|
|
| Crosspoint |
| ||
|
|
| Switch |
| ||
|
| Media Board |
|
| ||
|
| Receive | 16MB | FIFO |
| |
|
| TBIC | Buffer(1) |
| ||
7 | 3 | (1) |
| |||
|
|
| ||||
Receive |
|
|
| |||
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
6 | Proc & C | Send |
|
| ||
|
|
|
| |||
5 | 1 |
| Proc & C |
|
| |
4 | 0 | Send | 16MB | FIFO | Serial | |
(2) | Daughter | |||||
|
| TBIC | Buffer(2) | |||
|
| Card | ||||
SP Switch |
| |||||
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
| |||
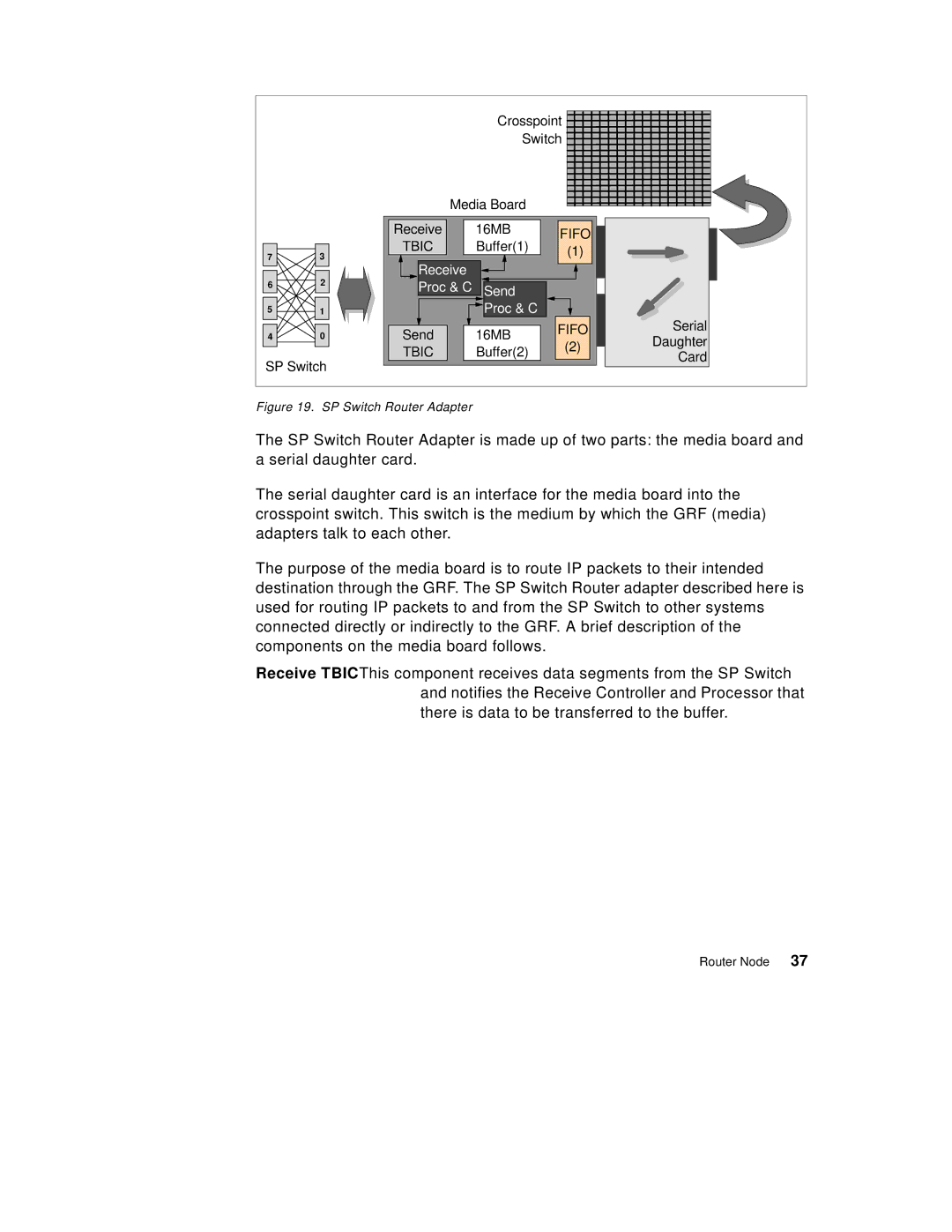
Figure 19. SP Switch Router Adapter
The SP Switch Router Adapter is made up of two parts: the media board and a serial daughter card.
The serial daughter card is an interface for the media board into the crosspoint switch. This switch is the medium by which the GRF (media) adapters talk to each other.
The purpose of the media board is to route IP packets to their intended destination through the GRF. The SP Switch Router adapter described here is used for routing IP packets to and from the SP Switch to other systems connected directly or indirectly to the GRF. A brief description of the components on the media board follows.
Receive TBICThis component receives data segments from the SP Switch and notifies the Receive Controller and Processor that there is data to be transferred to the buffer.
Router Node 37