OnSite 2800 Series User Manual | 8 • Link scheduler configuration |
|
|
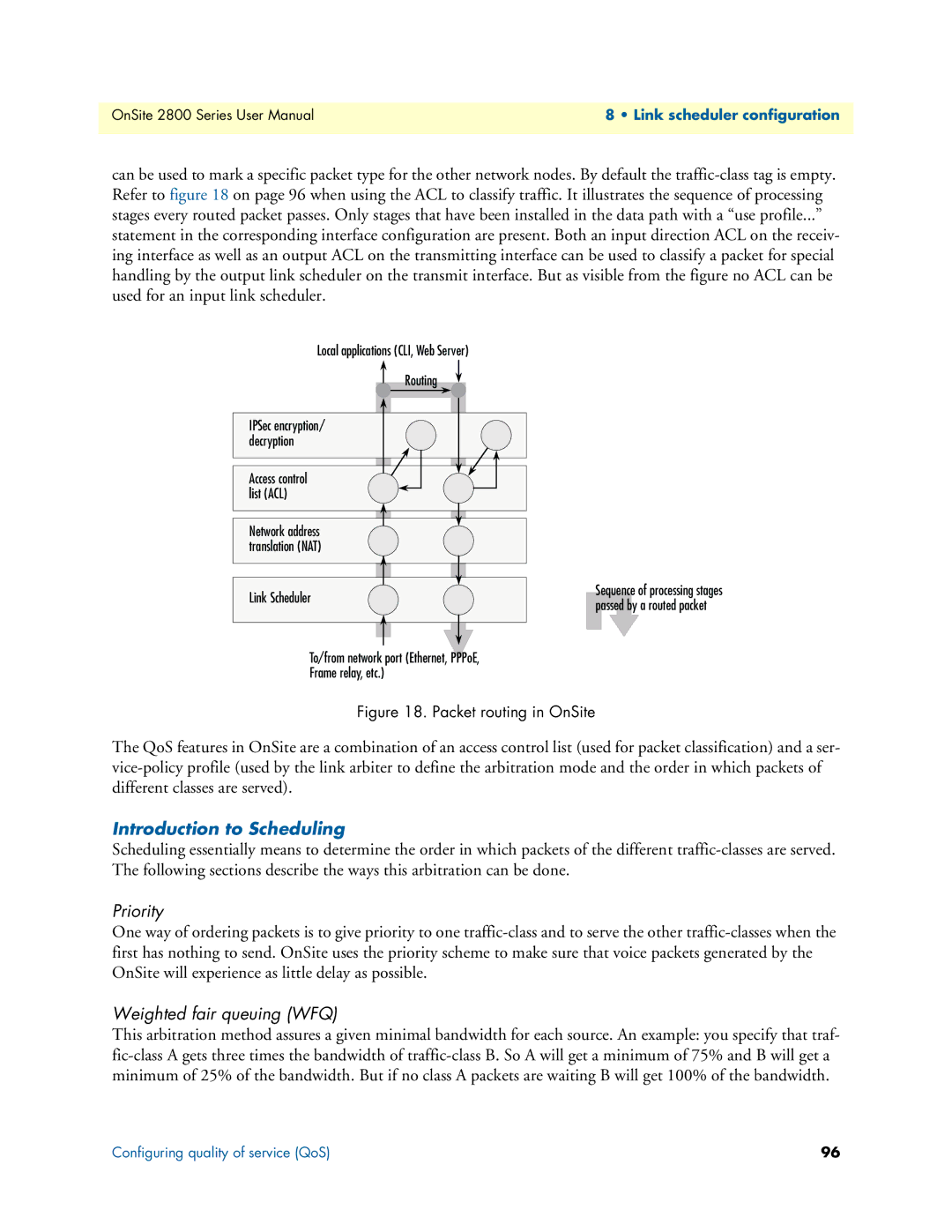
can be used to mark a specific packet type for the other network nodes. By default the
Local applications (CLI, Web Server)
Routing
IPSec encryption/ decryption
Access control list (ACL)
Network address translation (NAT)
Link Scheduler
Sequence of processing stages passed by a routed packet
To/from network port (Ethernet, PPPoE,
Frame relay, etc.)
Figure 18. Packet routing in OnSite
The QoS features in OnSite are a combination of an access control list (used for packet classification) and a ser-
Introduction to Scheduling
Scheduling essentially means to determine the order in which packets of the different
Priority
One way of ordering packets is to give priority to one
Weighted fair queuing (WFQ)
This arbitration method assures a given minimal bandwidth for each source. An example: you specify that traf-
Configuring quality of service (QoS) | 96 |