Page
Please Recycle
Product Family Name Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Fiber X4012A
European Union
EN 609502000, 3rd Edition IEC 609502000, 3rd Edition
Supplementary Information
Safety
Page
Regulatory Compliance Statements
FCC Class a Notice
FCC Class B Notice
ICES-003 Class B Notice Avis NMB-003, Classe B
ICES-003 Class a Notice Avis NMB-003, Classe a
Bsmi Class a Notice
Page
Contents
Configuring Driver Parameters
Installing the Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Board
Contents
Page
Contents
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting 119
Specifications
134
Third Party License Terms
Manual Pages Zeroizing the Hardware
Frequently Asked Questions
Tables
137
106
108
123
146
141
144
145
Page
How This Book Is Organized
Preface
Solaris Hardware Platform Guide
Using Unix Commands
Shell Prompts
Typographic Conventions
Sun Welcomes Your Comments
Accessing Sun Documentation Online
Key Protocols and Interfaces
Product Features
Key Features
Supported Applications
Supported Cryptographic Protocols
1IPsec Cryptographic Algorithms
Diagnostic Support
Cryptographic Algorithm Acceleration
Supported Cryptographic Algorithms
# rm /etc/opt/SUNWconn/cryptov2/sslreg
Bulk Encryption
3Supported SSL Algorithms
# touch /etc/opt/SUNWconn/cryptov2/sslreg
IPsec Hardware Acceleration
Hardware Overview
Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 MMF Adapter
LED Displays
4Front Panel Display LEDs for the MMF Adapter
2Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 UTP Adapter
Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 UTP Adapter
5Front Panel Display LEDs for the UTP Adapter
Load Sharing
Dynamic Reconfiguration and High Availability
6Hardware and Software Requirements
Hardware and Software Requirements
Required Patches
Apache Web Server Patch
Solaris 8 Patches
Solaris 9 Patches
There are currently no required Solaris 9 patches
Page
Handling the Board
Installing the Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Board
Installing the Board
To Install the Hardware
Ok show-devs
Ok cd /pci@8,600000/network@1 Ok .properties
Installing the Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Software
To Install the Software
# mount -F hsfs -o ro /dev/dsk/c0t6d0s2 /cdrom
VCA Administration
1Files in the /cdrom/cdrom0 Directory
VCA Firmware
# modinfo grep Crypto
Installing the Optional Packages
Install the required software packages by typing
# prtdiag
2Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Directories
Directories and Files
Development Application Support libraries
Apache configuration support
Encrypted keys
Application executables
To Remove the Software
Removing the Software
Page
Configuring Driver Parameters
1vca Driver Parameter, Status, and Descriptions
Driver Parameter Values and Definitions
Advertised Link Parameters
2Operational Mode Parameters
3Read-Write Flow Control Keyword Descriptions
Flow Control Parameters
Gigabit Forced Mode Parameter
4Gigabit Forced Mode Parameter
Interpacket Gap Parameters
5Parameters Defining enable-ipg0and ipg0
7RX Blanking Register for Alias Read
Interrupt Parameters
Random Early Drop Parameters
7describes the receive interrupt blanking values
When Fifo threshold is greater than 6,144 bytes
9PCI Bus Interface Parameters
PCI Bus Interface Parameters
Use the instance number to select the device
Setting vca Driver Parameters
Setting Parameters Using the ndd Utility
To Specify Device Instances for the ndd Utility
# ndd -set /dev/vcaN parameter value
Noninteractive and Interactive Modes
Device remains selected until you change the selection
To modify a parameter value, use the -setoption
# ndd /dev/vcaN
Ndd utility then prompts you for the name of the parameter
# ndd /dev/vca
Setting Autonegotiation or Forced Mode
To Disable Autonegotiation Mode
Set the adv-autoneg-capparameter to
# ndd -set /dev/vcaNadv-autoneg-cap
# grep vca /etc/driveraliases vca pci108e,3de8
Setting Parameters Using the vca.conf File
To Set Driver Parameters Using a vca.conf File
Refer to the online manual pages for pathtoinst4
10Device Path Name
Following is an example vca.conf file
Example vca.conf File
11Local Link Network Device Parameters
Ok boot netspeed=1000,duplex=half,link-clock=master
Ok boot netspeed=100,duplex=half
Refer to the Ieee 802.3 documentation for further details
Ok boot netspeed=10,duplex=auto
Ok boot netspeed=10
Cryptographic Driver Statistics
Ethernet Driver Statistics
13describes the Ethernet driver statistics
13Ethernet Driver Statistics
14TX and RX MAC Counters
14describes the transmit and receive MAC counters
Tx-underrun
16Read-Only vca Device Capabilities
15Current Ethernet Link Properties
Reporting the Link Partner Capabilities
17describes the read-only link partner capabilities
17Read-Only Link Partner Capabilities
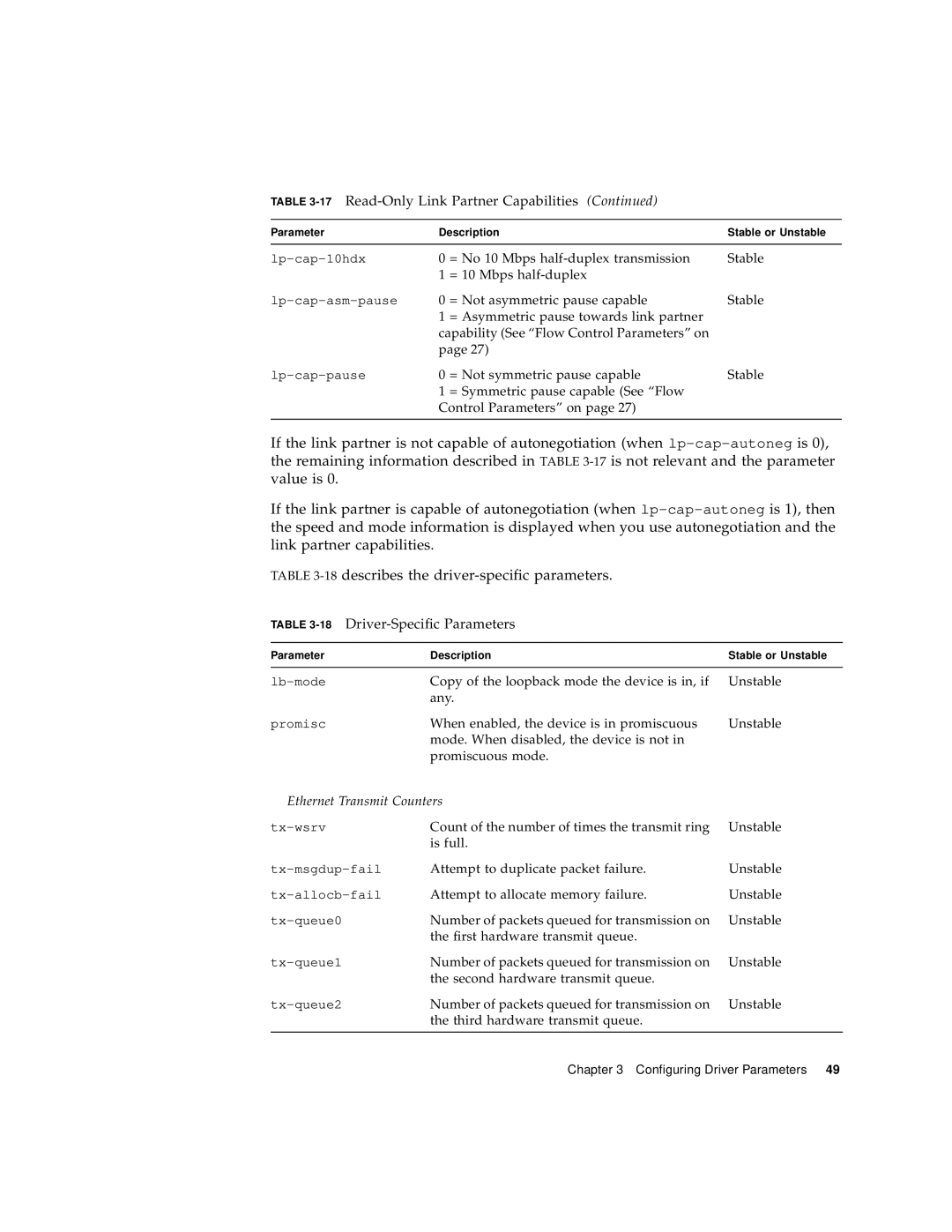
Ethernet Transmit Counters
18Driver-Specific Parameters
Ethernet Receive Counters
To Check Link Partner Settings
As superuser, type the kstat vcaN command
# kstat vcaN
Instance number in the previous example is
Network Configuration
Configuring the Network Host Files
Locate the correct vca interfaces and instance numbers
# Internet host table Localhost Zardoz Loghost Zardoz-11
# cat /etc/hosts
Page
$ PATH=$PATH/opt/SUNWconn/bin $ export Path
Using vcaadm
Vcaadm command-line syntax is
Modes of Operation
1shows the options for the vcaadm utility
$ vcaadm show user
Single-Command Mode
File Mode
$ vcaadm -s secofficer create user webadmin
Interactive Mode
Logging In and Out With vcaadm
$ vcaadm -f deluser.scr -y
Logging In to a New Board
Logging In to a Board With vcaadm
# vcaadm -h hostname
Logging In to a Board With a Changed Remote Access Key
2vcaadm Prompt Variable Definitions
Vcaadm prompt in Interactive mode is displayed as follows
Logging Out of a Board With vcaadm
Following table describes the vcaadm prompt variables
Vcaadm connect host hostname dev vca2
3connect Command Optional Parameters
Entering Commands With vcaadm
Webadmin
Tom
VcaadmvcaN@hostname, secofficer set ?
Getting Help for Commands
Quitting the vcaadm Program in Interactive Mode
Create a keystore name Refer to Naming Requirements on
Select Fips 140-2 mode or non-FIPS mode
Verify the configuration information
Enter the path and password to the backup file
Password Requirements
Managing Keystores With vcaadm
Naming Requirements
Setting the Password Requirements
5Password Requirement Settings
Populating a Keystore With Security Officers
Populating a Keystore With Users
Listing Users and Security Officers
Changing Passwords
Enabling or Disabling Users
To enable an account, enter the enable user command
Deleting Users
Deleting Security Officers
Backing Up the Master Key
Locking the Keystore to Prevent Backups
Managing Boards With vcaadm
Setting the Auto-Logout Time
VcaadmvcaN@hostname, secofficer show status Board Status
Displaying Board Status
Loading New Firmware
Resetting a Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Board
Key Types
Rekeying a Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Board
Zeroizing a Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Board
Using the vcaadm diagnostics Command
VcaadmvcaN@hostname, secofficer diagnostics
Vcadiag command-line syntax is
# vcadiag -D vca0
1shows the options for the vcadiag utility
Following is an example of the -Doption
Following is an example of the -Foption
Following is an example of the -Zoption
Following is an example of the -Koption
Following is an example of the -Qoption
Following is an example of the -Roption
Page
Administering Security for Sun ONE Web Servers
Concepts and Terminology
Token Files
Tokens and Token Files
Enabling and Disabling Bulk Encryption
Following is an example of the contents in a token file
Configuring Sun ONE Web Servers
Passwords
1Passwords Required for Sun ONE Web Servers
Populate the board’s keystore with users
Refer to Using vcaadm on
Populating a Keystore
To Populate a Keystore
Create a user with the create user command
Overview for Enabling Sun ONE Web Servers
Exit vcaadm
Installing and Configuring Sun ONE Web Server
Installing Sun ONE Web Server
To Install Sun ONE Web Server
Select OK
Start the Sun ONE Web Server 4.1 Administration Server
Response provides the URL for connecting to your servers
To Create a Trust Database
# /opt/SUNWconn/bin/iplsslcfg
Type 0 to quit
To Generate a Server Certificate
Create Trust Database page is displayed
This password is the usernamepassword Table
Select the Cryptographic Module you want to use
2Requestor Information Fields
To Install the Server Certificate
3Fields for the Certificate to Install
Configuring Sun ONE Web Server 4.1 for SSL
To Configure the Sun ONE Web Server
Fill out the form to install your certificate
Set encryption to On
Web server is now configured to run in secure mode
Usr/iplanet/servers
Start the Sun ONE Web Server 6.0 Administration Server
Create the trust database for the web server instance
# /usr/iplanet/servers/https-admserv/start
# /opt/SUNWconn/crypto/bin/iplsslcfg
To Generate a Server Certificate
Create Trust Database window is displayed
4Requestor Information Fields
To Install the Server Certificate
5Fields for the Certificate to Install
Configuring Sun ONE Web Server 6.0 for SSL
Select the OK button to apply these changes
Page
111
Enabling Apache Web Servers
To Enable the Apache Web Server
Create an httpd configuration file
Enabling the Board for Apache Web Servers
Create an RSA keypair for your system
Select 1 to configure your Apache Web Server to use SSL
Create your PEM pass phrase
Creating a Certificate
Choose a base name for the key material
Provide a key length between 512 and 2048 bits
To Create a Certificate
Modify the /etc/apache/httpd.conf file as directed
Select 0 to quit when you finish with apsslcfg
Copy your certificate request with the headers from
Start the Apache Web Server
# /usr/apache/bin/apachectl start
SunVTS Diagnostic Software
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Page
To Perform vcatest
As superuser, start SunVTS
# /opt/SUNWvts/bin/sunvts
Page
Vcatest Command-Line Syntax
Test Parameter Options for vcatest
2describes the vcatest subtests
To Perform netlbtest
To Perform nettest
VcaN up inet ip-addressplumb
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
# kstat Vca0
Using kstat to Determine Cryptographic Activity
Shut down the system
Using the OpenBoot Prom FCode Self- Test
Performing the Ethernet FCode Self-Test Diagnostic
Ok setenv auto-boot? false
Ok show-nets
Reset the system
Perform the self-test using the test command
Ok reset-all
If the test passes, you see the following messages
Set the auto-boot?configuration parameter to true
Reset and reboot the system
Type the following
Show-devs
Troubleshooting the Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Board
Properties
Watch-net
Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 MMF Adapter
Connectors
Table A-1SC Connector Link Characteristics Ieee P802.3z
Figure A-1Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 MMF Adapter Connector
Physical Dimensions
Performance Specifications
Power Requirements
Table A-6Environmental Specifications
Interface Specifications
Environmental Specifications
Table A-5Interface Specifications
Table A-7Cat-5 Connector Link Characteristics
Figure A-2Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 UTP Adapter Connector
Table A-10Power Requirements
Table A-9Performance Specifications
Table A-12Environmental Specifications
Table A-11Interface Specifications
Page
SSL Configuration Directives for Apache Web Servers
Table B-1SSL Protocols
Preceding statement is equivalent to
SSL Aliases
Default value of cipher-specis
Table B-4Special Characters to Configure Cipher Preference
Table B-3SSL Aliases
Table B-5SSL Verify Client Levels
Context Global, virtual host
Table B-6SSL Log Level Values
Table B-7Available SSL Options
Options are listed and described in Table B-7
Opt/SUNWconn/cryptov2/include
Page
Software Licenses
Page
Appendix D Software Licenses
Third Party License Terms
Openssl License Issues
Original SSLeay License
Modssl License
Appendix D Software Licenses
Page
Table E-1Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 Online Manual Pages
Man -M /opt/SUNWconn/man
Kcl2 device driver is a multithreaded loadable kernel module
Zeroizing the Hardware
Page
Reconnect to Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 board with vcaadm
Page
Frequently Asked Questions
# chmod 400 password.conf
Boot the operating environment
Enter the following command
Reboot the system
Enter the following command at the OBP prompt
How Do I Self-Sign a Certificate for Testing?
Index
Extension
Advertised link parameters
Commands
Failsafe mode
Page
Pause capability
Command-line syntax, 123 test parameter options
Rx-intr-pktsparameter, 25
Vca driver
Vca.conf file, example
URL
Watch-netcommand Zeroize command, 163 zeroizing the hardware