Operational Modes | Introduction |
|
|
Operational Modes
The FortiLog device can operate in two modes: Active mode or Passive mode. The
Active Mode
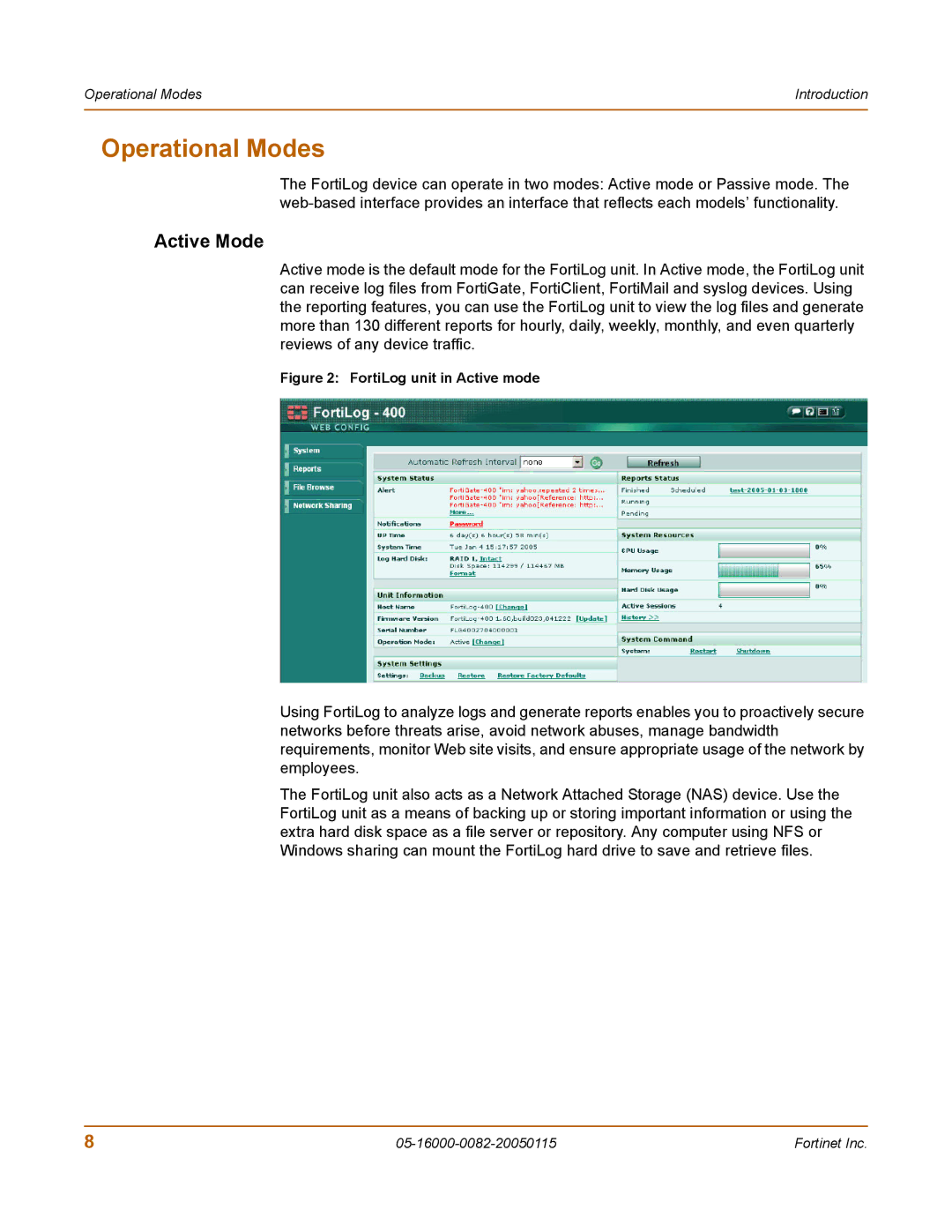
Active mode is the default mode for the FortiLog unit. In Active mode, the FortiLog unit can receive log files from FortiGate, FortiClient, FortiMail and syslog devices. Using the reporting features, you can use the FortiLog unit to view the log files and generate more than 130 different reports for hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, and even quarterly reviews of any device traffic.
Figure 2: FortiLog unit in Active mode
Using FortiLog to analyze logs and generate reports enables you to proactively secure networks before threats arise, avoid network abuses, manage bandwidth requirements, monitor Web site visits, and ensure appropriate usage of the network by employees.
The FortiLog unit also acts as a Network Attached Storage (NAS) device. Use the FortiLog unit as a means of backing up or storing important information or using the extra hard disk space as a file server or repository. Any computer using NFS or Windows sharing can mount the FortiLog hard drive to save and retrieve files.
8 | Fortinet Inc. |