PowerLogic™ PM5100 series user guide | Chapter |
|
|
8:00 am, select 0800 (in hhmm format). When setting up this type of demand, you can choose Clock Sync Block
Thermal demand
Thermal demand calculates the demand based on a thermal response, which imitates the function of thermal demand meters. The demand calculation updates at the end of each interval. You can set the demand interval from 1 to 60 minutes (in
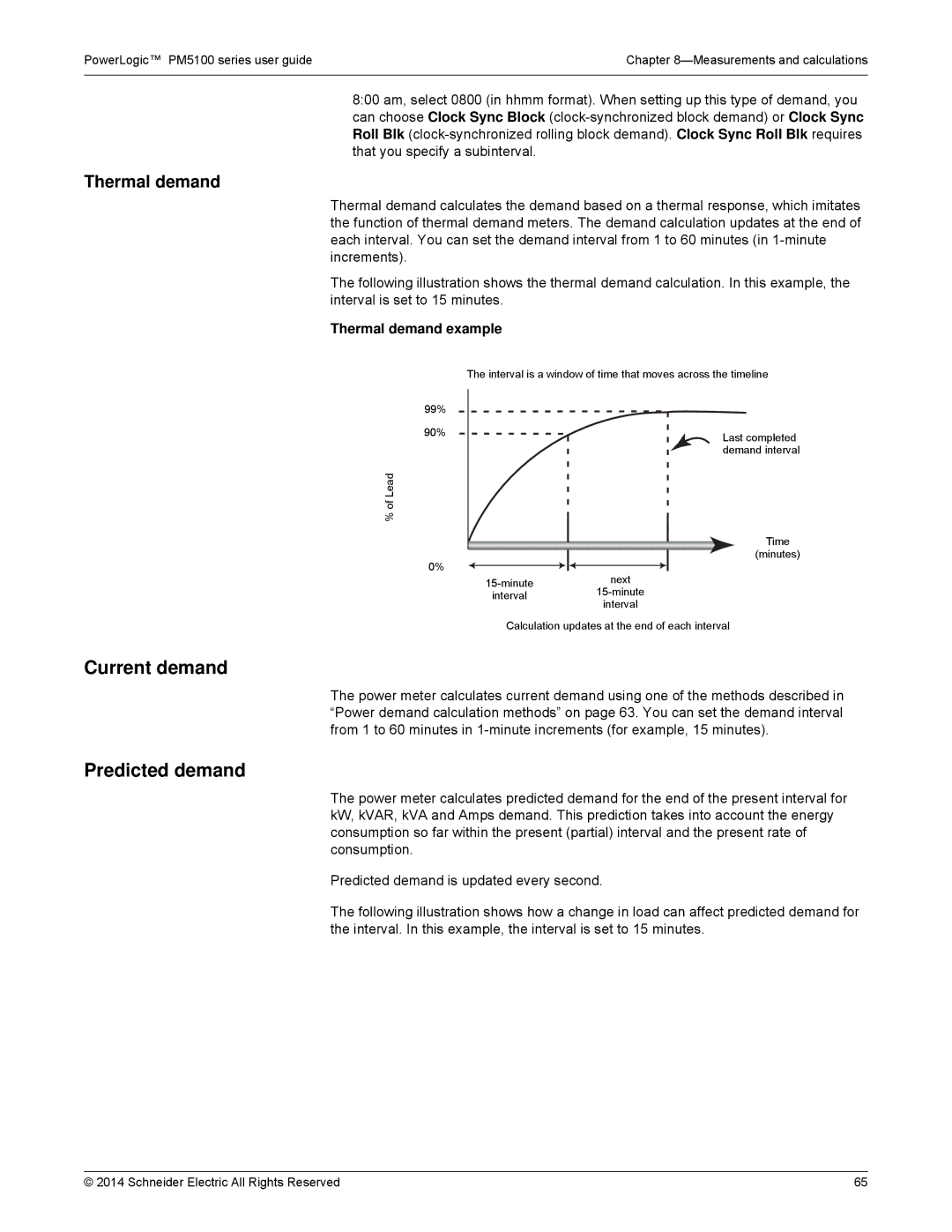
The following illustration shows the thermal demand calculation. In this example, the interval is set to 15 minutes.
Thermal demand example
The interval is a window of time that moves across the timeline
99%
90%
% of Lead
0%
next | ||
interval | ||
interval | ||
|
Last completed demand interval
Time
(minutes)
Calculation updates at the end of each interval
Current demand
The power meter calculates current demand using one of the methods described in “Power demand calculation methods” on page 63. You can set the demand interval from 1 to 60 minutes in
Predicted demand
The power meter calculates predicted demand for the end of the present interval for kW, kVAR, kVA and Amps demand. This prediction takes into account the energy consumption so far within the present (partial) interval and the present rate of consumption.
Predicted demand is updated every second.
The following illustration shows how a change in load can affect predicted demand for the interval. In this example, the interval is set to 15 minutes.
© 2014 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved | 65 |