative
Model No
Specifications Unit Specifications Way Cassette Type
Indoor Unit 36PU1U6 Outdoor Unit 36PE1U6
Indoor Unit 42PU1U6 Outdoor Unit 42PE1U6
Indoor Unit 26PU1U6 Outdoor Unit
Indoor Unit 36PU1U6 Outdoor Unit 36PS1U6
Indoor Unit 42PU1U6 Outdoor Unit 42PS1U6
Data Subject to Change Without Notice
Specifications Unit Specifications Wall Mounted Type
Indoor Unit 26PK1U6 Outdoor Unit
Performance
Specifications Unit Specifications Ceiling Type
Indoor Unit 36PT1U6 Outdoor Unit
Indoor Unit 42PT1U6 Outdoor Unit
Indoor Unit 26PT1U6 Outdoor Unit 26PS1U6
17˚F BTU / h Moisture removal High Pints / h
Indoor Unit 42PT1U6 Outdoor Unit 42PS1U6
Net weight Lbs. kg 128 Shipping weight 148 Shipping volume
Specifications Unit Specifications Low Silhouette Duct Type
Indoor Unit 36PF1U6 Outdoor Unit 36PE1U6
RCZ-RTC2
CZ-RWSC1U
Fan motor
Major Component Specifications Indoor Unit
Model No 36PU1U6 Source
Model No 42PU1U6 Source
Model No 26PK1U6 Source
Model No 26PT1U6 Source
Model No 36PT1U6 Source
Model No 42PT1U6 Source
Model No 26PF1U6 Source
Model No 36PF1U6 Source
Compressor
Specifications Major Component Specifications Outdoor Unit
CR-CH4872R Microprocessor
Lbs. kg R410A 7.9
26PS1U6
230V, 40µF
42PS1U6
Model No 26PE1U6, U-26PS1U6
Specifications Other Component Specifications Outdoor Unit
Model No 36PE1U6, U-36PS1U6
Model No 42PE1U6, U-42PS1U6
Ø1/8
Hol
Page
19/32
31/32 12-7/32
Dimension inch
56-25/32 Air outlet duct flange
Thickness more than T1/16 inch
Page
Page
Specifications
Operating Range
Temperature Indoor Air Intake Outdoor Air Intake
Page
Source
Specifications Noise Criterion Curves Way Cassette Type
Specifications Noise Criterion Curves Wall Mounted Type
Specifications Noise Criterion Curves Ceiling Type
Sound
Noise Criterion Curves Low Silhouette Duct Type
Specifications Noise Criterion Curves Outdoor Units
How to read the diagram
Specifications Increasing the Fan Speed
Indoor Fan Performance Type
Type
Air throw distance chart Way Cassette Type
Model 26 Type
Model 36, 42 Type
Specifications Air throw distance chart Wall Mounted Type
Air throw distance chart Ceiling Type
Model 36 Type
Model 42 Type
Outdoor Unit Type Time delay fuse or Circuit capacity
Wiring System Diagrams
How to Connect Wiring to the Terminal For stranded wiring
Installation Instructions
Ashrae
Selecting the Installation Site
Air-Discharge Chamber for Top Discharge
① Air discharge chamber ② Air discharge chamber base
For U-42PES1U6 unit
Direction
42PES1U6 unit
Front and both sides must remain open
25-13/32 25/32
30-5/64 Wind direction
Obstacle to the front of unit
Installation in front-rear rows
Installing the Outdoor Unit
Routing the Tubing and Wiring
Drainage Work
Low Silhouette Ducted Type Way Cassette Type
Preparation for Suspending
Way Cassette Type U1 Type Suspending the Indoor Unit
Placing the Unit Inside the Ceiling
Installing the Drain Piping
Checking the Drainage
Unit body
Before Installing the Ceiling Panel
When Removing the Ceiling Panel for Servicing
Installing the Ceiling Panel
Accessories
Installing the ceiling panel
Selecting and Making a Hole
Trical wiring or conduits are
Located
Hole Dia. inch
Installing the Rear Panel on the Wall
If Wooden Wall
If Block, Brick, Concrete or Similar Type Wall
How to remove the grille
Removing the Grille to Install the Indoor Unit
How to replace the grille
To mount the indoor unit on the rear panel
How to remove the cover plate
Wiring Instructions General Precautions on Wiring
Shaping the Tubing
Installing the Drain Hose
Ceiling Type T1 Type Suspending the Indoor Unit
Hinge Slide toward front side Side panel Unit
Outside
Good Not good
Duct for Fresh Air
Low Silhouette Ducted Type F1 Type
Required Minimum Space for Installation and Service
26PF1U6
36PF1U6
It is important that you use
Enough to support the weight
Extreme care in supporting
Indoor unit inside the ceiling
Their locking nuts face upward
Tighten the hose clamps so
Be careful since the fan will start
When you short the pin on
Indoor control board
To mount the tube cover, use 5/16
Indoor Fan Performance
Increasing the Fan Speed
When Installing the Indoor Unit
Checkpoint Symptom Remark
Checkpoint after installation
Wireless Remote Controller Installation
How to Install Batteries
If Wall-mounted Fixed Position
Room Temperature Sensor Setting
Address Switches
Setting the Model Code
CZ-RWSU1U
Ceiling Type T1 Type Indicator Section Installation
Electrical Wiring
Test Run Switch
How to use the test run setting U1, T1 Types
Alarm
Misoperation Alarm Indicators
Cause of Trouble
Lamp
If Wall mounted Fixed Position
107
Excessive load on
To avoid placing an
Equipment, use this
Function only when
Bright Cause of Trouble
Timer Standby
Will damage the equipment
Wiring procedure
Group control using 2 signal receiving units
Wiring System Diagram for Group Control
Setting method
Test Run Procedure Wall mounted Type K1 Type
Wireless remote controller transmitter
Check Items Before the Test Run
Test run Using the controller For S-26PK1U6
Indicator
Controller
Test OFF
Precautions
26PK1U6
Nos , 2 OFF, No on
Nos , 2, 3 all OFF
Diagnosis Table
Cause
Indoor unit
HOW to Install the Timer Wired Remote Controller
Tube diameter Tightening torque Tube thickness
Never grasp the drain or refrigerant connecting
Precautions for Packed Valve Operation
Insulating the Refrigerant Tubing Tubing Insulation
Tubes arranged together
Taping the Tubes
Finishing the Installation
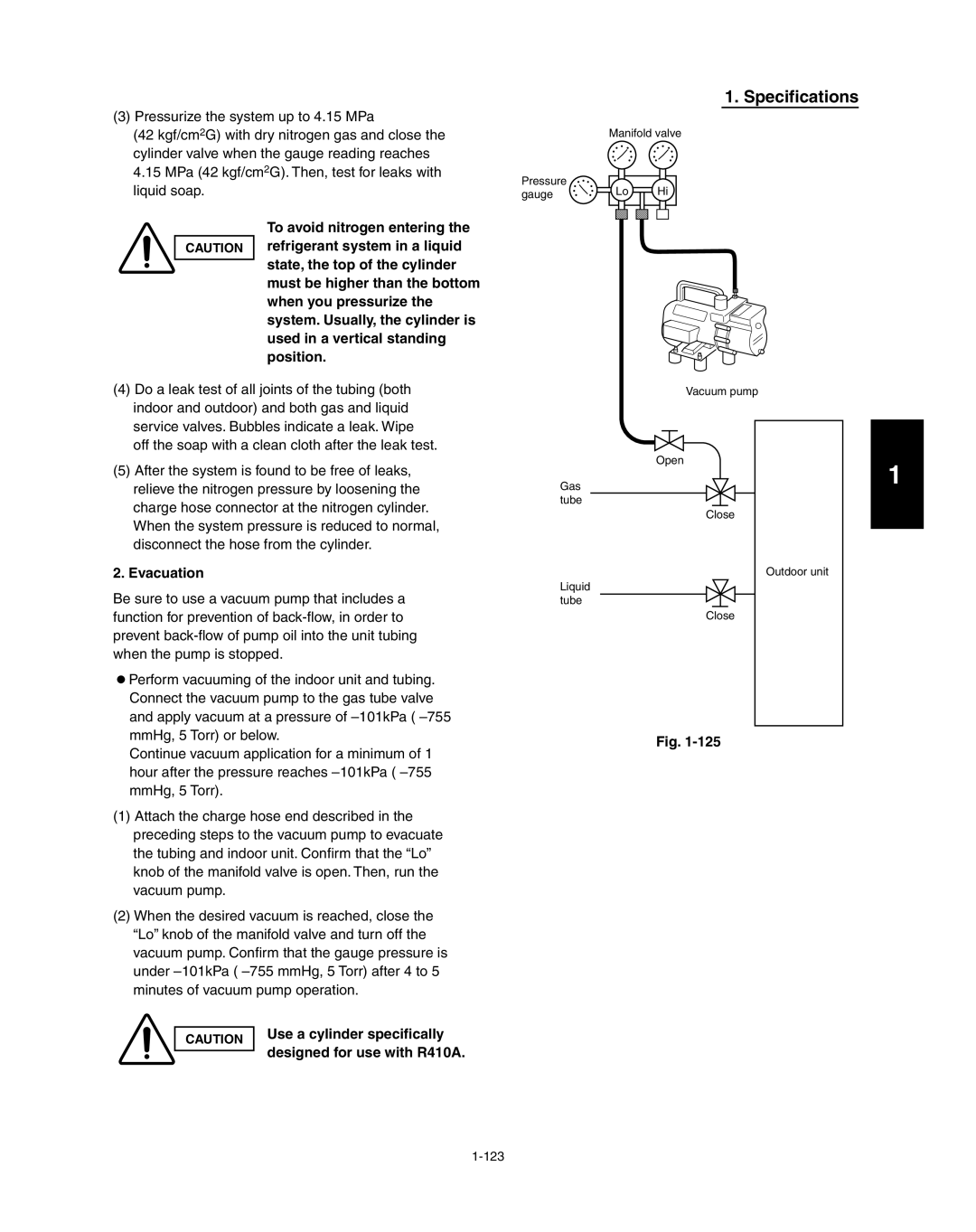
Air Purging with a Vacuum Pump for Test Run Preparation
Manifold gauge Vacuum pump
Leak Test
Evacuation
Use a cylinder specifically
Designed for use with R410A
Charging Additional Refrigerant
Finishing the Job
R410A
Processes and Functions
Processes and functions Room Temperature Control
Chart Summary and Explanations
Cooling
Processes and functions Heating
Cold Draft Prevention Heating Cycle
Automatic Fan Speed Indoor Unit
Chart Explanations and notes
Current release control
Discharge temperature release control
Outdoor unit fan control
Coil heating control
Overcurrent protection control
Freeze prevention low-temperature release control
Current release value shift control
Heating high-load control
Defrost control
Outdoor Unit Control PCB
Outdoor Unit Control PCB CR-CH4272R
Example of wiring
Method of System Address Setting
Page
Electrical Data
Indoor Units
Page
Electrical data Wall Mounted Type S-26PK1U6
Electrical data Wall Mounted Type S-26PK1U6
Electrical data Ceiling Type S-26PT1U6, S-36PT1U6, S-42PT1U6
Electrical data Ceiling Type S-26PT1U6, S-36PT1U6, S-42PT1U6
Page
Page
Outdoor Units
Outdoor Units
26PS1U6
Outdoor Units
36PE1U6
Outdoor Units
36PS1U6
Outdoor Units
42PE1U6
Outdoor Units
42PS1U6
Outdoor Units
Page
Service Procedures
Contents of remote controller switch alarm display
Service procedures Meaning of Alarm Messages
Wireless
Remarks
Contents Correction
Remote Alarm Judgment condition Clear condition
Alarm
Eeprom
Service procedures Details of Alarm Messages
Alarm P29
MDC trouble
HIC PCB trouble
Alarm P26
HIC-CH4872R HIC-CH2672R
Alarm E31
26, 36 Type
Communications Trouble within unit
Alarm P22
Alarms F04, F06, F07, F08, F12
Check procedure
Sensor Temperature Correlation Table
Sensor installation Sensor type Location
Outdoor Air Temp. TO, Intake Temp. TS, Heat
Check Pin
Exchanger Temp. C1 Sensor, Heat Exchanger Temp. C2 Sensor
Discharge Temp. TD Sensors
Outdoor Unit Maintenance Remote Control
Outdoor unit maintenance remote control Overview
Switching between cooling/heating Operation
All units start/stop Operation
All units test run Operation
Sample displays
Item code Display contents
Display for unit Nos
Item code Meaning of Code
Display of first 3 digits Display of last 3 digits
Item code Parameter
List of Item Codes
Outdoor unit maintenance remote control
Figures represent the capacity data for each model
Test RUN
Test run
Preparing for Test Run
Test run U1, K1, T1, F1 Type 6-2. Caution
Items to Check Before the Test Run
Cause
Basic wiring diagram
Test run Examples of Wiring Diagrams
Remote controller crossover wiring for group control
Automatic address setting using the remote controller
Setting the outdoor unit system addresses
2P DIP switch Rotary switch
System address No
Main-sub remote controller control
Connecting 2 remote controllers to control 1 indoor unit
Remote controller setting mode
201201