10.The header is examined by the CPU, which uses the information to build a new header that will deliver the data across the media interface.
11.The DMA engine transfers the packet to the media interface. 12.The packet is transferred across the media.
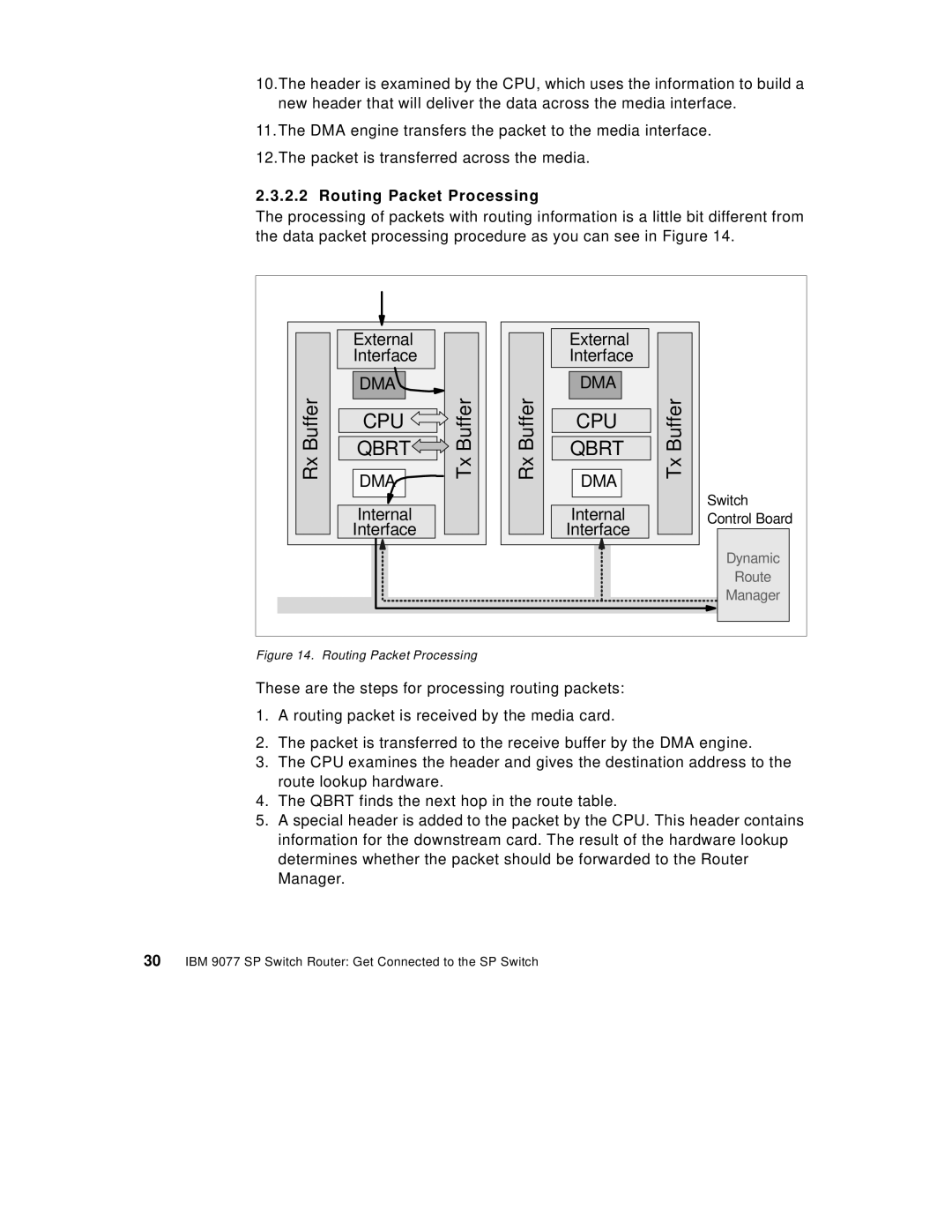
2.3.2.2 Routing Packet Processing
The processing of packets with routing information is a little bit different from the data packet processing procedure as you can see in Figure 14.
| External |
|
| External |
| |
| Interface |
|
| Interface |
| |
| DMA |
|
| DMA |
| |
Buffer | CPU | Buffer | Buffer | CPU | Buffer | |
QBRT | QBRT | |||||
Rx | Tx | Rx | Tx | |||
DMA | DMA | |||||
|
|
|
| |||
| Internal |
|
| Internal | Switch | |
|
|
| Control Board | |||
| Interface |
|
| Interface |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Dynamic | |
|
|
|
|
| Route | |
|
|
|
|
| Manager |
Figure 14. Routing Packet Processing
These are the steps for processing routing packets:
1.A routing packet is received by the media card.
2.The packet is transferred to the receive buffer by the DMA engine.
3.The CPU examines the header and gives the destination address to the route lookup hardware.
4.The QBRT finds the next hop in the route table.
5.A special header is added to the packet by the CPU. This header contains information for the downstream card. The result of the hardware lookup determines whether the packet should be forwarded to the Router Manager.