Hp psc Photosmart series All-in-one Reference guide
Page
Hp psc Photosmart series All-in-one
Safety information
Contents
Use the fax features
Vii
Technical information
Viii
Troubleshooting information
Help Description
Get help
Hp psc 2500 series
Hp psc overview
Output tray Paper-width guide
Feature Purpose
Power connection USB port
Hp psc 2500 series at a glance
Button
Front panel overview
Button
Menu overview
Select the HP PSC 2500 Series
Use the hp director software to do more with your hp psc
Open the hp director for Windows users
Rotate
HP PSC
Feature
Open the hp director for Macintosh users
Open the hp director all-in-one using Macintosh OS
Open the hp photo and imaging director using Macintosh OS
Feature
Load an original
Load originals and load paper
Load paper
Replace the output tray
Load the input tray
Load envelopes
Load 4 by 6 inch 10 by 15 cm photo paper
Load postcards or Hagaki cards
Remove the output tray Remove all paper from the input tray
Recommended papers
Load other types of paper in the input tray
Paper Tips
Continuous banner
Set the paper type
Set paper type from the copy menu
Together
Set the paper size from the photo menu
Set the paper size
Set paper type from the photo menu
Set the paper size from the copy menu
Avoid jams
Load originals & paper
Use a photo memory card
What is a memory card?
Insert a memory card and save the files to your computer
Print photos from a proof sheet
All Last Custom Range
Print a proof sheet
Complete the proof sheet
Create a video action print by scanning a proof sheet
Print photos by scanning a proof sheet
Set photo print options
Borderless print
Change photo menu print options
Print photos directly from a memory card
Set new print photo defaults
Create borderless prints
Print individual photos
Deselect photos
Use quick print to print the current photo
Print a Dpof file
View photos in a slide show
Change the speed of the slide show
To print camera-selected photos
Share photos through e-mail
Share digital photos through hp instant share
Share photos through the Share Menu
Use the hp photo & imaging gallery
Use the copy features
Overview
This section contains the following topics Overview on
Increase copy speed or quality
Change default copy settings
Press to highlight a quality setting, and then press OK
Press 9 to select Set New Defaults from the Copy Menu
Remove the first page from the glass and load the second
Copy a two-page black-and-white document
Hp photo & imaging help that came with your software
Press Start Black
Make a 4 by 6 inch 10 by 15 cm borderless copy of a photo
Brochure Glossy *. Brochure Matte
Press Start Color
Make multiple copies of the same original
Copy a 4 by 6 inch 10 by 15 cm photo onto a full-size
Paper sizes available vary by country/region
Copy a photo several times on one
Resize an original to fit onto letter paper
Press to highlight Fit to Page, and then press OK
Press 8 to select Color Intensity from the Copy Menu
Copy a washed-out original
Copy a document that has been faxed several times
Press to darken the copy, and then press OK
Enhance light areas of your copy
Make a poster
Prepare a color t-shirt transfer
To stop copying, press Cancel on the front panel
Stop copying
Press to highlight Iron-On, and then press OK
Send the scan to a memory card loaded in your hp psc on
Use the scan features
Scan an original
Scan an original on Stop scanning on
Imaging help that came with your software
Send the scan to a computer connected directly to the hp psc
On the keypad
Scan
To save your scan to an hp instant share destination
Press 2 to select HP Instant Share
Image saved on the secure HP Instant Share server
To stop scanning, press Cancel on the front panel
Stop scanning
Send the scan to a memory card loaded in your hp psc
Send a fax
Use the fax features
Send a basic fax
Enable fax confirmation
Send a color original or photo fax
Send a two-page black-and-white fax
Send a fax using speed dials
Set number of rings before answering
Receive a fax
Set up your hp psc to answer fax calls manually
Receive a fax manually
Set the fax header
Enter text
Print reports
Generate automated reports on Generate manual reports on
Generate manual reports
Generate automated reports
Set up speed dialing
Create speed-dial entries
Create speed-dial entries on Delete speed-dial entries on
Delete speed-dial entries
Control resolution and contrast
Change resolution
Change resolution on Change contrast on Set new defaults on
Change contrast
Set fax options
Set new defaults
Redial a busy or unanswered number automatically
Use error correction mode ECM
Adjust the volume
Set automatic reduction for incoming faxes
Change the answer ring pattern distinctive ringing
Set the date and time
Set the paper size
Set tone or pulse dialing
Stop faxing
Set backup fax reception
To stop a fax you are sending or receiving, press Cancel
Reprint the faxes in memory
Fax
Use the network configuration tools
Access the network menu
Network
Field Description
Print a network configuration
General network settings
Use network menu options
Pieces of hardware have the same MAC address
DSL modem during installation
Default Gateway
Hardware Address
Addresses to refer to one another
Enabled device that appears on the network
Admin Password
Domain name hp.com. The Internets domain name servers DNS
Wireless network settings
Region
Access point
Range of approved channels
Number value ranging from 1 to 14, depending on country
Networks
Authentication and encryption
Used on an authentication server
Security method is common on wireless networks
Data transmission and receipt information
Enable or disable the wireless radio
Then
Restore wireless defaults
To enable or disable the wireless radio
To restore wireless defaults
To change the link speed
Manage your hp psc using the embedded web server
To access the embedded web server
Change the link speed
Adding security to the network
Network config tools
Print from your computer
Print from a software application
Windows users
Click Print to begin printing
Make changes to the print settings, and click Apply
Set print options
Macintosh users
Output options panel Paper type/quality panel
To change the print settings for the current print job
Copies & pages panel
Layout panel
Stop a print job
Print cartridges Hp reorder number
Order supplies
Order media
Order print cartridges
Order supplies
Clean the glass
Clean the lid backing
Maintain your hp psc
Estimated ink levels appear for the print cartridges
Clean the exterior
Work with print cartridges
Check the ink levels
To check the ink level for Macintosh users
Print a self-test report
Lines of color extend across
Handle print cartridges
Replace the print cartridges
Maintain your hp psc
Use the print cartridge protector
Use a photo print cartridge
Align the print cartridges
To align the cartridges from the front panel
100
101
Clean the print cartridges
Clean the print cartridge contacts
Turn the HP PSC on and open the print-carriage access door
102
103
Restore factory defaults
Set the power save time
Press until the appropriate time appears, then press OK
104
Set the prompt delay time
105
Get hp psc support
Get support and other information from the Internet
Hp customer support
Call in North America during warranty
Call elsewhere in the world
106
107
Call in Australia post-warranty
Prepare your hp psc for shipment
108
109
Hp distribution center
110
Warranty upgrades
Warranty information
Duration of limited warranty
Warranty service
112
Returning your hp psc for service
Hewlett-packard limited global warranty statement
Extent of limited warranty
113
Limitations of warranty
Limitations of liability
Local law
114
Limited warranty information for EU countries
Technical information
System requirements
115
116
Paper specifications
Paper tray capacities
Technical
117
Paper sizes
Print specifications
Print margin specifications
118
119
Copy specifications
Fax specifications
Photo memory card specifications
120
Environmental specifications
Scan specifications
Physical specifications
Power specifications
Environmental product stewardship program
Regulatory model identification number
Regulatory notices
Recycling program
Hp inkjet supplies recycling program
124
FCC statement
125
Exposure to radio frequency radiation
126
Declaration of conformity European Union
Geräuschemission
127
128
Arib STD-1066 Japan
129
Declaration of Conformity
130
Cables on
Wired network setup
Wired networking basics
Hubs, switches, and routers on
Hubs
Hubs, switches, and routers
Switches
Cables
Ethernet network without an Internet connection
Recommended network configurations
Ethernet network with Internet access provided by modem
Internet connections
134
Set up your hp psc for wired network use
Connect your hp psc to the network
To connect your hp psc to the network
135
Install your hp psc software on a Windows computer
To install your hp psc software
136
137
Install your hp psc software on a Macintosh
Select the appropriate Language and Device
Click Network Option
138
Printers Found
139
140
Complete the Print Queue Setup
Click Continue
At the Congratulations! screen, click Continue
Communication modes on
Wireless network setup
Wireless networking basics
Communication modes
142
143
Authentication
Security
Encryption
144
Wireless network configurations
Media access control address authentication
Ad-hoc
145
Infrastructure
Ethernet to infrastructure
Infrastructure to 802.3 Ethernet
Set up your hp psc for wireless network use
Optimize your wireless network
146
147
Connect your hp psc to a wireless network or computer
148
Printer Found
149
Ssid that WEP is
Next
150
151
Wireless Encryption WEP
Unplug the network cable
152
153
154
155
156
Select a Network Name screen appears
157
Verify that the settings are correct, and then click Next
158
Install your hp psc software on a Macintosh ad-hoc mode
159
160
8GS97TW
161
162
AirPort is active in your machine
163
164
Wireless network setup
165
Use the embedded web server
Enter multiple WEP keys
166
167
Enter WPA encryption data
To enter multiple WEP keys onto the embedded Web server
To enter WPA encryption data onto the embedded Web server
Select Infrastructure and click Next
Enter advanced authentication data
Glossary of terms
Term Definition
169
Server-based EAP/802.1x authentication provides
Authentication
Network with No Authentication Open System does
Network using Shared Key authentication provides
Dynamic encryption such as WPA Each device has a
Static encryption such as WEP The same key is used for
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol. a mutual
Network. It can also work with any other Ethernet-enabled
Switching of wireless LAN cards on a PC. This works
API that is used in its AiO software solution
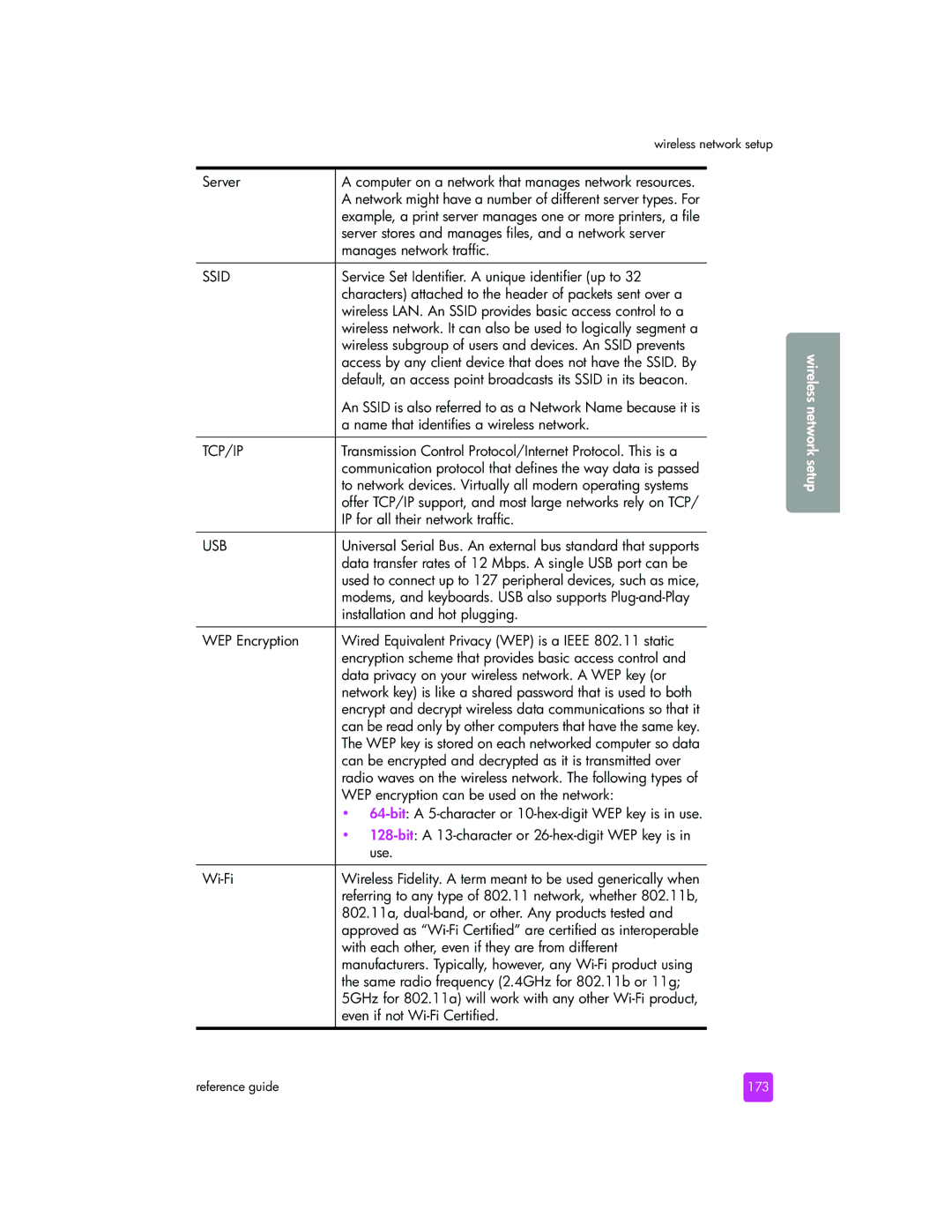
Access by any client device that does not have the SSID. By
Service Set Identifier. a unique identifier up to
Wireless LAN. An Ssid provides basic access control to a
Wireless subgroup of users and devices. An Ssid prevents
Implements 802.1x and the Extensible Authentication
AirPort adapter a wireless card that plugs directly into
Wi-Fi Protected Access. Provides standards-based
Protocol TKIP. To strengthen user authentication, WPA
175
Fax setup
176
How to choose the right fax setup for your office
Venezuela
Vietnam
177
Select your fax setup case from this table
Case a separate fax line no voice calls received
179
How your hp psc will answer fax calls
180
Case C shared voice/fax line
How to answer fax calls automatically
How to answer fax calls manually
181
182
Case D fax line shared with PC modem no voice calls received
183
Case E shared voice/fax line with PC modem
184
Case F shared voice/fax line with answering machine
185
186
187
Case H shared voice/fax line with voice mail
188
Case I shared voice/fax line with PC modem and voice mail
189
190
Faxing from a DSL line
191
Hp instant share direct connect setup Use
Use hp instant share in five easy steps Windows
From the HP Instant Share tab, click Start HP Instant Share
192
Use the e-mail button
Click the HP Instant Share tab
Access hp instant share from the hp director
Use the hp instant share photo menu option
Use a scanned image
Click Next
Send a photo or image using your hp psc Macintosh
Open the HP Director
Select an image from the folder in which it is stored
195
Why should I register with hp instant share Windows
Access the e-mail option from the hp director
196
197
Hp instant share network setup
Before you start
Use hp instant share in five easy steps
Register with hp instant share Windows
Click If you don’t have an account, click here
198
199
Register with hp instant share Macintosh
200
201
Use the hp instant share scan menu option
Edit or add hp instant share destinations
To edit a destination Open the HP Director
203
Print a network configuration
Why should I register with hp instant share
To create an e-mail destination Open the HP Director
Hp psc 2500 series
Computer is unable to discover device hp psc
Troubleshooting information
Installation troubleshooting
Wired network setup troubleshooting
You received a System Requirements Error No TCP/IP
Printer not Found screen appears during installation
206
Wireless network setup troubleshooting
You are using a cable modem without a router
207
208
Verification fails at end of installation
209
210
Setup failed
211
Computer is unable to discover device
Wireless infrastructure mode troubleshooting
Hp psc cannot find the Wlan
Hp psc cannot find your computer
Wireless ad-hoc mode troubleshooting
Software installation troubleshooting
213
Minimum system checks screen appears
Red X appears on the USB connect prompt
214
Received a message that an unknown error has occurred
Some of the icons are missing in the hp director
215
216
Double-click the ApplicationsHP All-in-One Software folder
Fax wizard does not start
Digital Imaging Monitor does not appear in the task tray
217
Hardware installation troubleshooting
Front panel displays the wrong language
218
219
My hp psc does not turn on
Hp psc does not print
My USB cable is not connected
You can also find more information on the HP website at
Additional installation troubleshooting help
Fax setup troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
221
222
Cannot receive faxes, but I can send faxes
Cannot send faxes, but I can receive faxes
Fax tones are recorded on my answering machine
223
224
Hp instant share setup troubleshooting
Hp instant share service temporarily unavailable
Hp instant share incorrect network settings
Hp instant share connection lost
Operational troubleshooting
Hp instant share troubleshooting
Hp instant share connection not established
No destinations created
Hp instant share error
Cannot read destination file
Too many destinations specified
Unsupported file
Problem Possible cause and solutions
Photo memory card troubleshooting
Networking troubleshooting
File name is uppercase
When I type a file name, I get an error message
Other users on the network can access my photo memory card
File name is truncated
Index
Numerics
229
230
HP PSC
231
232
233
234
Page
Q3093-90182